Effect of ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 zeolites prepared by solid phase epitaxial growth method on CO2 hydrogenation and toluene alkylation reactions
-
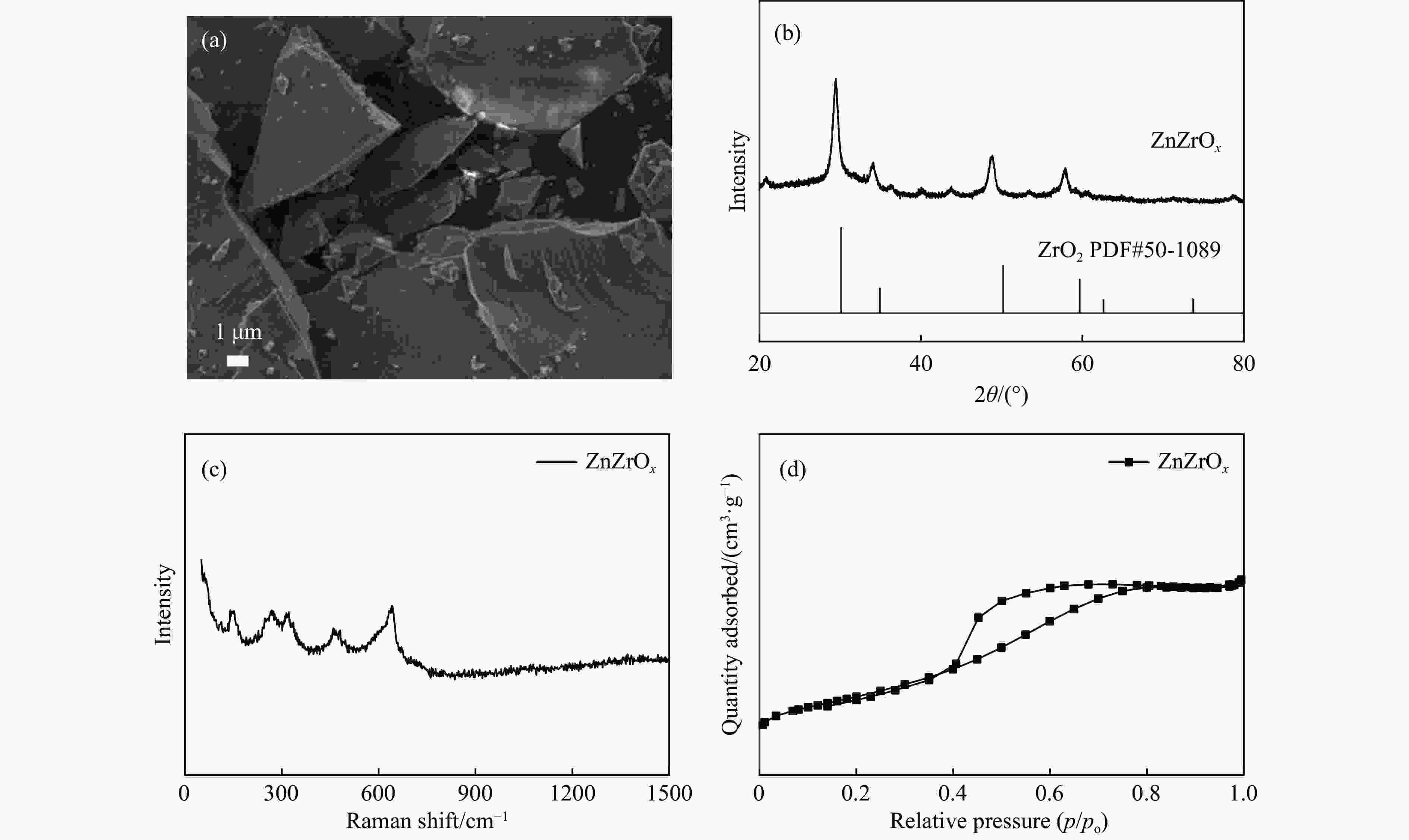
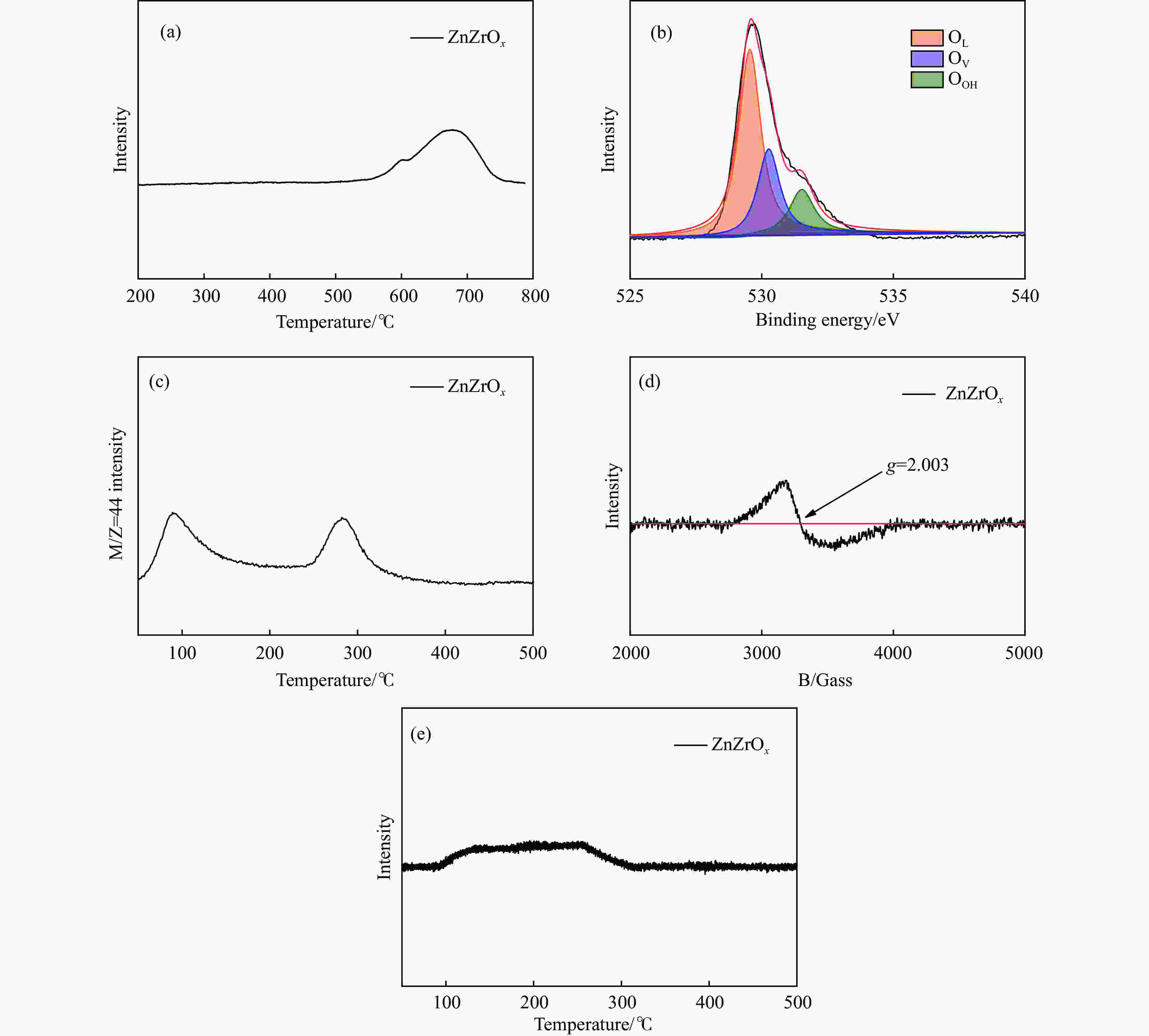
摘要: CO2加氢合成高附加值的芳烃对于缓解CO2排放引起的能源气候问题具有重要意义。本研究采用固相法在ZSM-5表面外延生长Silicalite-1,制备出ZSM-5@Silicalite-1分子筛。同时制备高活性氧化物ZnZrOx,并与ZSM-5@Silicalite-1物理混合组成ZnZrOx/ ZSM-5@Silicalite-1双功能催化剂,研究了CO2加氢耦合甲苯烷基化催化性能。相比于ZnZrOx/ZSM-5催化剂,分子筛改性后的双功能催化剂提高了对二甲苯(PX)选择性。研究了晶化条件(硅源、晶化过程、晶化次数)对ZSM-5外延生长Silicalite-1的影响,以及Silicalite-1钝化层厚度对CO2加氢耦合甲苯烷基化反应性能的影响。在400 ℃、3 MPa反应条件下,ZZO/1:3.5Z5-Na-SiO2催化剂的甲苯转化率为12.0%,二甲苯选择性为77.4%,在二甲苯中对二甲苯选择性为73.4%。通过SEM、XRD、N2吸附-脱附、XPS、NH3-TPD、Py-FTIR等表征,研究了分子筛的结构和酸性质。结果表明,通过固相外延生长,延长ZSM-5的孔道,增加间二甲苯(MX)、邻二甲苯(OX)的扩散阻力,同时钝化外表面的酸性,可以有效提高对二甲苯(PX)的选择性。固相外延生长法改性ZSM-5分子筛,摒弃了以往堵塞孔以缩小孔口改性分子筛的缺点,在保证催化剂活性的同时提高了产物选择性。
-
关键词:
- MFI型分子筛 /
- 外延生长 /
- 对二甲苯 /
- 固相法 /
- CO2加氢耦合甲苯烷基化
Abstract: CO2 hydrogenation to synthesize high value-added aromatics is of great significance to alleviate the energy climate problem caused by CO2 emission. It is generally believed that the reaction course of CO2 hydrogenation of toluene coupled with alkylation to produce xylenes is as follows: firstly, CO2 reacts with H2 to produce methanol intermediates, and then the methanol intermediates react with toluene on zeolite catalysts to produce para-xylene (PX) by alkylation. According to the reaction pathway, it is necessary to construct a bifunctional catalyst with synergistic matching of the two process conditions to simultaneously realize the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol intermediate and the alkylation of the intermediate and toluene to generate para-xylene. The ZnZrOx/ZSM-5 catalytic system, in which the ZnZrOx has strong thermal stability and CO2 activation ability, and the ZSM-5 has a good morphology selectivity for PX, is considered to be a promising CO2 hydrogenated toluene coupled alkylation catalyst. However, this system still suffers from low PX selectivity, mainly due to the presence of non-selective acidic sites on the outer surface of the zeolite or near the pore orifice, which leads to the generation of side reactions, such as deep methylation and toluene isomerization, and reduces the selectivity. In this paper, ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 zeolites were prepared by epitaxial growth of Silicalite-1 on the surface of ZSM-5 using solid-phase synthesis. At the same time, the highly active oxide ZnZrOx was prepared and physically mixed with ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 to form a ZnZrOx/ ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 bifunctional catalyst to study the catalytic performance of CO2 hydrogenation coupled with toluene alkylation. Compared with the ZnZrOx/ZSM-5 catalyst, the modified zeolite improved the para-xylene (PX) selectivity. The effect of crystallization conditions (silicon source, crystallization process, and number of crystallizations) on the epitaxial growth of Silicalite-1 from ZSM-5 was investigated, as well as the effect of the thickness of the Silicalite-1 passivation layer on the performance of the reaction between carbon dioxide hydrogenation and toluene alkylation. The ZZO/1:3.5Z5-Na-SiO2 catalyst showed a toluene conversion of 12.0%, a xylene selectivity of 77.4%, and a PX selectivity of 73.4% in xylene under 400 ℃ and 3 MPa reaction conditions. The structure and acid properties of the zeolites were investigated in detail by SEM, XRD, N2 adsorption-desorption, XPS, NH3-TPD and Py-FTIR characterization, and the results show that the selectivity of para-xylene (PX) can be effectively improved by solid-phase epitaxial growth to extend the pore channels of ZSM-5, increase the diffusion resistance of m-xylene (MX) and o-xylene (OX), and passivate the acidity of the outer surface at the same time. This method abandons the disadvantage of previous modification of molecular sieves by blocking the pores to narrow the orifice, and upgrades the product selectivity while ensuring the catalyst activity. -
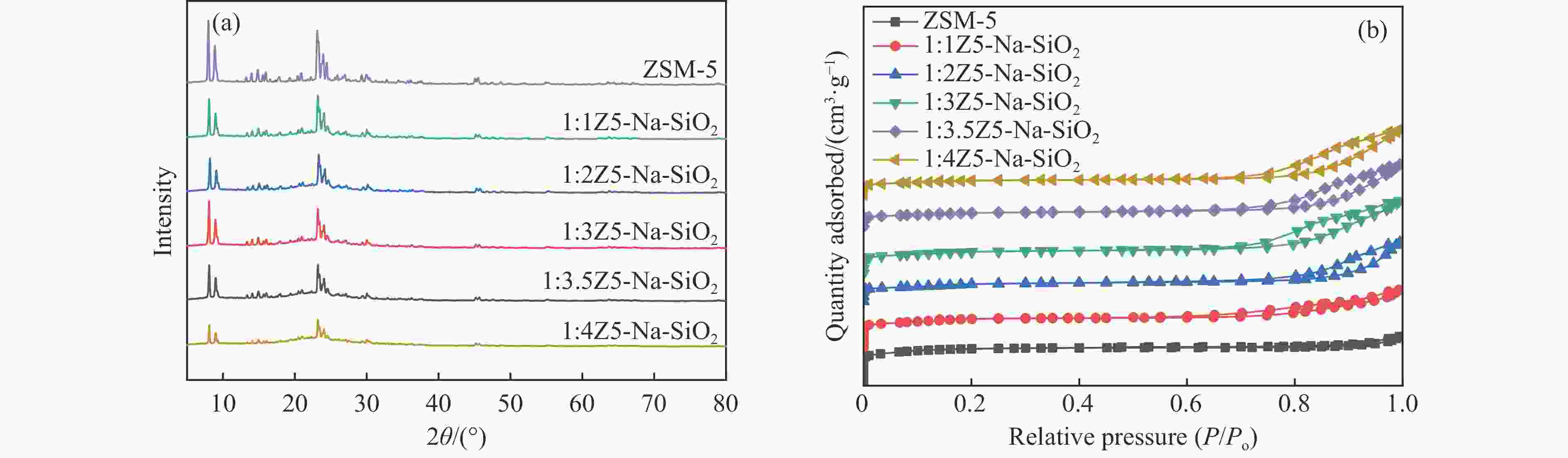
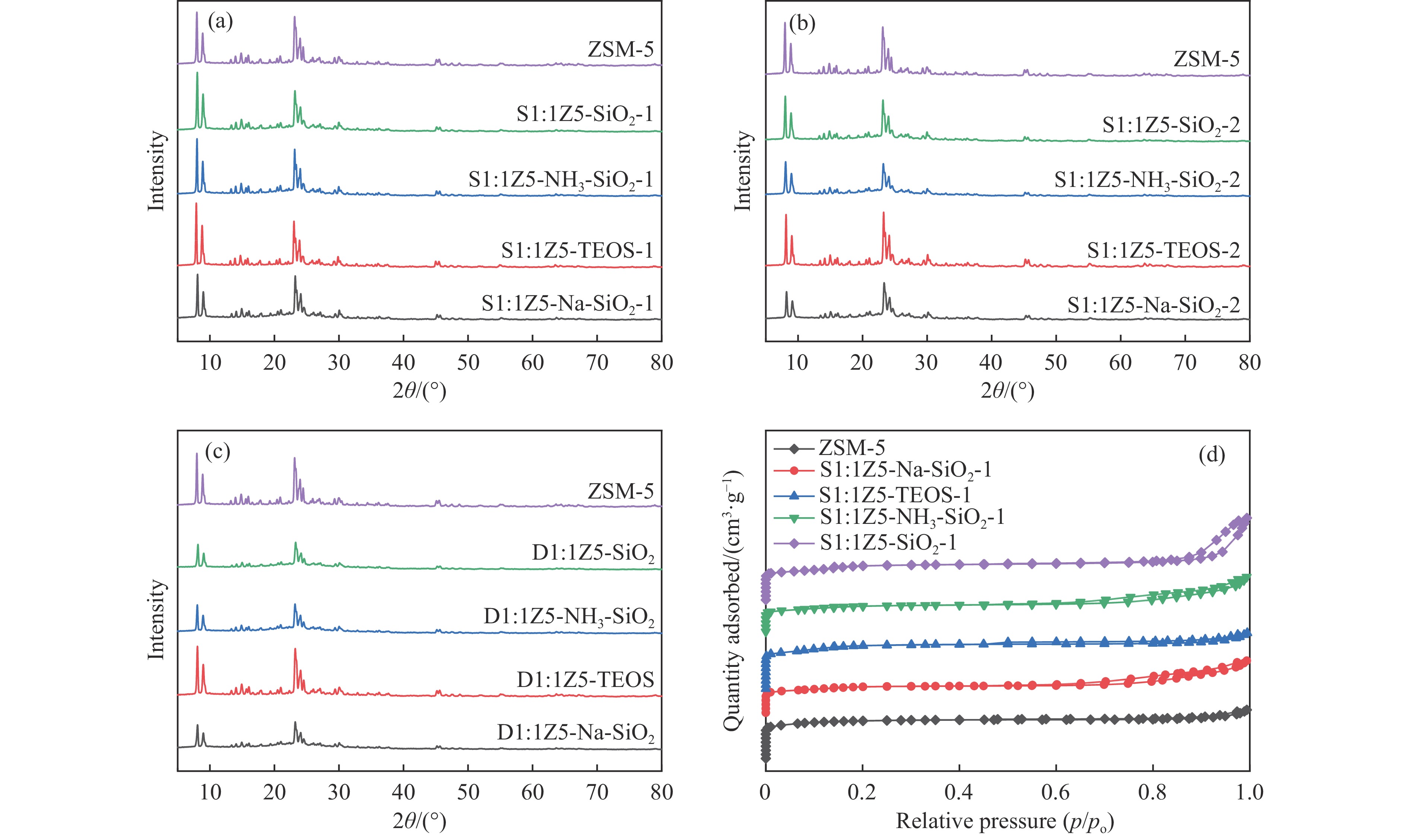
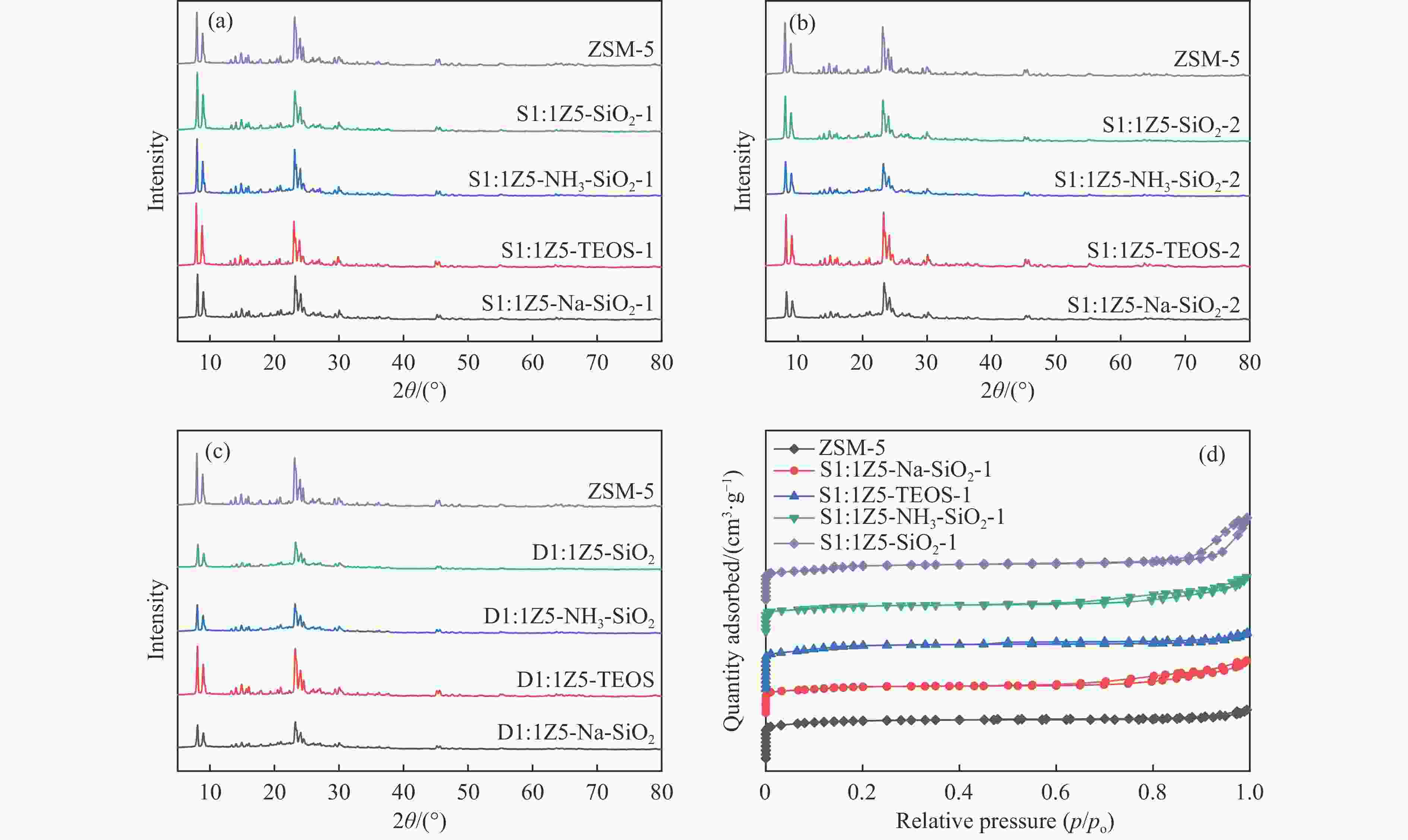
图 1 样品(a)ZSM-5、S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-TEOS-1、S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-SiO2-1,(b)S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2、S1:1Z5-TEOS-2、S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2、S1:1Z5-SiO2-2,(c)D1:1Z5-Na-SiO2、D1:1Z5-TEOS、D1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2、D1:1Z5-SiO2的XRD谱图;(d)ZSM-5、S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-TEOS-1、S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-SiO2-1的N2吸附-脱附等温线
Figure 1 (a) XRD patterns of ZSM-5, S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1, S1:1Z5-TEOS-1, S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1, and S1:1Z5-SiO2-1; (b) XRD patterns of S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2, S1:1Z5-TEOS-2, S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2, and S1:1Z5-SiO2-2; (c) XRD patterns of D1:1Z5-Na-SiO2, D1:1Z5-TEOS, D1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2, and D1:1Z5-SiO2; and (d) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of ZSM-5, S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1, S1:1Z5-TEOS-1, S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1, and S1:1Z5-SiO2-1
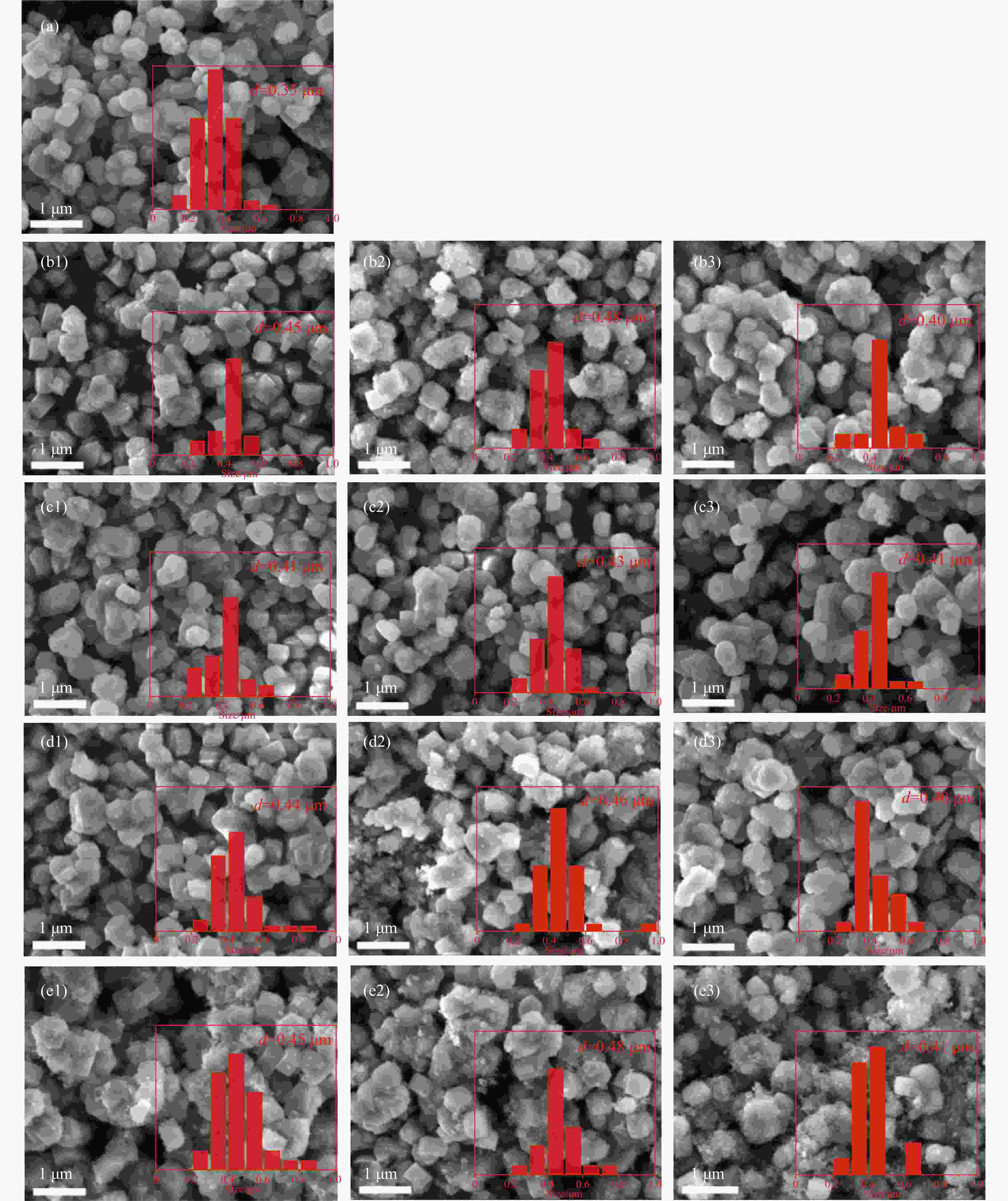
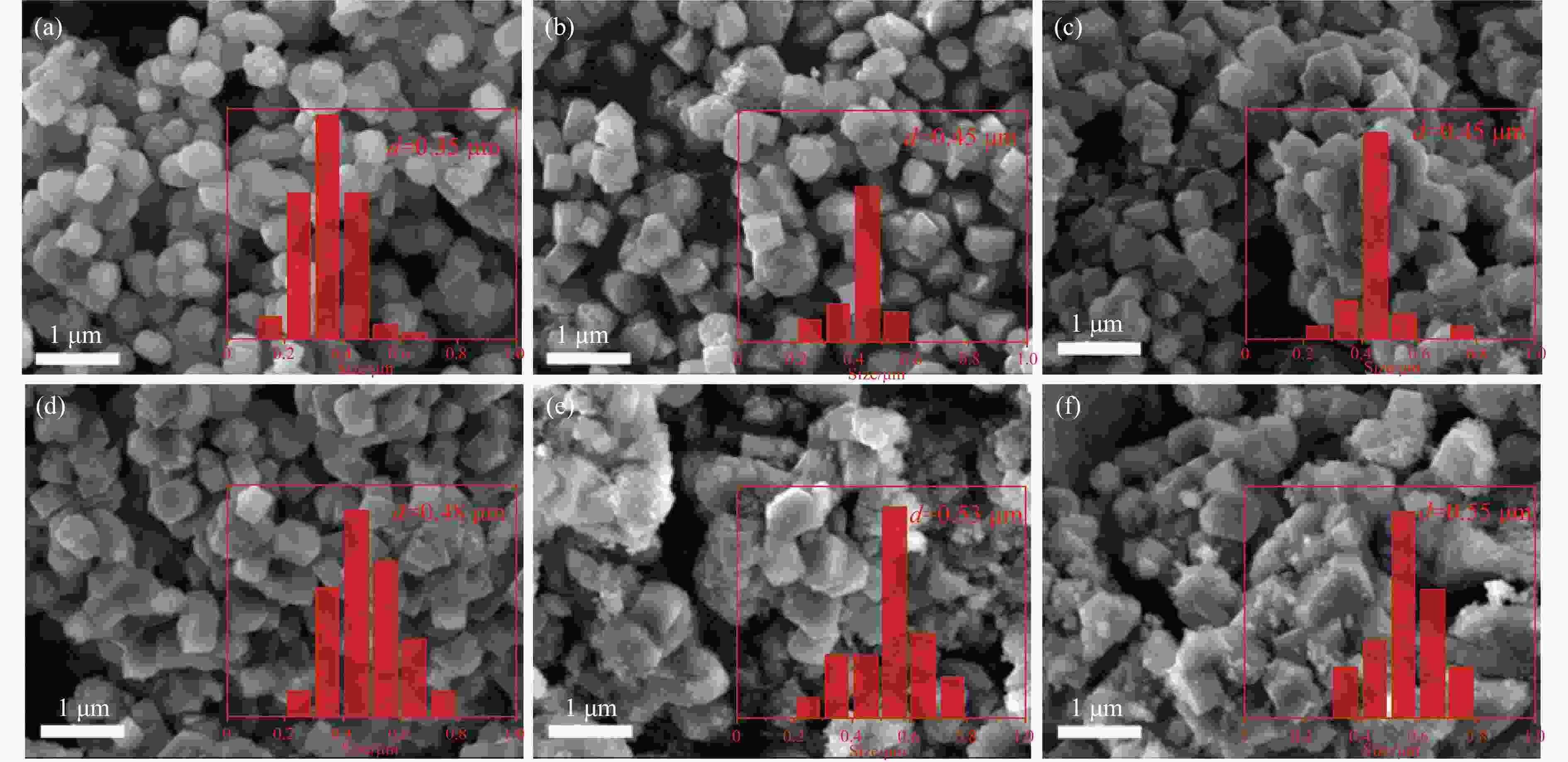
图 2 样品(a)ZSM-5,(b1-e1)S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2-1,(b2-e2)S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2-2,(b3-e3)D1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2的SEM图像
Figure 2 SEM images of samples (a) ZSM-5, (b1-e1) S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2-1, (b2-e2) S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2-2, and (b3-e3) D1:1Z5-Na-SiO2/TEOS/NH3-SiO2/SiO2
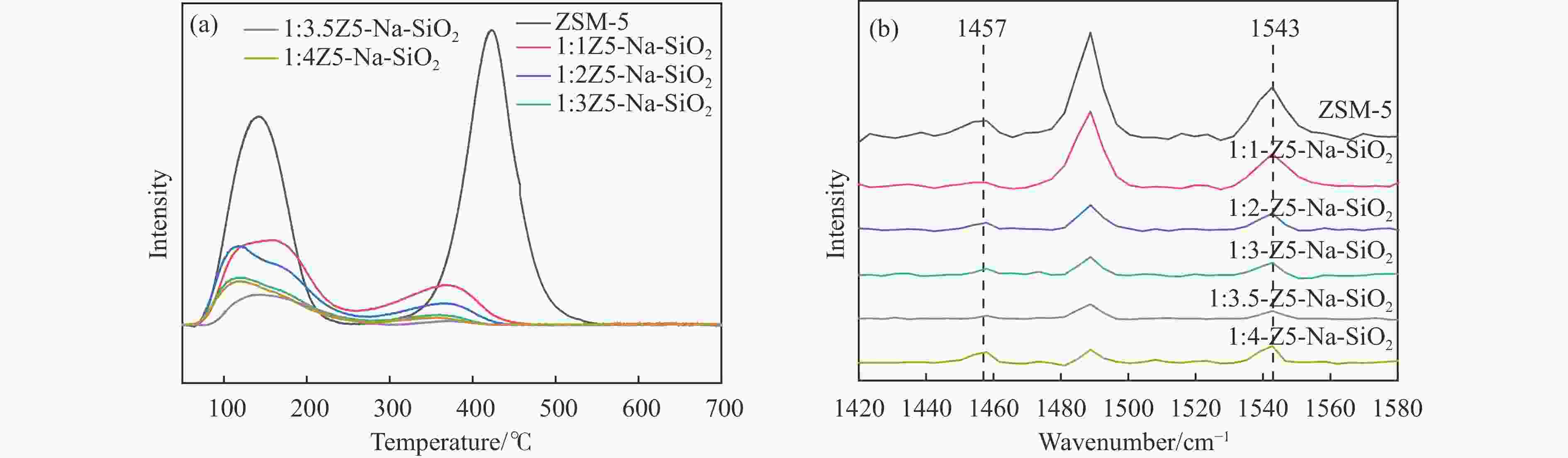
图 3 ZSM-5、S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-TEOS-1、S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1、S1:1Z5-SiO2-1的(a)XPS Al 2p谱图,(b)NH3-TPD曲线,(c)350 ℃的Py-FTIR谱图和(d)ZSM-5、S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2、S1:1Z5-TEOS-2、S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2和S1:1Z5-SiO2-2的350 ℃ Py-FTIR谱图
Figure 3 (a) XPS Al 2p spectra, (b) NH3-TPD curves and (c) Py-FTIR spectra at 350°C for ZSM-5, S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1, S1:1Z5-TEOS-1, S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1, S1:1Z5-SiO2-1, and (d) 350°C Py-FTIR spectra of ZSM-5, S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2,S1:1Z5-TEOS-2, S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2, and S1:1Z5-SiO2-2
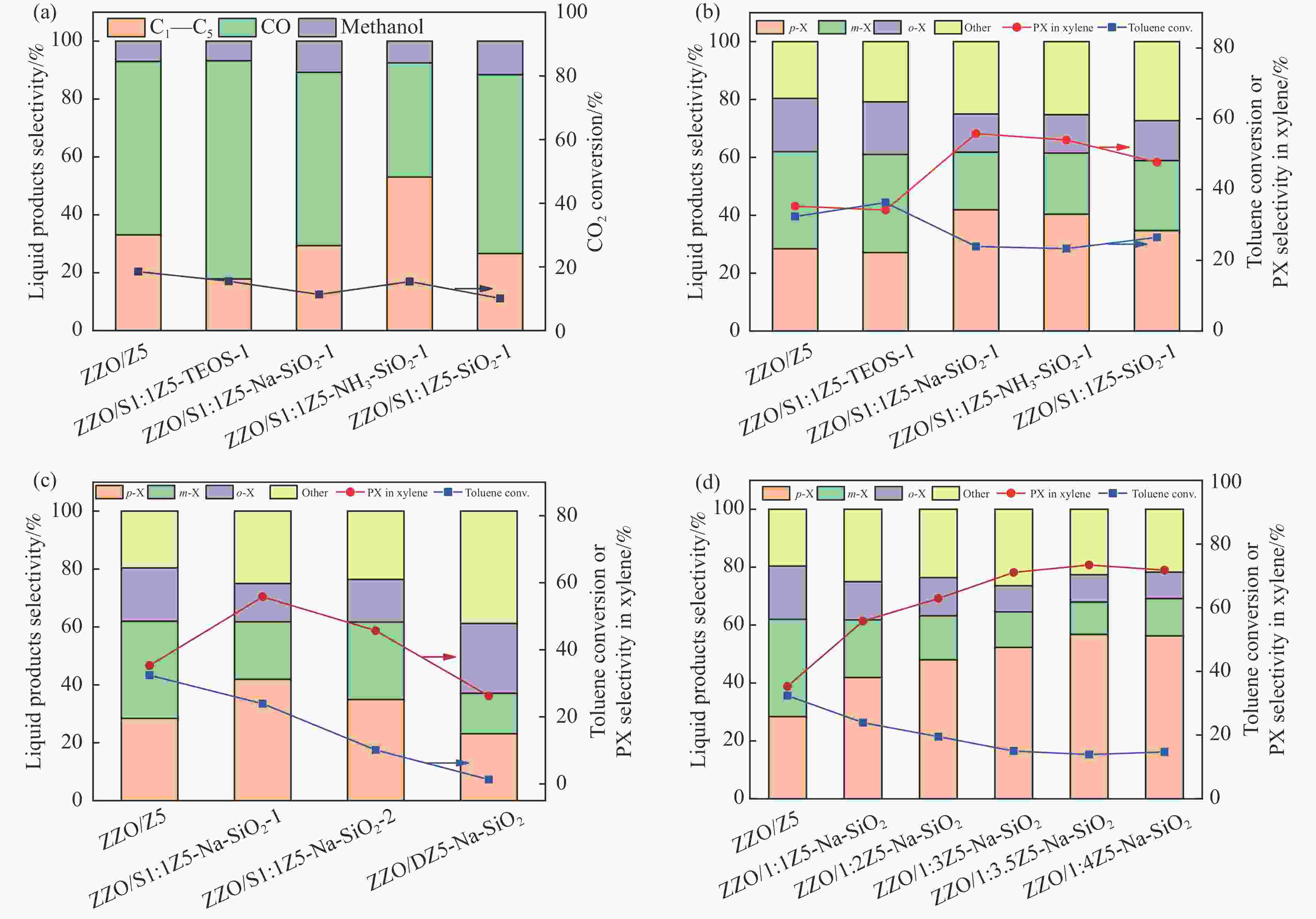
图 9 CO2加H2与甲苯烷基化反应(a)在不同硅源制备的ZSM-5@Silicalite-1和ZnZrOx的双功能催化剂上的液相产物选择性,(b)气相产物选择性,(c)不同晶化次数的ZSM-5@Silicalite-1和ZnZrOx的双功能催化剂上的液相产物选择性和(d)不同钝化层厚度分子筛和ZnZrOx的双功能催化剂上的液相产物选择性,反应条件:400 ℃,3 MPa,H2/CO2为3∶1,GHSV为9000 h−1,甲苯LHSV为2 h−1
Figure 9 CO2 hydrogenation and toluene alkylation reactions (a) liquid-phase product selectivity over bifunctional catalysts of ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 and ZnZrOx prepared with different silicon sources, (b) gas-phase product selectivity, (c) liquid-phase product selectivity over bifunctional catalysts of ZSM-5@Silicalite-1 and ZnZrOx with different numbers of crystallizations and (d) liquid-phase product selectivity over bifunctional catalysts of zeolites with different shell thicknesses and ZnZrOx. Reaction conditions: 400 ℃, 3 MPa, H2/CO2=3/1, GHSV=9000 h−1, and LHSV of toluene = 2 h−1.
表 1 ZSM-5和S1:1Z5@Silicalite-1分子筛的织构性质
Table 1 Textural properties of ZSM-5 and S1:1Z5@Silicalite-1 zeolite
Catalyst Relative crystallinity/% BET surface area S/(m2·g−1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g−1) Pore size d/nm ZSM-5 100 364 0.15 1.92 S1:1Z5-SiO2-1 87 325 0.13 3.96 S1:1Z5-SiO2-2 84 443 0.18 5.68 S1:Z5- Na-SiO2-1 95 337 0.11 3.21 S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2 82 324 0.14 4.95 S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1 96 258 0.10 3.41 S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2 73 253 0.10 5.09 S1:1Z5-TEOS-1 96 413 0.17 2.17 S1:1Z5-TEOS-2 97 360 0.15 1.96 表 2 350 ℃下从Py-FTIR得到的ZSM-5和S1:1Z5@Silicalite-1分子筛的B酸和L酸量
Table 2 Amounts of Brønsted and Lewis acids of ZSM-5 and S1:1Z5@Silicalite-1 zeolite from Py-FTIR at 350°C
Catalyst L/(μmol·g−1) B+L/(μmol·g−1) B/(μmol·g−1) B/L Total/(μmol·g−1) ZSM-5 2.8 29.6 15.2 5.4 47.5 S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1 1.2 25.1 5.7 4.75 32.0 S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2 0.8 26.0 9.2 11.5 36.0 S1:1Z5-TEOS-1 3.3 57.5 33.5 10.2 94.3 S1:1Z5-TEOS-2 2.2 35.6 25.6 11.6 63.3 S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1 2.2 25.6 10.1 4.6 37.9 S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2 0.7 30.5 11.7 16.7 43.0 S1:1Z5-SiO2-1 1.2 24.8 11.0 9.2 37.0 S1:1Z5-SiO2-2 1.0 28.5 15.5 15.5 45.0 表 3 不同钝化层厚度ZSM@Silicalite-1分子筛的织构性质
Table 3 Textural properties of ZSM@Silicalite-1 zeolites with different shell thicknesses
Catalyst BET surface area S/(m2·g−1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g−1) Pore size d/nm ZSM-5 383 0.14 1.63 1:1Z5- Na-SiO2 337 0.11 3.21 1:2Z5- Na-SiO2 202 0.05 5.13 1:3Z5- Na-SiO2 165 0.04 5.18 1:3.5Z5- Na-SiO2 139 0.03 6.5 1:4Z5- Na-SiO2 143 0.03 6.6 表 4 350 ℃下从Py-FTIR得到的不同钝化层厚度分子筛的B酸和L酸量
Table 4 Amounts of Brønsted and Lewis acids of zeolite with different shell thicknesses from Py-FTIR at 350 ℃
Catalyst L/(μmol·g−1) B+L/(μmol·g−1) B/(μmol·g−1) B/L Total/(μmol·g−1) ZSM-5 2.8 29.6 15.2 5.4 47.5 1:1Z5-Na-SiO2 1.2 23.1 9.8 8.2 34.1 1:2Z5-Na-SiO2 0.8 7.5 4.3 5.4 12.6 1:3Z5-Na-SiO2 0.8 3.9 2.7 3.4 7.5 1:3.5Z5-Na-SiO2 0.6 3.8 1.9 3.2 6.3 1:4Z5-Na-SiO2 1.9 2.5 3.8 2 8.2 表 5 ZnZrOx的织构性质
Table 5 Textural properties of ZnZrOx
Catalyst BET surface area S/(m2·g−1) Pore volume v/(cm3·g−1) Pore size d/nm ZnZrOx 29 0.03 3 表 6 不同晶化条件催化剂上CO2加氢耦合甲苯烷基化反应气相产物分析
Table 6 Gas-phase products analysis of CO2 hydrogenation and toluene alkylation over catalysts with different crystallization conditions
Catalyst CO2 conv./% C1−C5 CO Smethy ZZO/Z5 18.6 33.1 59.9 7.0 ZZO/S1:1Z5-TEOS-1 15.5 17.9 75.4 6.7 ZZO/S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1 11.3 29.4 59.9 10.7 ZZO/S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1 15.4 53.1 39.5 7.4 ZZO/S1:1Z5-SiO2-1 10.1 26.7 61.7 11.6 表 7 不同晶化条件催化剂上CO2加氢耦合甲苯烷基化反应液相产物分析
Table 7 Liquid phase product analysis of CO2 hydrogenation and toluene alkylation over catalysts with different crystallization conditions
Catalyst Conv.
T/%Selectivity/% PX/X PX MX OX other ZZO/Z5 32.4 28.4 33.6 18.4 19.6 35.3 ZZO/S1:1Z5-TEOS-1 36.3 27.1 33.9 18.2 20.8 34.2 ZZO/S1:1Z5-TEOS-2 29.0 33.9 30.2 18.4 17.5 41.1 ZZO/D1:1Z5-TEOS 29.3 20.4 41.0 18.4 20.2 25.5 ZZO/S1:1Z5-SiO2-1 26.5 34.7 24.2 13.8 27.3 47.7 ZZO/S1:1Z5-SiO2-2 29.5 23.8 35.2 17.3 23.7 28.4 ZZO/D1:1Z5-SiO2 29.1 18.8 34.7 12.7 33.8 17.4 ZZO/S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-1 23.3 40.4 21.1 13.3 25.2 54.0 ZZO/S1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2-2 25.5 30.5 32.5 15.1 21.9 39.0 ZZO/D1:1Z5-NH3-SiO2 12.7 29.7 28.8 27.9 13.6 34.4 ZZO/S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-1 23.9 41.9 19.9 13.2 25.0 55.8 ZZO/S1:1Z5-Na-SiO2-2 10.1 34.9 26.8 14.7 23.6 45.7 ZZO/D1:1Z5-Na-SiO2 1.3 23.1 14.0 24.1 38.8 26.2 -
[1] TSAI T C, LIU S B, WANG I. Disproportionation and transalkylation of alkylbenzenes over zeolite catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,1999,181(2):355−398. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(98)00396-2 [2] VERMEIREN W, GILSON J P. Impact of zeolites on the petroleum and petrochemical industry[J]. Top Catal,2009,52(9):1131−1161. doi: 10.1007/s11244-009-9271-8 [3] DOOLAN P, PUJADO P. Make aromatics from LPG[J]. Hydrocarb Process, 1989, 68 (9). [4] BADURAIG A, ODEDAIRO T, AL-KHATTAF S. Disproportionation and methylation of toluene with methanol over zeolite catalysts[J]. Top Catal,2010,53:1446−1456. doi: 10.1007/s11244-010-9605-6 [5] LEE S, KIM D, LEE J, et al. An in situ methylation of toluene using syngas over bifunctional mixture of Cr2O3/ZnO and HZSM-5[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,2013,466:90−97. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.025 [6] ZUO J, CHEN W, LIU J, et al. Selective methylation of toluene using CO2 and H2 to para-xylene[J]. Sci Adv,2020,6(34):2375−2548 . [7] WEN D, ZUO J, HAN X, et al. Synthesis of durene by methylation of 1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene with syngas over bifunctional CuZnZrO x–HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2022,12(8):2555−2565. doi: 10.1039/D2CY00037G [8] WANG Y, TAN L, TAN M, et al. Rationally designing bifunctional catalysts as an efficient strategy to boost CO2 hydrogenation producing value-added aromatics[J]. ACS Catal,2018,9(2):895−901. [9] NI Y, CHEN Z, FU Y, et al. Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics[J]. Nat Commun,2018,9(1):3457. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05880-4 [10] LI Z, QU Y, WANG J, et al. Highly selective conversion of carbon dioxide to aromatics over tandem catalysts[J]. Joule,2019,3(2):570−583. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.10.027 [11] MA Y, WANG N, QIAN W, et al. Molded MFI nanocrystals as a highly active catalyst in a methanol-to-aromatics process[J]. RSC Adv,2016,6(84):81198−81202. doi: 10.1039/C6RA19035A [12] PINILLA-HERRERO I, BORFECCHIA E, HOLZINGER J, et al. High Zn/Al ratios enhance dehydrogenation vs hydrogen transfer reactions of Zn-ZSM-5 catalytic systems in methanol conversion to aromatics[J]. J Catal,2018,362:146−163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.032 [13] ZHU Z, XIE Z, CHEN Q, et al. Chemical liquid deposition with polysiloxane of ZSM-5 and its effect on acidity and catalytic properties[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2007,101(1-2):169−175. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.12.016 [14] KIM J-H, ISHIDA A, OKAJIMA M, et al. Modification of HZSM-5 by CVD of various silicon compounds and generation of para-selectivity[J]. J Catal,1996,161(1):387−392. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1996.0196 [15] BAUER F, CHEN W, BILZ E, et al. Surface modification of nano-sized HZSM-5 and HFER by pre-coking and silanization[J]. J Catal,2007,251(2):258−270. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.08.009 [16] SAYED M B, VéDRINE J C. The effect of modification with boron on the catalytic activity and selectivity of HZSM-5: I. Impregnation with boric acid[J]. J Catal,1986,101(1):43−55. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(86)90227-7 [17] JANARDHAN H, SHANBHAG G, HALGERI A. Shape-selective catalysis by phosphate modified ZSM-5: Generation of new acid sites with pore narrowing[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,2014,471:12−18. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.11.029 [18] DE MENEZES S C, LAM Y, DAMODARAN K, et al. Modification of H-ZSM-5 zeolites with phosphorus. 1. Identification of aluminum species by 27Al solid-state NMR and characterization of their catalytic properties[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2006,95(1-3):286−295. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.05.032 [19] HODALA J L, HALGERI A B, SHANBHAG G V. Phosphate modified ZSM-5 for the shape-selective synthesis of para-diethylbenzene: Role of crystal size and acidity[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,2014,484:8−16. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2014.07.006 [20] LI J, TONG K, XI Z, et al. Highly-efficient conversion of methanol to p-xylene over shape-selective Mg–Zn–Si-HZSM-5 catalyst with fine modification of pore-opening and acidic properties[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2016,6(13):4802−4813. doi: 10.1039/C5CY01979F [21] QU Y, LI Z, HU H, et al. Highly selective conversion of CO 2 to para-xylene over tandem catalysts[J]. ChemComm,2023,59(49):7607−7610. [22] VéDRINE J C, AUROUX A, DEJAIFVE P, et al. Catalytic and physical properties of phosphorus-modified ZSM-5 zeolite[J]. J Catal,1982,73(1):147−160. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(82)90089-6 [23] BREEN J P, BURCH R, KULKARNI M, et al. Improved selectivity in the toluene alkylation reaction through understanding and optimising the process variables[J]. Appl Catal A:Gen,2007,316(1):53−60. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2006.09.017 [24] Lü R, TANGBO H, WANG Q, et al. Properties and characterization of modified HZSM-5 zeolites[J]. J Energy Chem,2003,12(1):56. [25] GHORBANPOUR A, GUMIDYALA A, GRABOW L C, et al. Epitaxial growth of ZSM-5@ Silicalite-1: A core–shell zeolite designed with passivated surface acidity[J]. ACS Nano,2015,9(4):4006−4016. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01308 [26] VAN VU D, MIYAMOTO M, NISHIYAMA N, et al. Catalytic activities and structures of silicalite-1/H-ZSM-5 zeolite composites[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2008,115(1-2):106−112. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.12.034 [27] WU Q, WANG X, QI G, et al. Sustainable synthesis of zeolites without addition of both organotemplates and solvents[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2014,136(10):4019−4025. doi: 10.1021/ja500098j [28] WU Q, MENG X, GAO X, et al. Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites: mechanism and utility[J]. Acc Chem Res,2018,51(6):1396−1403. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00057 [29] BIAN C, ZHANG C, PAN S, et al. Generalized high-temperature synthesis of zeolite catalysts with unpredictably high space-time yields (STYs)[J]. J Mater Chem A,2017,5(6):2613−2618. doi: 10.1039/C6TA09866E [30] ZHANG C, WU Q, LEI C, et al. Solvent-free and mesoporogen-free synthesis of mesoporous aluminosilicate ZSM-5 zeolites with superior catalytic properties in the methanol-to-olefins reaction[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2017,56(6):1450−1460. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.7b00062 [31] WANG C, WANG L, ZHANG J, et al. Product selectivity controlled by zeolite crystals in biomass hydrogenation over a palladium catalyst[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2016,138(25):7880−7883. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04951 [32] WU Q, LIU X, ZHU L, et al. Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from anhydrous starting raw solids[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2015,137(3):1052−1055. doi: 10.1021/ja5124013 [33] LIU Z, WU D, REN S, et al. Solvent-Free synthesis of c-Axis oriented ZSM-5 crystals with enhanced methanol to gasoline catalytic activity[J]. ChemCatChem,2016,8(21):3317−3322. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201600896 [34] LU X, YANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Solvent-free secondary growth of highly b-oriented MFI zeolite films from anhydrous synthetic powder[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2019,141(7):2916−2919. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b00018 [35] ZHANG J, WANG L, WU Z, et al. Solvent-free synthesis of core–shell Zn/ZSM-5@ silicalite-1 catalyst for selective conversion of methanol to BTX aromatics[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2019,58(34):15453−15458. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.9b03357 [36] MOHAMED R M, ALY H M, EL-SHAHAT M F, et al. Effect of the silica sources on the crystallinity of nanosized ZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2005,79(1-3):7−12. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2004.10.031 [37] AL-JUBOURI S M. Synthesis of hierarchically porous ZSM-5 zeolite by self-assembly induced by aging in the absence of seeding-assistance[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2020,303:110296. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110296 [38] WANG C, ZHANG L, HUANG X, et al. Maximizing sinusoidal channels of HZSM-5 for high shape-selectivity to p-xylene[J]. Nat Commun,2019,10(1):4348. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12285-4 [39] JIN D, YE G, ZHENG J, et al. Hierarchical silicoaluminophosphate catalysts with enhanced hydroisomerization selectivity by directing the orientated assembly of premanufactured building blocks[J]. ACS Catal,2017,7(9):5887−5902. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.7b01646 [40] 吴保强, 马晓迅, 梁斌, 等. 甘油辅助HZSM-5分子筛的制备及其甲烷无氧芳构化催化性能研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(7):821−832.WU Baoqiang, MA Xiaoxun, LIANG Bin, et al. Preparation of HZSM-5 zeolite assisted by glycerin and its catalytic performance for methane aromatization[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(7):821−832. [41] WANG Y, GUO X, ZHANG C, et al. Influence of calcination temperature on the stability of fluorinated nanosized HZSM-5 in the methylation of biphenyl[J]. Catal Letters,2006,107:209−214. doi: 10.1007/s10562-006-0004-3 [42] LIU J, LI X, ZHAO Q, et al. The selective catalytic reduction of NO with propene over Cu-supported Ti–Ce mixed oxide catalysts: Promotional effect of ceria[J]. J Mol Catal A Chem,2013,378:115−123. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.06.005 [43] EMEIS C. Determination of integrated molar extinction coefficients for infrared absorption bands of pyridine adsorbed on solid acid catalysts[J]. J Catal,1993,141(2):347−354. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1993.1145 [44] HAN X, ZUO J, WEN D, et al. Toluene methylation with syngas to para-xylene by bifunctional ZnZrO x-HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Chinese J Catal,2022,43(4):1156−1164. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63975-X [45] DENG Y Q, ZHOU W F, LV H M, et al. Synthesis of HZSM-5@silicalite-1 core-shell composite and its catalytic application in the generation of p-xylene by methylation of toluene with methyl bromide[J]. RSC Adv,2014,4(70):37296−37301. doi: 10.1039/C4RA04126G [46] 潘旭, 杜冰, 黄鑫, 等. 孪晶 HZSM-5@ Silicalite-1 核壳结构催化剂的制备及甲苯甲醇烷基化性能研究[J]. 燃料化学学报 (中英文),2022,50(5):611−620.PAN Xu, DU Bing, HUANG Xin, et al. Preparation of core-shell structural twin HZSM-5@Silicalite-1 catalysts and its performance for toluene alkylation with methanol[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2022,50(5):611−620. [47] ZHANG J, QIAN W, KONG C, et al. Increasing para-xylene selectivity in making aromatics from methanol with a surface-modified Zn/P/ZSM-5 catalyst[J]. ACS Catal,2015,5(5):2982−2988. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b00192 [48] WANG J, TANG C, LI G, et al. High-performance MaZrO x (Ma= Cd, Ga) solid-solution catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J]. ACS Catal,2019,9(11):10253−10259. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b03449 [49] VASANTHAVEL S, KANNAN S. Structural investigations on the tetragonal to cubic phase transformations in zirconia induced by progressive yttrium additions[J]. J Phys Chem Solids,2018,112:100−105. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.09.010 [50] GAO P, ZHONG L, ZHANG L, et al. Yttrium oxide modified Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts via hydrotalcite-like precursors for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2015,5(9):4365−4377. doi: 10.1039/C5CY00372E [51] ZHANG W, WANG S, GUO S, et al. Effective conversion of CO2 into light olefins over a bifunctional catalyst consisting of La-modified ZnZrO x oxide and acidic zeolite[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2022,12(8):2566−2577. doi: 10.1039/D2CY00210H [52] DANG S, QIN B, YANG Y, et al. Rationally designed indium oxide catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol with high activity and selectivity[J]. Sci Adv,2020,6(25):eaaz2060. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz2060 [53] SHANG X, LIU G D, SU X, et al. Preferential Synthesis of Toluene and Xylene from CO2 Hydrogenation in the Presence of Benzene through an Enhanced Coupling Reaction[J]. ACS Catal,2022,12(21):13741−13754. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c04314 [54] YASHIMA T, SAKAGUCHI Y, NAMBA S. Selective formation of p-xylene by alkylation of toluene with methanol on ZSM-5 type zeolites[J]. Stud Surf Sci Catal,1981,7:739−751. -




 下载:
下载: