Theoretical calculations of pyridine adsorption on the surfaces of Ti, Zr, N doped graphene
-
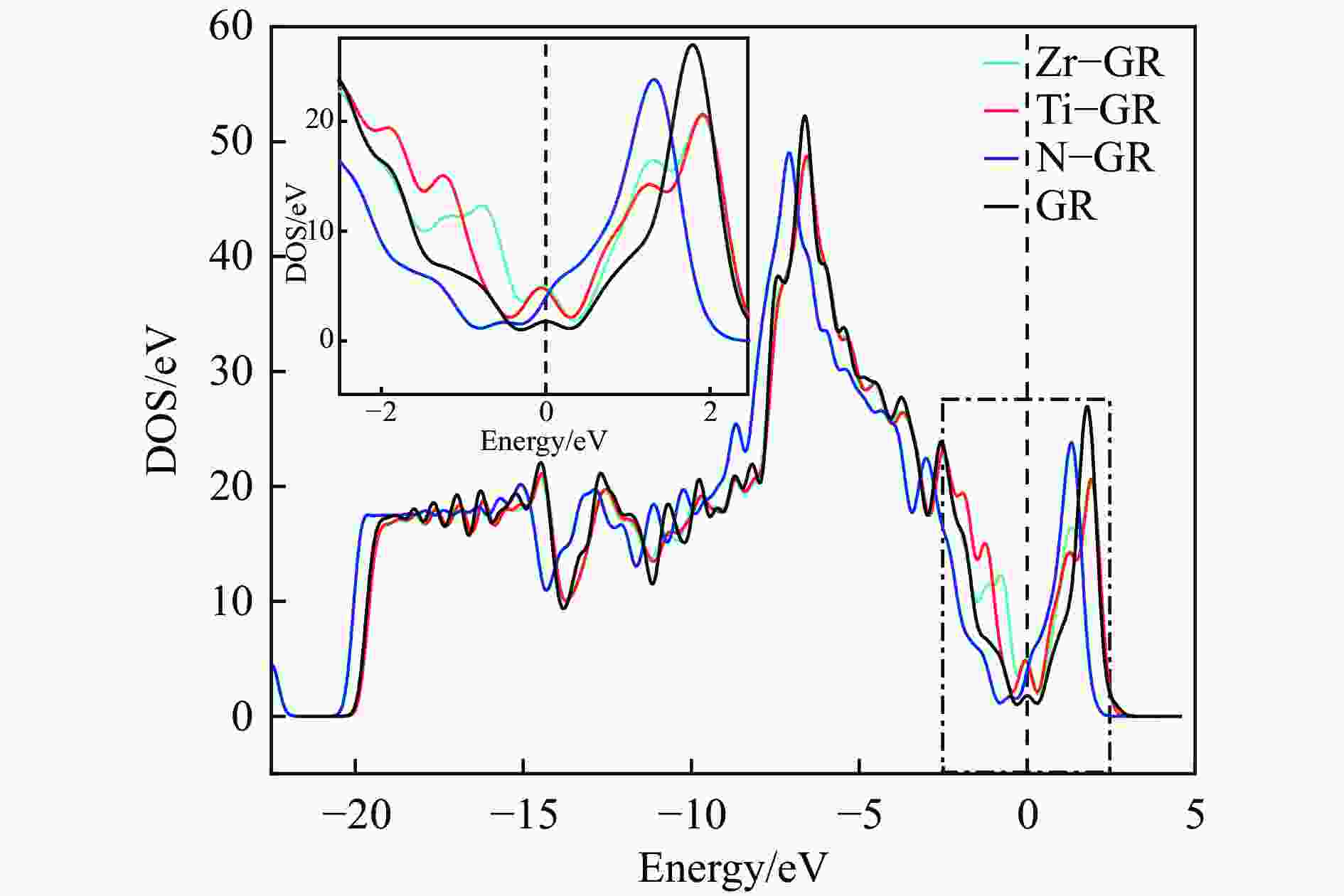
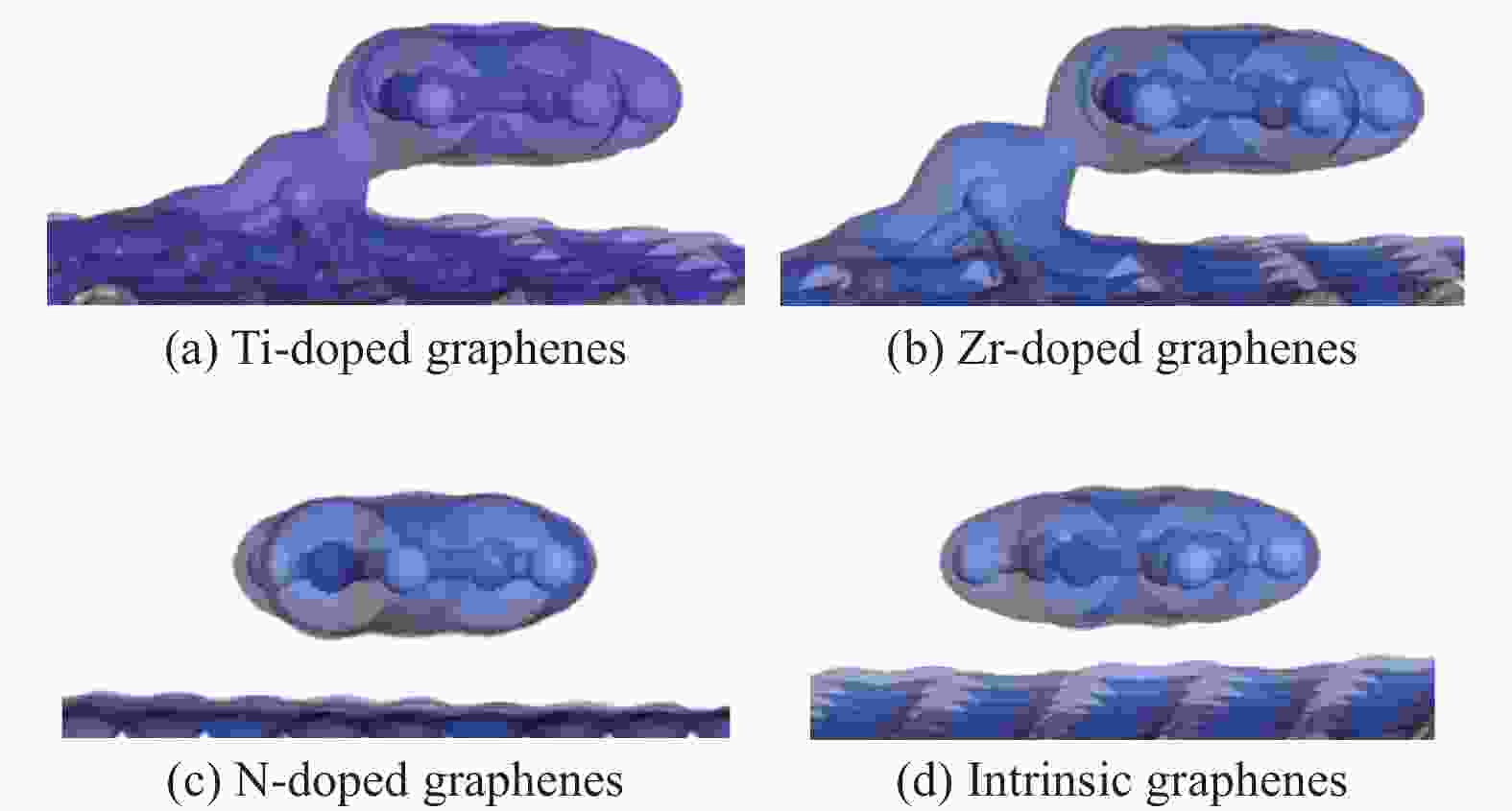
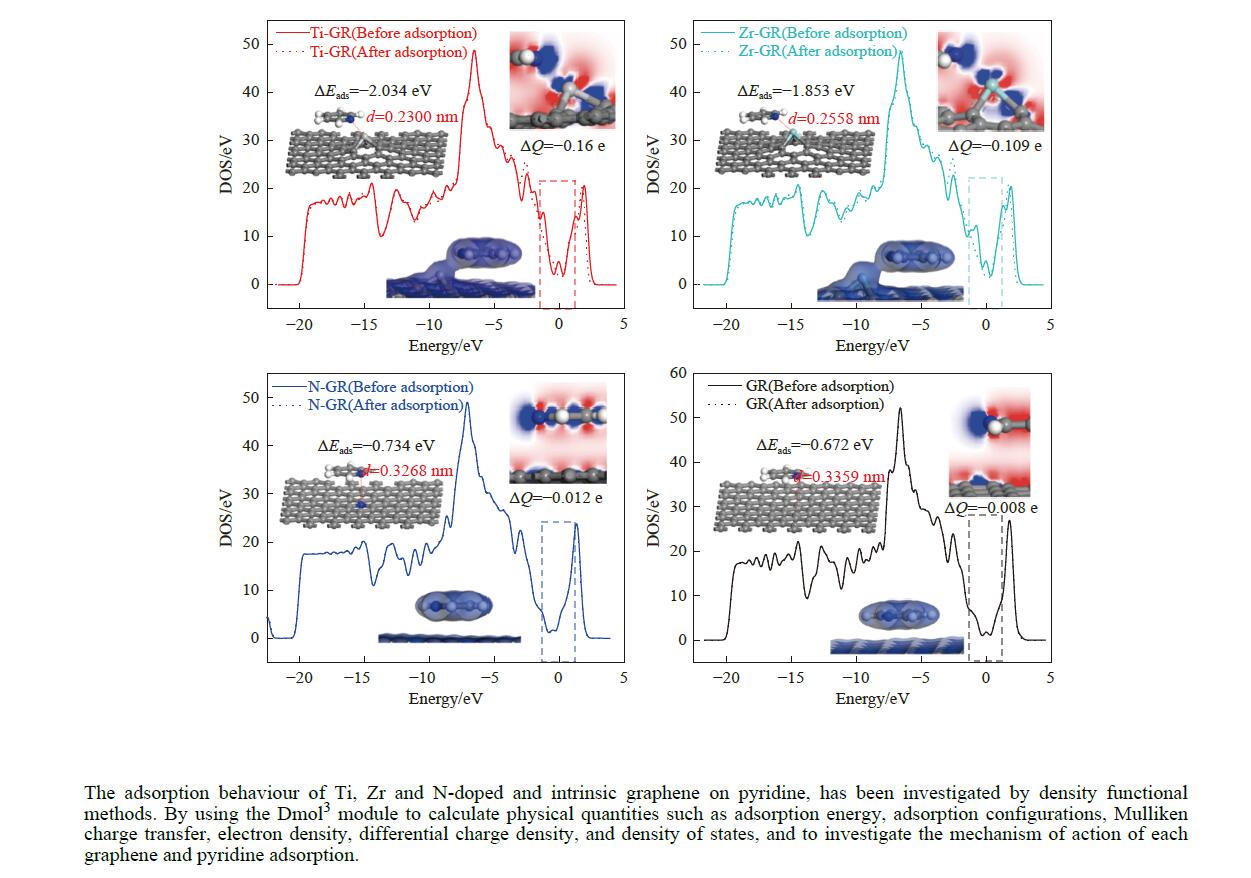
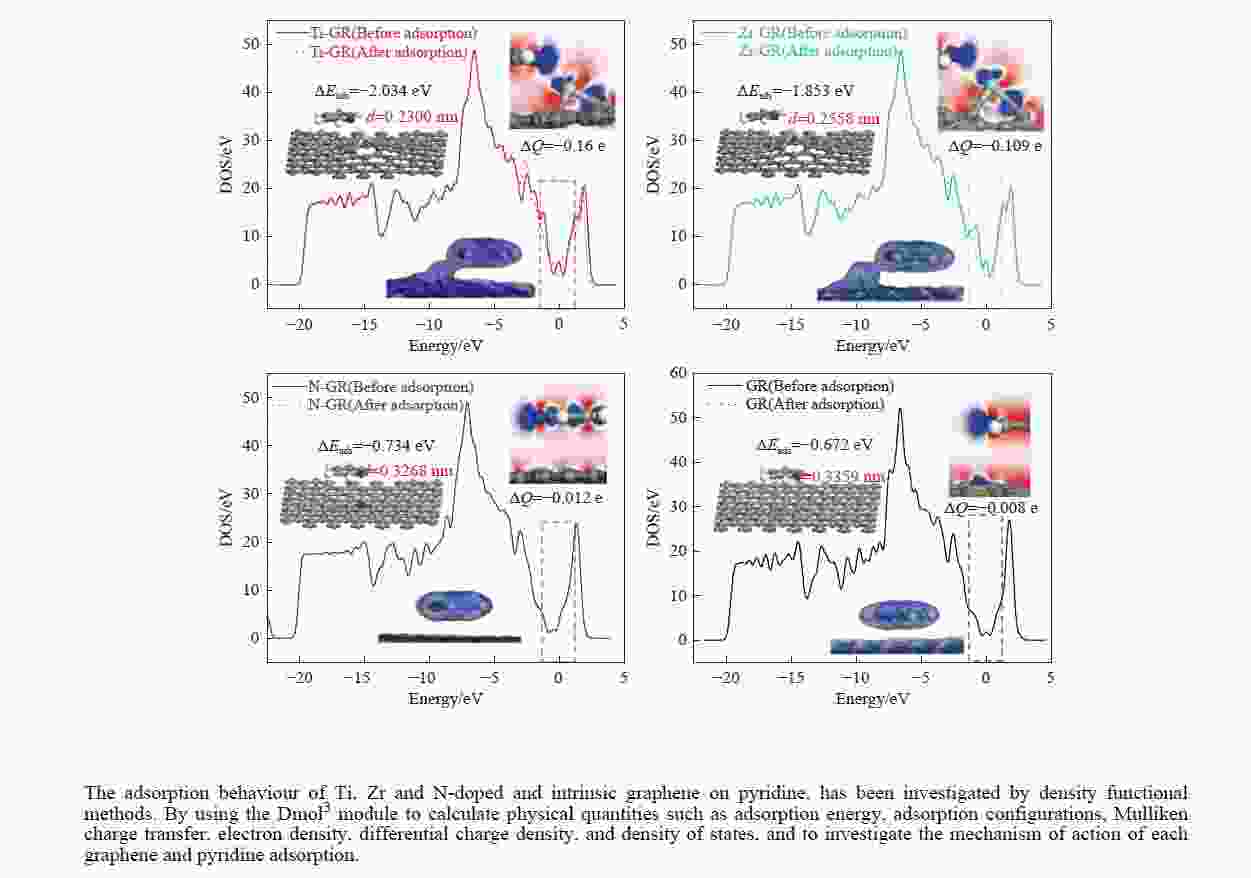
摘要: 采用密度泛函方法,研究了Ti、Zr和N掺杂及本征石墨烯对柴油中典型碱性氮化物吡啶的吸附行为,讨论了相应的吸附能、吸附构型、马利肯电荷转移、差分电荷密度和态密度。结果表明,金属Ti、Zr掺杂能显著增强吡啶在石墨烯表面的吸附能,非金属N掺杂可略微增加吡啶和石墨烯表面间的吸附能。吡啶在不同原子修饰的石墨烯表面的吸附能大小顺序为Ti掺杂石墨烯>Zr掺杂石墨烯>N掺杂石墨烯>本征石墨烯,吡啶可与Ti、Zr掺杂石墨烯发生N−Ti、N−Zr和π−π作用,与N掺杂石墨烯、本征石墨烯发生N−N、C−N和π−π作用。进一步分析发现,吡啶和金属Ti、Zr掺杂石墨烯表面存在明显的电子转移和化学键的形成,而和非金属N掺杂石墨烯及本征石墨烯间并无化学键形成。吡啶与Ti、Zr掺杂石墨烯发生化学吸附,与N掺杂石墨烯、本征石墨烯发生物理吸附。吡啶更稳定的吸附在Ti、Zr掺杂石墨烯表面。Abstract: In this paper, the adsorption behavior of pyridine, a typical basic nitrogen compound in diesel oil, on Ti-doped, Zr-doped, N-doped and intrinsic graphene has been investigated by density functional methods. The corresponding adsorption energy, adsorption configurations, Mulliken charge transfer, differential charge density and density of states were discussed. The results show that doping graphene with metal atoms such as Ti or Zr can significantly obviously enhance the adsorption energy between pyridine and graphene surfaces, while non-metal N doping has a relatively minor effect. The magnitude of the adsorption energy of pyridine on the surfaces of graphene modified with different atoms follows the order: Ti-doped>Zr-doped>N-doped>intrinsic graphene. Pyridine interacts with Ti- or Zr-doped graphene through N−Ti, N−Zr and π−π interactions, while with N-doped and intrinsic graphene, it interacts via N−N, C−N and π−π interactions. There are significant electron transfer and chemical bond formation between pyridine and metal-doped (Ti, Zr) graphene surfaces, indicating chemical adsorption. However, there is no chemical bond formation with non-metal N-doped graphene and intrinsic graphene, suggesting physical adsorption in these cases. Overall, pyridine exhibits more stable adsorption on the surfaces of Ti, Zr-doped graphene.
-
Key words:
- graphene /
- dope /
- adsorption /
- denitrification /
- simulation /
- surfaces
-
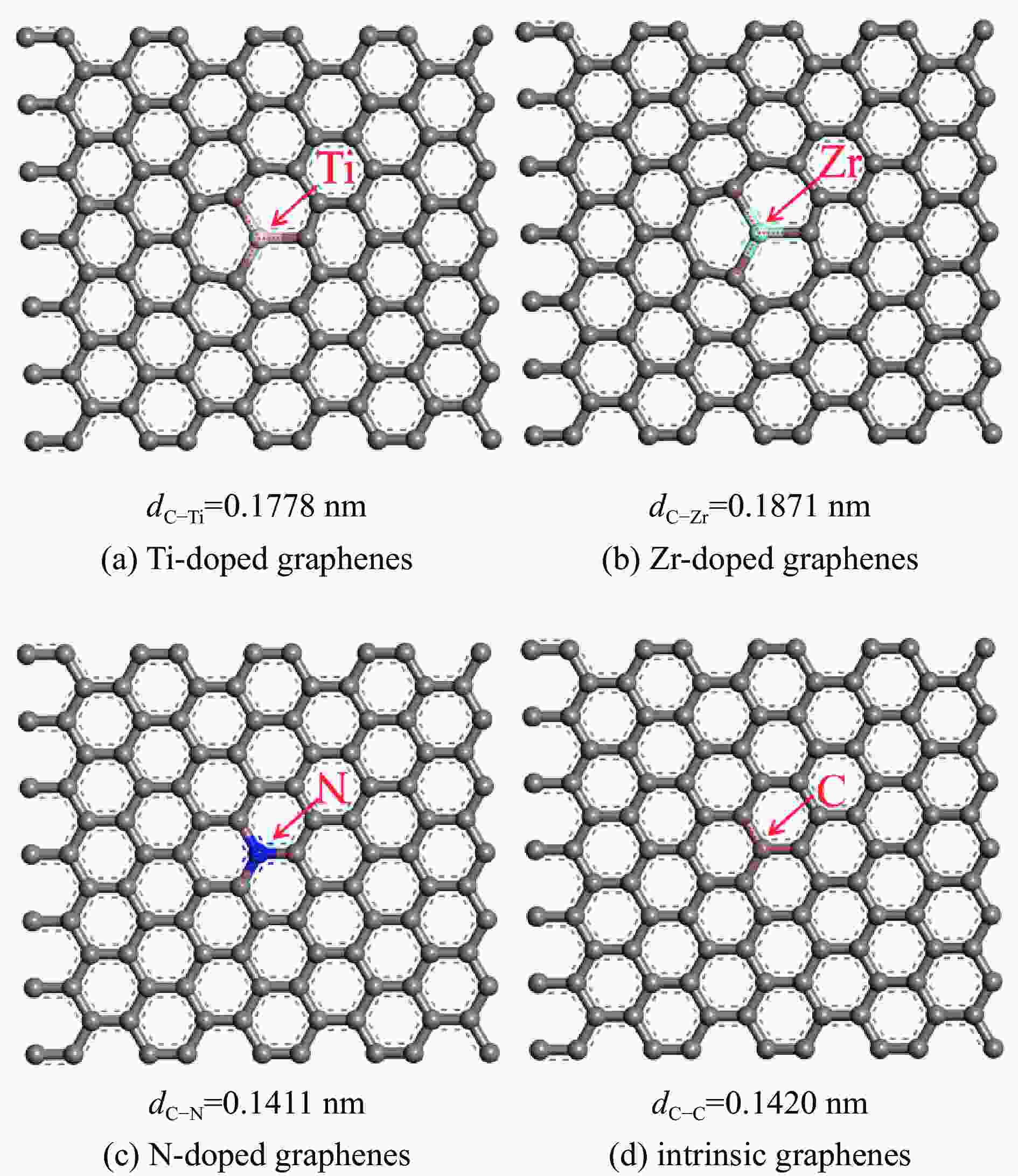
表 1 各石墨烯表面的几何参数
Table 1 Geometrical parameters of the Ti, Zr or N-doped and intrinsic graphene
Doped graphenes Bond length dC−x/nm Bond angle ∠C−X−C/(°) Ti-doped graphenes 0.1775−0.1778 119.905−120.048 Zr-doped graphenes 0.1869−0.1871 119.836−120.082 N-doped graphenes 0.1409−0.1411 119.997−120.006 Intrinsic graphenes 0.1420 120 表 2 吡啶在各石墨烯表面上三种吸附构型的吸附能
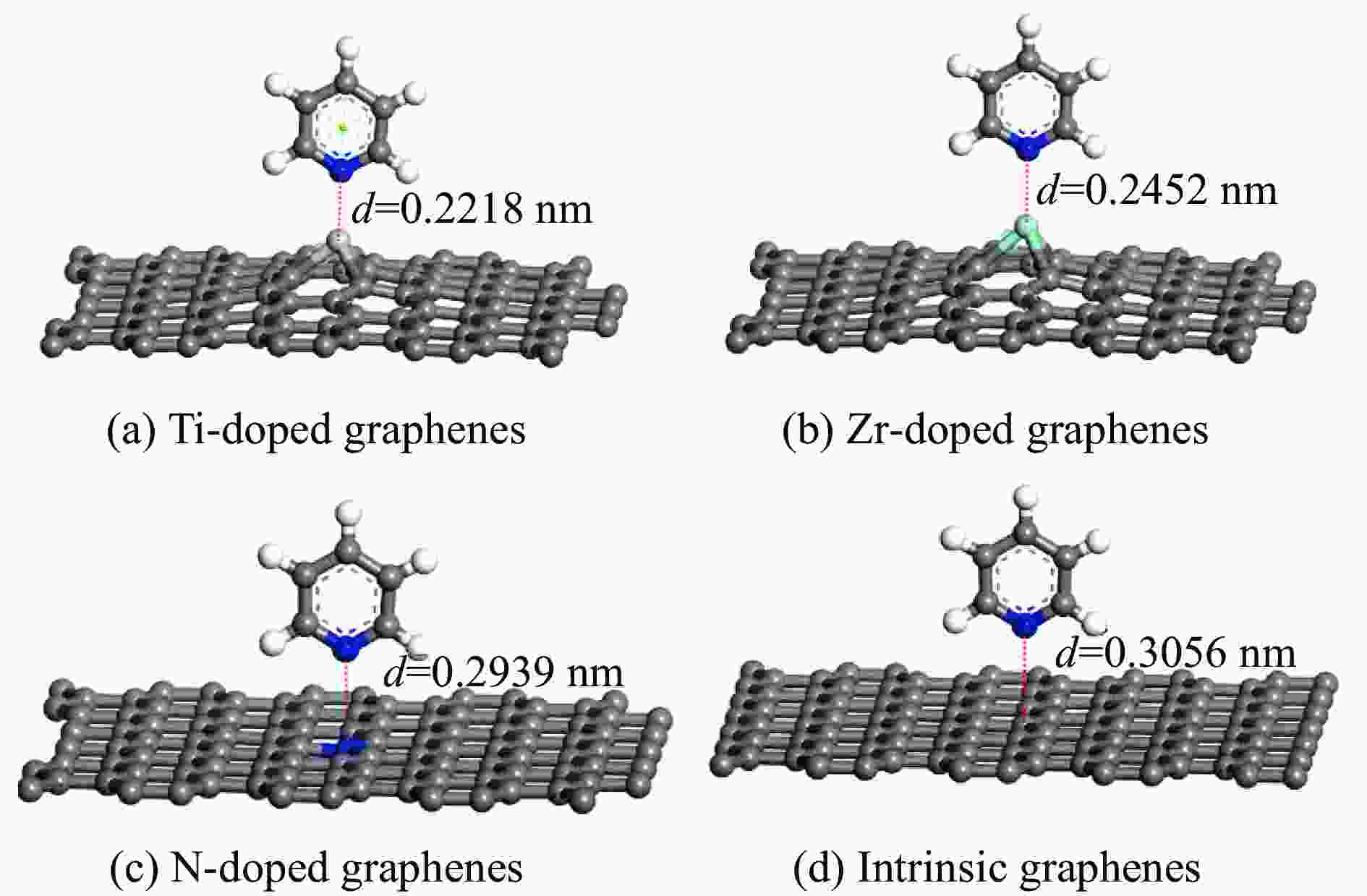
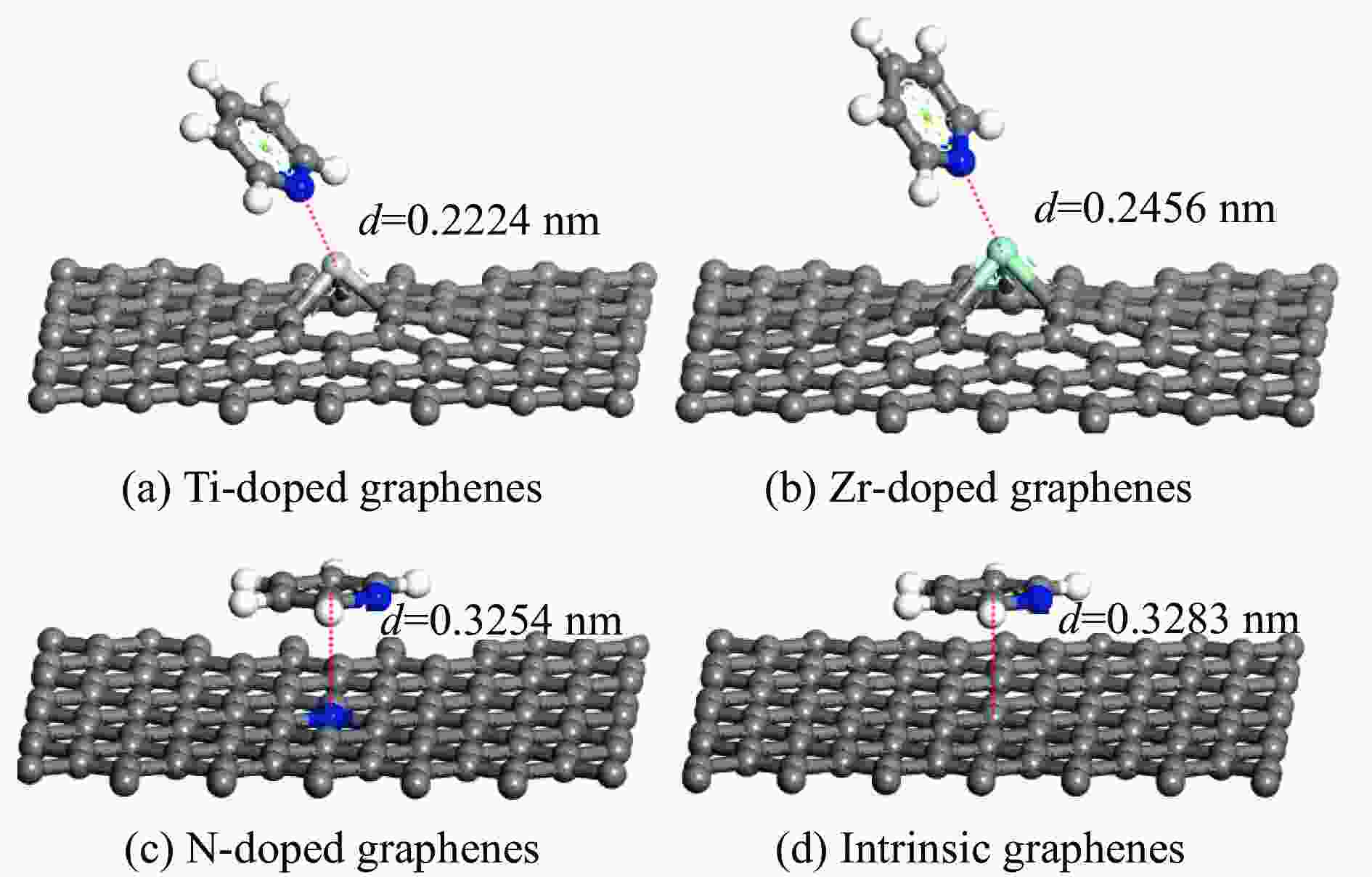
Table 2 Adsorption energy of pyridine adsorption on Ti, Zr or N-doped and intrinsic graphene
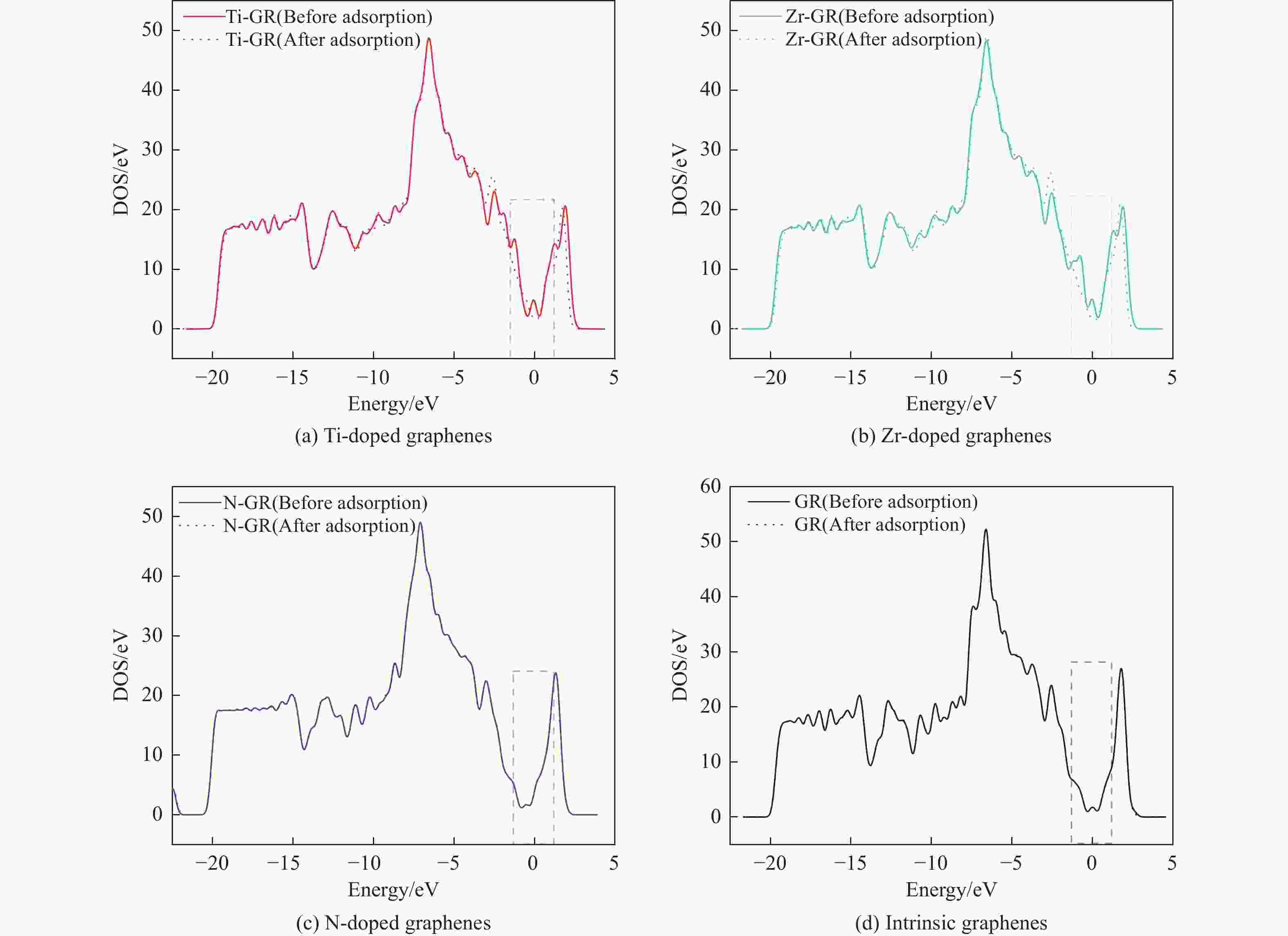
Adsorption structure Energy/eV Ti-doped graphenes Zr-doped graphenes N-doped graphenes Intrinsic graphenes Vertical −1.857 −1.590 −0.499 −0.374 Parallel (ring) −1.854 −1.583 −0.767 −0.736 Parallel (N) −2.034 −1.853 −0.734 −0.672 表 3 吡啶在各石墨烯表面吸附前后吡啶的马利肯电荷布居
Table 3 Mulliken charge of pyridine adsorption on Ti, Zr or N-doped and intrinsic graphene
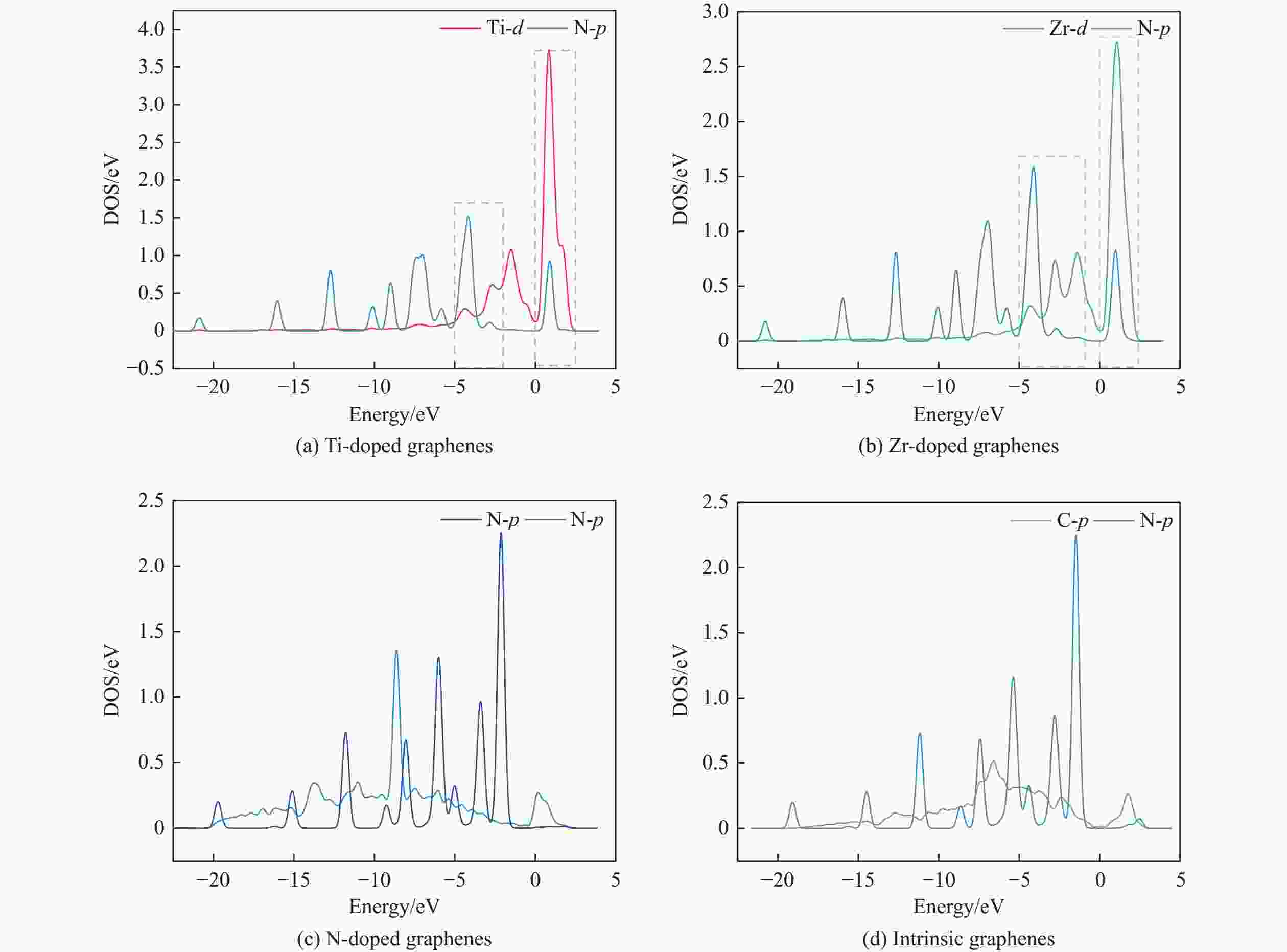
Atom or molecule Before adsorption/e After adsorption (Ti-GR)/e After adsorption (Zr-GR)/e After adsorption (N-GR)/e After adsorption (GR)/e s-orbital electron p-orbital electron Mulliken population s-orbital electron p-orbital electron Mulliken population s-orbital electron p-orbital electron Mulliken population s-orbital electron p-orbital electron Mulliken population s-orbital electron p-orbital electron Mulliken population C1 1.242 2.8 −0.042 1.236 2.819 −0.056 1.23 2.823 −0.053 1.242 2.798 −0.041 1.242 2.799 −0.04 C2 1.242 2.834 −0.076 1.237 2.865 −0.101 1.23 2.867 −0.096 1.246 2.832 −0.076 1.245 2.832 −0.08 C3 1.205 2.738 0.057 1.195 2.685 0.121 1.184 2.687 0.129 1.21 2.73 0.06 1.21 2.731 0.058 N 1.59 3.705 −0.295 1.603 3.908 −0.511 1.602 3.929 −0.531 1.59 3.732 −0.322 1.591 3.709 −0.3 C5 1.205 2.738 0.057 1.194 2.676 0.13 1.184 2.691 0.125 1.21 2.728 0.062 1.21 2.73 0.059 C6 1.242 2.834 −0.076 1.237 2.865 −0.102 1.23 2.866 −0.095 1.246 2.832 −0.076 1.245 2.832 −0.08 H7 0.923 0 0.077 0.87 0 0.13 0.876 0 0.124 0.918 0 0.082 0.921 0 0.079 H8 0.925 0 0.075 0.868 0 0.132 0.874 0 0.126 0.92 0 0.08 0.923 0 0.077 H9 0.925 0 0.075 0.859 0 0.141 0.872 0 0.128 0.917 0 0.083 0.921 0 0.079 H10 0.925 0 0.075 0.854 0 0.146 0.872 0 0.128 0.918 0 0.082 0.922 0 0.078 H11 0.925 0 0.075 0.868 0 0.132 0.874 0 0.126 0.92 0 0.08 0.923 0 0.077 py 12.349 17.649 0.002 12.021 17.818 0.162 12.03 17.863 0.111 12.337 17.652 0.014 12.353 17.633 0.01 表 4 吡啶在各石墨烯表面吸附前后各石墨烯的马利肯电荷布居
Table 4 Mulliken charge of Ti, Zr or N-doped and intrinsic graphene of pyridine before and after adsorption
Atom or
moleculeBefore adsorption/e After adsorption/e s-orbital electron p-orbital electron d-orbital electron Mulliken population s-orbital electron p-orbital electron d-orbital electron Mulliken population Ti 2.616 6.135 2.824 0.425 2.658 6.384 2.625 0.333 Zr 2.471 6.015 2.786 0.728 2.747 6.317 2.394 0.541 N 1.551 3.907 − −0.458 1.542 3.87 − −0.412 C 1.301 2.699 − 0 1.302 2.665 − 0.032 Ti-GR − − − 0 − − − −0.160 Zr-GR − − − 0 − − − −0.109 N-GR − − − 0 − − − −0.012 GR − − − 0 − − − −0.008 -
[1] 李玲. 燃油脱氮的可见光光催化剂制备及其性能研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2013.LI Ling. Visible-light photocatalysts for denitrogenation of fuel oil: Preparation and characterization[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2013.) [2] WU Y, XIAO J, WU L M, et al. Adsorptive denitrogenation of fuel over metal organic frameworks: Effect of N-types and adsorption mechanisms[J]. J Phys Chem C,2014,118(39):22533−22543. doi: 10.1021/jp5045817 [3] AHMED I, KHAN N A, JHUNG S H. Adsorptive denitrogenation of model fuel by functionalized UiO-66 with acidic and basic moieties[J]. Chem Eng J,2017,321(1):40−47. [4] ZHANG J, HUANG L, LIN X C, et al. Effective adsorptive denitrogenation from model fuels over CeY zeolite[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2022,61(39):14586−14597. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.2c01204 [5] WEN J, LIN H F, HAN X, et al. Physicochemical studies of adsorptive denitrogenation by oxidized activated carbons[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 2017, 56(17): 5033-5041. [6] XIN H, ZAREEN Z, SHAFQAT A, et al. Adsorptive denitrogenation of model oil by MOF(Al)@GO composites: Remarkable adsorption capacity and high selectivity[J]. New J Chem,2023,47(7):3306−3311. doi: 10.1039/D2NJ06032A [7] LI Z M, LIANG H W, LI X L, et al. Adjusting surface acidity of hollow mesoporous carbon nanospheres for enhanced adsorptive denitrogenation of fuels[J]. Chem Eng Sci, 2020, 228 : 115963. [8] ARVIN S D, AMIR V, SAHAR B, et al. Deep denitrogenation of model diesel fuel using Ni-doped mesoporous carbon: synthesis route and adsorption study[J]. ChemistrySelect,2021,6(5):1073−1081. doi: 10.1002/slct.202004522 [9] NARJES G, MUHIEDDINE A S, MOHAMMED S A, et al. Adsorptive denitrogenation of coker diesel over carbon-based adsorbents for producing ultralow-sulfur diesel[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2023,62(50):21777−21786. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.3c03424 [10] 原卫华, 毕世华, 曹茂盛. 石墨烯吸附甲醛的第一性原理研究[J]. 材料导报,2015,29(18):156−159.YUAN Weihua, BI Shihua, CAO Maosheng. Formaldehyde molecule adsorbed on graphene: A first principles study[J]. Mater Rep,2015,29(18):156−159. [11] 罗慧娟. 石墨烯的结构掺杂及分子吸附性能研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2017.LUO Hui-juan. Structural modifications and adsorption properties of graphene[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017.) [12] ZHANG H P, HE W D, LUO X G, et al. Adsorption of 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrochlorodibenzo-p-dioxins on intrinsic, defected, and Ti (N, Ag) doped graphene: A DFT study[J]. J Mol Model,2014,20(5):1−7. [13] DELLEY B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules[J]. J Chem Phys,1990,92(1):508−517. doi: 10.1063/1.458452 [14] DELLEY B. From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach[J]. J Chem Phys,2000,113(18):7756−7764. doi: 10.1063/1.1316015 [15] DELLEY B. DMol3 DFT studies: from molecules and molecular environments to surfaces and solids[J]. Comp Mater Sci,2000,17(2):122−126. [16] KRESSE G, FURTHMÜLLER J. Generalized gradient approximation made simple[J]. Phys Rev Lett,1996,77(18):3865−3868. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865 [17] TKATCHENKO A, SCHEFFLER M. Accurate molecular van der Waals interactions from ground-state electron density and free-atom reference data[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102(7): 073005(1-4). [18] YOSHITAKA F, SUSUMU S. Formation, stabilities, and electronic properties of nitrogen defects in graphene[J]. Phys Rev B, 2011, 84(24): 245446(1-7). [19] WANG M H, GUO Y N, WANG Q, et al. Density functional theory study of interactions between glycine and TiO2/graphene nanocomposites[J]. Chem Phys Lett,2014,599(4):86−91. [20] ZHANG H P, LUO X G, LIN X Y, et al. Density functional theory calculations of hydrogen adsorption on Ti-, Zn-, Zr-, Al-, and N-doped and intrinsic graphene sheets[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2013,38(33):14269−14275. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.098 [21] BEATRIZ C, VERONICA G, ANA E, et al. Covalent radii revisited[J]. Dalton Trans,2008,37(21):2832−2838. [22] LI J Y, HOU M L, CHEN Y Q, et al. Enhanced CO2 capture on graphene via N, S dual-doping[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2017,399(6):420−425. [23] HOU M L, ZHANG X, YUAN S D, et al. Double graphitic-N doping for enhanced catalytic oxidation activity of carbocatalysts[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2019,21(10):5481−5488. doi: 10.1039/C8CP07317A [24] DAI J Y, YUAN J M, GIANNOZZI P. Gas adsorption on graphene doped with B, N, Al, and S: A theoretical study[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 95(23): 232105(1-3). [25] CHEN Y, LIU Y J, Wang H X, et al. Silicon-doped graphene: an effective and metal-free catalyst for NO reduction into N2O ?[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces,2013,5(13):5994−6000. doi: 10.1021/am400563g [26] CHEN J H, CHEN H T. Computational explanation for interaction between amino acid and nitrogen-containing graphene[J]. Theor Chem Acc,2018,137(12):176−187. doi: 10.1007/s00214-018-2392-z [27] 李巧灵, 吴晓宇, 王学伟, 等. 多孔BN选择性去除燃油中硫化合物的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报,2020,71(10):4601−4610.LI Qiaoling, WU Xiaoyu, WANG Xuewei, et al. Porous BN for selective adsorption of sulfur-containing compounds from fuel oil: DFT study[J]. CIESC J,2020,71(10):4601−4610. [28] SANTIAGO A. A cartography of the van der Waals territories[J]. Dalton Trans,2013,42(24):8617−8636. doi: 10.1039/c3dt50599e [29] 厉志鹏, 牛胜利, 赵改菊, 等. Sr掺杂对CaO(100)表面吸附甲醇影响的分子模拟[J]. 燃料化学学报,2020,48(2):172−178. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30008-6LI Zhipeng, NIU Shengli, ZHAO Gaiju, et al. Molecular simulation study of strontium doping on the adsorption of methanol on CaO(100) surface[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(2):172−178. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30008-6 [30] 张文杰, 侯美伶, 周兴, 等. 基于第一性原理计算硫化氢(H2S)在Pt-graphene上的吸附性能和解离机理[J]. 燃料化学学报,2022,50(9):1211−1220.ZHANG Wenjie, HOU Meiling, ZHOU Xing, et al. A theoretical study of H2S adsorption and dissociation mechanism on defected graphene doped with Pt[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2022,50(9):1211−1220. [31] 王建辉, 崔建中, 王兴尧, 等. 无机化学[M]. 五版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2018.WANG Jianhui, CUI Jianzhong, WANG Xingxiao, et al. Inorganic Chemistry[M]. 5nd ed, Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2018.) [32] 柴汝宽, 刘月田, 杨莉, 等. 乙酸在方解石表面吸附的密度泛函研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2019,50(5):1252−1262.CHAI Rukuan, LIU Yuetian, YANG Li, et al. Density functional theory analysis of acetic acid adsorption on CaCO3(104) surface[J]. J Cent South Univ (Science and Technology),2019,50(5):1252−1262. -




 下载:
下载: