The effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on the catalytic performance of Zn/HZSM-5 catalysts for ethylene aromatization reaction
-
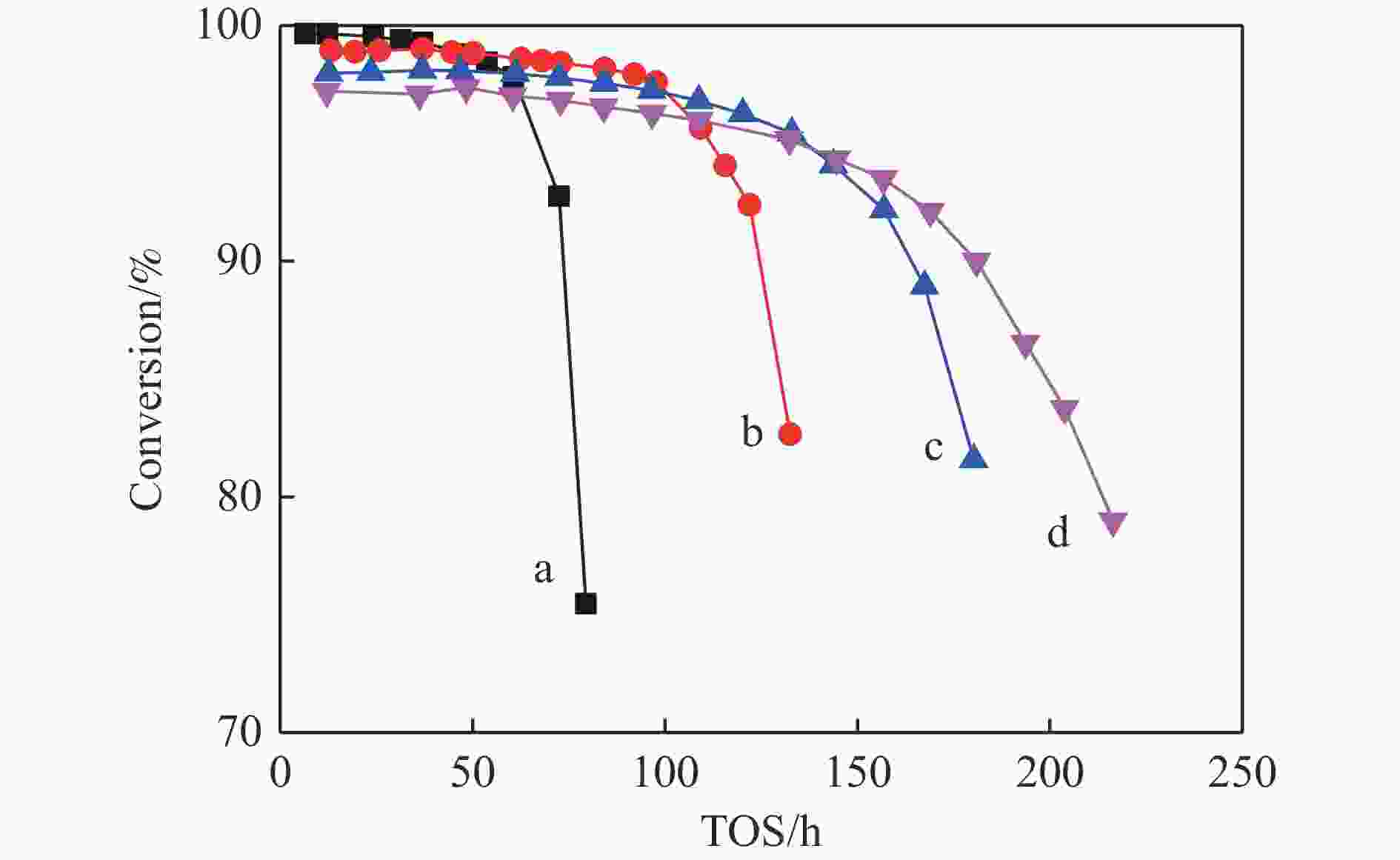
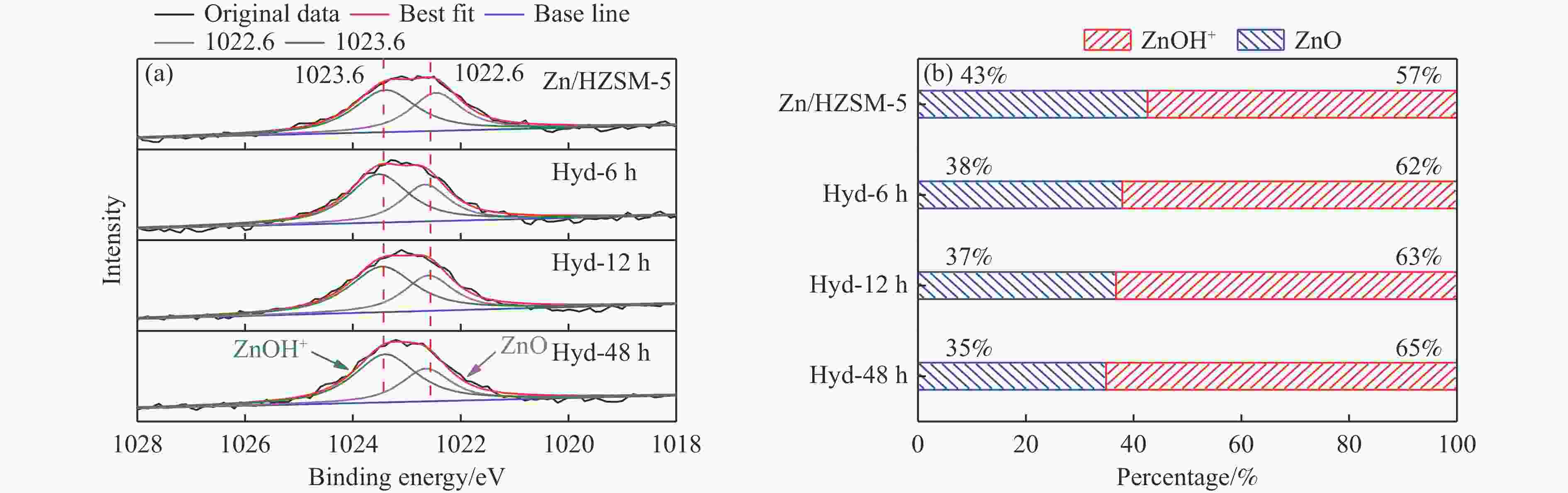
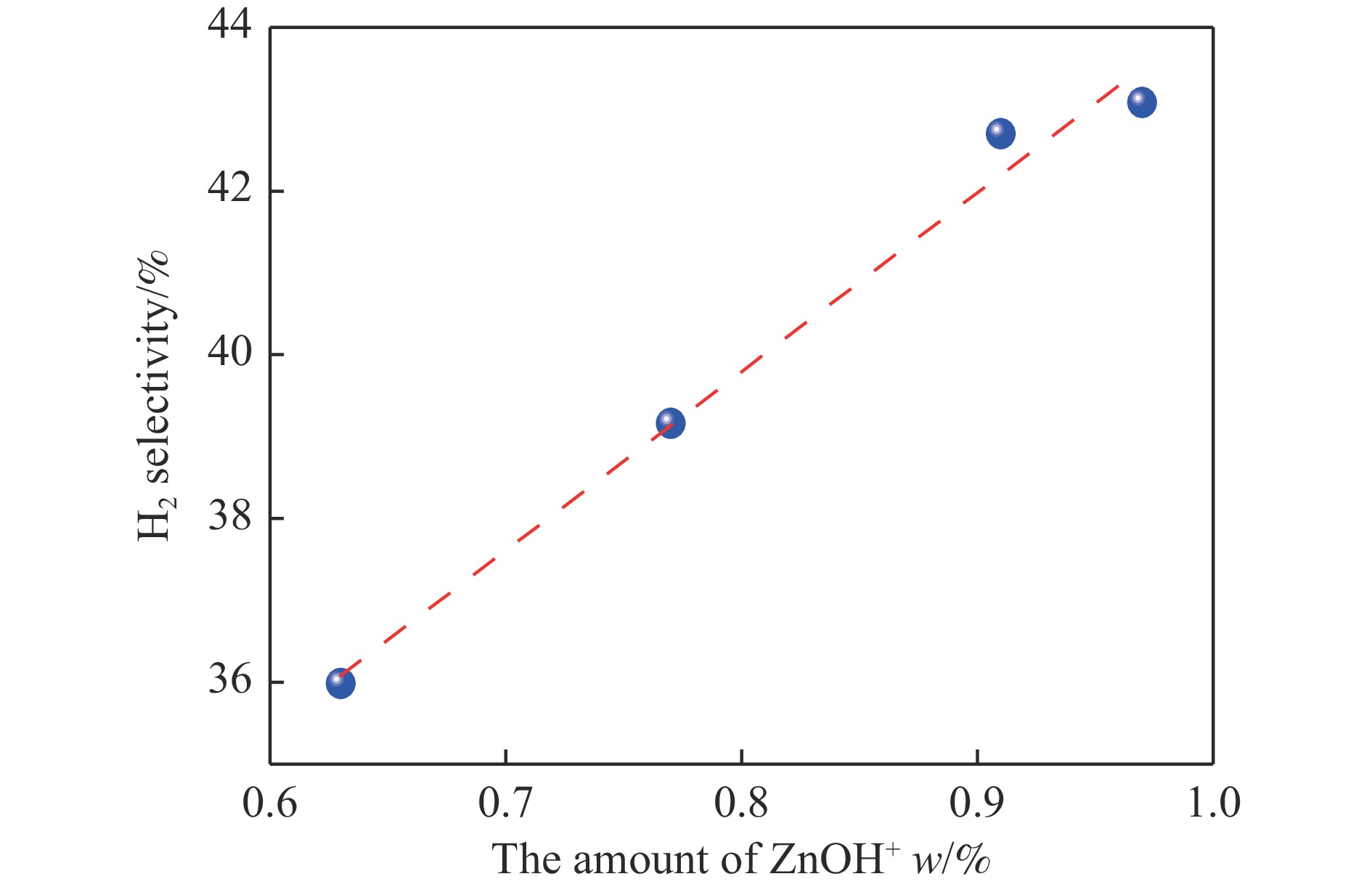
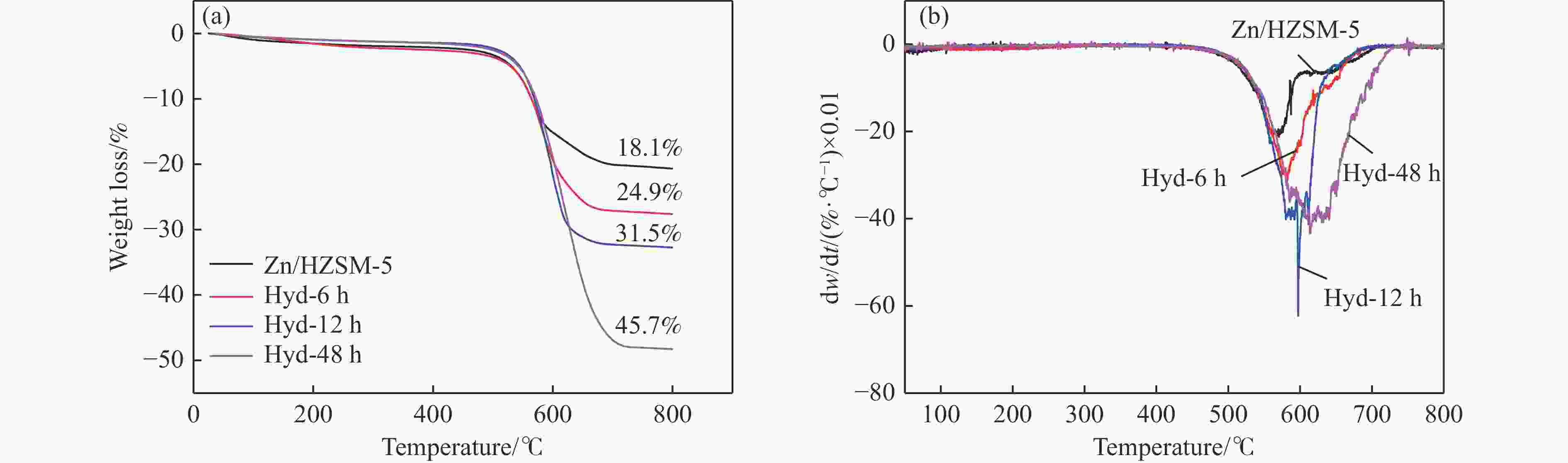
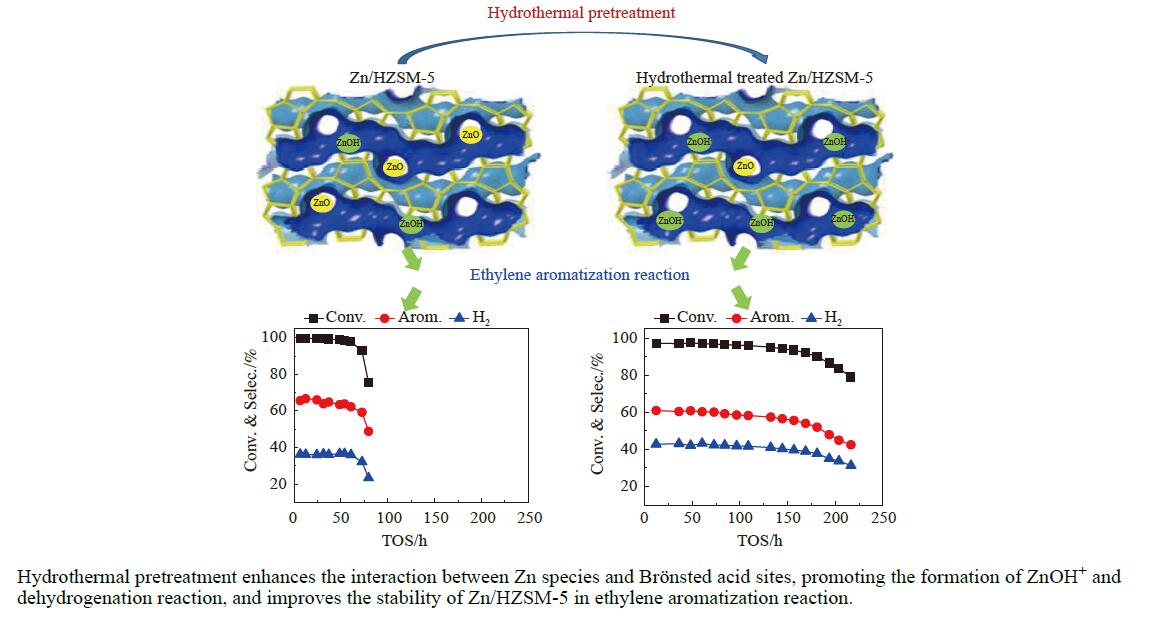
摘要: 针对用于低碳烯烃芳构化的Zn/HZSM-5催化剂存在易于结焦失活的问题,采用高温水热的方法对催化剂进行预处理,通过XRD、N2物理吸附-脱附、NH3-TPD、Py-FTIR、XPS和TG等技术对样品进行表征,并以乙烯芳构化为探针反应考察了高温水热预处理对催化剂反应性能和稳定性的影响。结果表明,Zn/HZSM-5催化剂经高温水热预处理48 h后表现出优异的催化性能,虽然乙烯转化率略微降低,但是催化剂寿命显著延长,由72 h延长至216 h,同时芳烃选择性保持在60%以上;水热处理促进了ZnO物种与B酸中心的相互作用及ZnOH+物种的生成,在抑制氢转移反应的同时显著促进了催化剂的脱氢性能,提高了氢气选择性;此外,水热处理后催化剂容碳量明显增加、积炭速率降低,表现出优异的抗结焦积炭特性。Abstract: To address the issue of coking and deactivation of Zn/HZSM-5 catalysts used for light olefins aromatization, a high-temperature hydrothermal method was employed for catalyst pretreatment. The catalysts were characterized using XRD, N2 physical adsorption-desorption, NH3-TPD, Py-FTIR, XPS and TG techniques. The effect of high-temperature hydrothermal pretreatment on the catalytic performance and stability of the catalyst was investigated using ethylene aromatization as a probe reaction. The results showed that the Zn/HZSM-5 catalyst exhibited excellent catalytic performance after 48 h of high-temperature hydrothermal pretreatment. Although the conversion of ethylene slightly decreased, the catalyst lifetime was significantly extended, increasing from 72 to 216 h, while the aromatics selectivity remained above 60%. It was suggested that the hydrothermal treatment enhanced the interaction between ZnO species and Brønsted acid sites, promoting the generation of ZnOH+ species. This not only suppressed the hydrogen transfer reaction but also significantly enhanced the dehydrogenation performance of the catalyst, improving the selectivity towards hydrogen. Additionally, the catalyst exhibited increased carbon capacity and reduced carbon deposition rate after hydrothermal treatment, demonstrating excellent anti-coking properties.
-
Key words:
- Zn/HZSM-5 /
- hydrothermal pretreatment /
- ethylene aromatization /
- Zn species
-
表 1 新鲜和水热预处理不同时间的Zn/HZSM-5催化剂上乙烯芳构化反应产物分布和积炭速率
Table 1 Products distribution and carbon deposition rate of ethylene aromatization reaction over fresh and hydrothermal pretreated Zn/HZSM-5 catalystsa
Catalyst Product selectivity/% H2 selec./% C4-HTIb Carbon deposition
rate/(%·h−1)CH4 ${\rm{C}}_{2}^{0}- {\rm{C}}_{4}^{0}$ ${\rm{C}}_{3}^{=} -{\rm{C}}_{4}^{=} $ C5+ arom. Zn/HZSM-5 5.05 26.31 1.42 1.2 66.01 35.98 0.91 0.23 Hyd-6h 4.78 27.97 2.46 1.42 63.17 39.16 0.87 0.19 Hyd-12h 4.46 26.88 4.10 2.18 62.30 42.70 0.86 0.17 Hyd-48h 3.69 24.88 6.56 4.37 60.47 43.08 0.82 0.21 a: Reaction conditions: 470 ℃, 0.1 MPa, ethylene WHSV 1.8 h−1, TOS=24 h; b: C4-HTI = ${\rm{C}}_{4}^{0} $/(${\rm{C}}_{4}^{=}+{\rm{C}}_{4}^{0} $). 表 2 Zn/HZSM-5和Hyd-xh催化剂的组成及结构性质
Table 2 Composition and textural properties of Zn/HZSM-5 and Hyd-xh
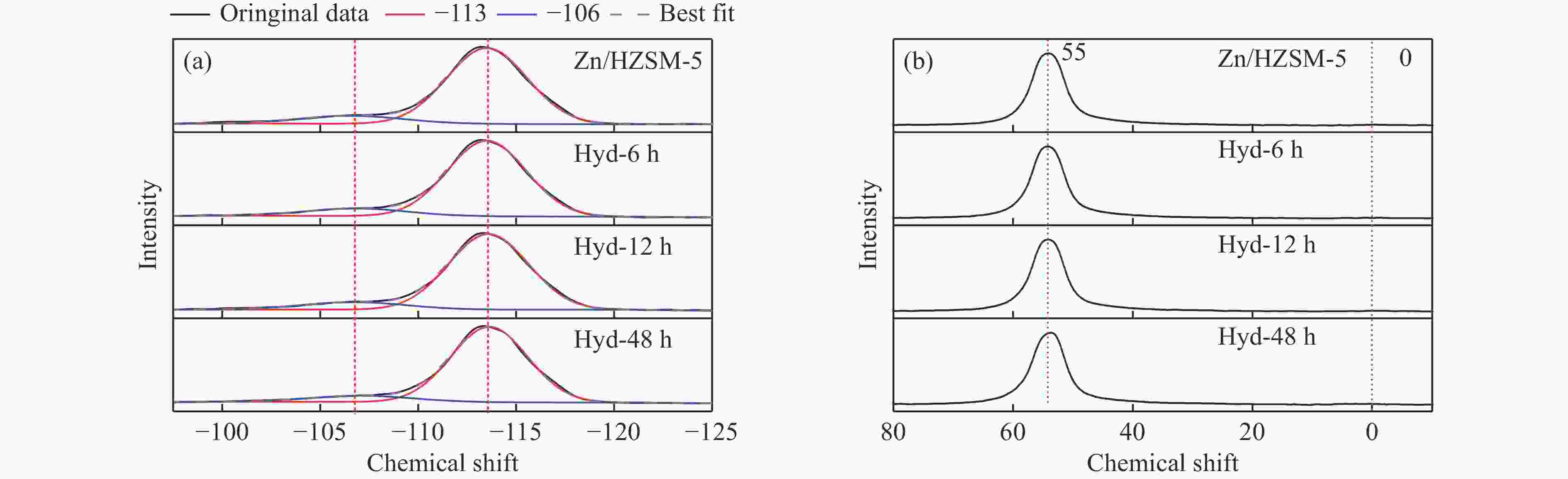
Sample Si/AlFa Zn contentb/% SBET/(m2·g−1) SE/(m2·g−1) Smicro/(m2·g−1) vtotal/(m3·g−1) vmicro/(m3·g−1) Zn/HZSM-5 33 1.1 315 102 213 0.31 0.09 Hyd-6h 35 1.2 325 98 227 0.33 0.10 Hyd-12h 35 1.4 341 105 236 0.33 0.11 Hyd-48h 39 1.5 348 100 248 0.35 0.11 a: Si/AlF were obtained from 29Si MAS NMR spectra; b: Obtained from XPS. 表 3 Zn/HZSM-5和Hyd-xh催化剂的酸性
Table 3 Acidic properties of Zn/HZSM-5 and Hyd-xh catalysts
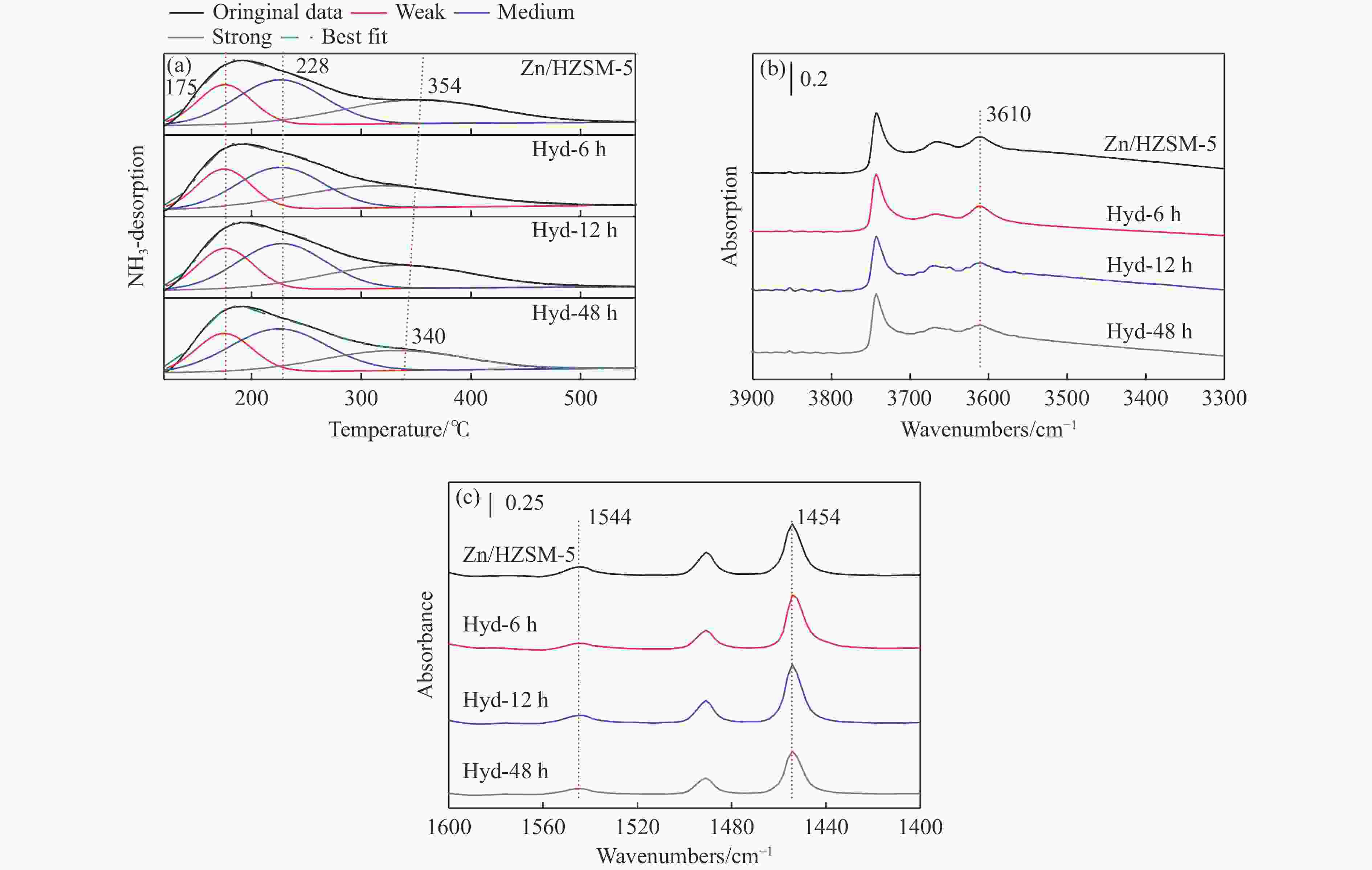
Sample Acidity by Py-FTIR at 150 ℃/(μmol·g−1) Acidity by NH3-TPD/(mmol·g−1) Brönsted Lewis L/B weak medium strong total Zn/HZSM-5 97 445 4.58 0.10 0.19 0.17 0.46 Hyd-6h 61 471 7.72 0.10 0.16 0.16 0.42 Hyd-12h 69 420 6.09 0.09 0.16 0.14 0.40 Hyd-48h 64 364 5.69 0.09 0.17 0.12 0.37 -
[1] NI Y, SUN A, WU X, et al. The preparation of nano-sized H[Zn, Al]ZSM-5 zeolite and its application in the aromatization of methanol[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2011,143(2/3):435−442. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.03.029 [2] MEHDAD A, LOBO R. Ethane and ethylene aromatization on zinc-containing zeolites[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2017,7(16):3562−3572. [3] 王殿中, 何鸣元. 稀乙烯在ZSM-5沸石上转化为异丁烯与汽油的反应[J]. 石油炼制与化工,1995,(8):59−63.WANG Dianzhong, HE Mingyuan. Reaction of dilute ethylene converting to iso-butylene and gasoline over ZSM-5[J]. Pet Process Petrochem,1995,(8):59−63. [4] WANG H, HOU Y, SUN W, et al. Insight into the effects of water on the ethene to aromatics reaction with HZSM-5[J]. ACS Catal,2020,10(9):5288−5298. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b05552 [5] SHI D, WANG S, WANG H, et al. Synthesis of HZSM-5 rich in paired Al and its catalytic performance for propane aromatization[J]. Catalysts,2020,10(6):1−19. [6] XING M, ZHANG L, CAO J, et al. Impact of the aluminum species state on Al pairs formation in the ZSM-5 framework[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2022,334:111769−11777. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2022.111769 [7] ONO Y, KITAGAWA H, SENDODA Y. Transformation of But-1-ene into aromatic-hydrocarbons over ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. J Chem Soc -Faraday Trans,1987,83:2913−2923. doi: 10.1039/f19878302913 [8] GUISNET M, GNEP N S, ALARIO F. Aromatization of short chain alkanes on zeolite catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,1992,89(1):1−30. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(92)80075-N [9] KOSINOV N, COUMANS F J A G, LI G, et al. Stable Mo/HZSM-5 methane dehydroaromatization catalysts optimized for high-temperature calcination-regeneration[J]. J Catal,2017,346:125−133. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.12.006 [10] LIU J F, JIN L, LIU Y, et al. Methane aromatization over cobalt and gallium-impregnated HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Catal Lett,2008,125(3/4):352−358. doi: 10.1007/s10562-008-9458-9 [11] TAN P L, AU C T, LAI S Y. Methane dehydrogenation and aromatization over 4 wt% Mn/HZSM-5 in the absence of an oxidant[J]. Catal Lett,2006,112(3-4):239−245. doi: 10.1007/s10562-006-0209-5 [12] SHARFIF K, HALLADJ R, ROYAEE S J, et al. Synthesis of W/HZSM-5 catalyst for simultaneous octane enhancement-desulfurization process of gasoline production[J]. Powder Technol,2018,338:638−644. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.07.079 [13] LIANG T, TOGHIANI H, XIANG Y. Transient kinetic study of ethane and ethylene aromatization over zinc-exchanged HZSM-5 catalyst[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2018,57:15301−15309. [14] RAAD M, HAMIEH S, TOUFAILY J, et al. Propane aromatization on hierarchical Ga/HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. J Catal,2018,366:223−236. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.07.035 [15] MA Z, CAO F, YANG Y, et al. Role of the nonstoichiometric Zn-Cr spinel in ZnCrO x/ZSM-5 catalysts for syngas aromatization[J]. Fuel,2022,325:124809. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124809 [16] WANG N, LI J, SUN W, et al. Rational design of zinc/zeolite catalyst: Selective formation of p-xylene from methanol to aromatics reaction[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed,2022,61(10):1−7. [17] CHEN G, FANG L, LI T, et al. Ultralow-loading pt/zn hybrid cluster in zeolite HZSM-5 for efficient dehydroaromatization[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2022,144(26):11831−11839. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c04278 [18] BHATIA S, BELTRAMINI J, DO D D. Deactivition of zeolite catalysts[J]. Catal Rev -Sci Eng,1989,31(4):431−480. doi: 10.1080/01614948909349937 [19] DE LUCAS A, CANIZARES P, DURAN A. Improving deactivation behaviour of HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2001,206(1):87−93. doi: 10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00586-X [20] LEE K Y, KANG M Y, IHM S K. Deactivation by coke deposition on the HZSM-5 catalysts in the methanol-to-hydrocarbon conversion[J]. J. Phys Chem Solids,2012,73(12):1542−1545. doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.09.005 [21] TRAINTAFYLLID K S, VLESSIDIS A G, NALBANDIAN L, et al. Effect of the degree and type of the dealumination method on the structural, compositional and acidic characteristics of H-ZSM-5 zeolites[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2001,47(2/3):369−388. doi: 10.1016/S1387-1811(01)00399-7 [22] MAIJANEN A, DEROUANE E G, NAGY J B. FT-IR and Solid-state NMR investigation of surface hydroxyl-groups on dealuminated ZSM-5[J]. Appl Surf Sci,1994,75:204−212. doi: 10.1016/0169-4332(94)90160-0 [23] BRUNNER E, ERNST H, FREUDE D, et al. Solid-state NMR and catalytic studios of mildly hydrothermally dealuminated HZSM-5[J]. Zeolites,1989,9(4):282−286. doi: 10.1016/0144-2449(89)90072-9 [24] ALMUTAIRI S, MEZARI B, PIDKO E, et al. Influence of steaming on the acidity and the methanol conversion reaction of HZSM-5 zeolite[J]. J Catal,2013,307:194−203. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.07.021 [25] ARAMBURO L R, KARWACKI L, CUBILLAS P, et al. The porosity, acidity, and reactivity of dealuminated zeolite ZSM-5 at the single particle level: The influence of the zeolite architecture[J]. Chemistry,2011,17(49):13773−13781. doi: 10.1002/chem.201101361 [26] WEI Z, CHEN L, CAO Q, et al. Steamed Zn/ZSM-5 catalysts for improved methanol aromatization with high stability[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2017,162:66−77. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.03.026 [27] MADEIRA F F, BEN TAYEB K, PINARD L, et al. Ethanol transformation into hydrocarbons on ZSM-5 zeolites: Influence of Si/Al ratio on catalytic performances and deactivation rate. Study of the radical species role[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2012,443:171−180. [28] SU X, ZHANG K, SNATENKOVA Y, et al. High-efficiency nano [Zn, Al]ZSM-5 bifunctional catalysts for dimethyl ether conversion to isoparaffin-rich gasoline[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2020,198:106242−106253. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106242 [29] CHEN L, HU J, LIN F, et al. Self-assembled single-crystalline ZnO nanostructures[J]. CrystEngComm,2013,15(19):3780−3784. doi: 10.1039/c3ce40167g [30] SAZAMA P, DEDECEK J, GABOVA V, et al. Effect of aluminium distribution in the framework of ZSM-5 on hydrocarbon transformation. Cracking of 1-butene[J]. J Catal,2008,254(2):180−189. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.12.005 [31] LIANG T, CHEN J, QIN Z, et al. Conversion of methanol to olefins over H-ZSM-5 zeolite: Reaction pathway is related to the framework aluminum siting[J]. ACS Catal,2016,6(11):7311−7325. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01771 [32] JIAO J, WANG W, SULIKOWSKI B, et al. 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR characterization of non-hydrated zeolites Y upon adsorption of ammonia[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2006,90(1/3):246−250. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.08.006 [33] CHEN K, GAN Z, HORSTMEIER S, et al. Distribution of aluminum species in zeolite catalysts: 27Al NMR of framework, partially-coordinated framework, and non-framework moieties[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2021,143(17):6669−6680. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c02361 [34] NIU X, GAO J, MIAO Q, et al. Influence of preparation method on the performance of Zn-containing HZSM-5 catalysts in methanol-to-aromatics[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2014,197:252−261. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.06.027 [35] PINILLA-HERRERO I, BORFUCCHIA E, HOLZINGER J, et al. High Zn/Al ratios enhance dehydrogenation vs hydrogen transfer reactions of Zn-ZSM-5 catalytic systems in methanol conversion to aromatics[J]. J Catal,2018,362:146−163. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2018.03.032 [36] GENG R, LIU Y, GUO Y, et al. structure evolution of zn species on fresh, deactivated, and regenerated Zn/ZSM-5 catalysts in ethylene aromatization[J]. ACS Catal,2022,12(23):14735−14747. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.2c04074 [37] CHEN X, DONG M, NIU X, et al. Influence of Zn species in HZSM-5 on ethylene aromatization[J]. Chin J Catal,2015,36(6):880−888. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60289-8 [38] GENG R, LIU Y, GAO J, et al. The migration of Zn species on Zn/ZSM-5 catalyst during the process of ethylene aromatization[J]. catal sci technol,2022,12(13):4201−4210. doi: 10.1039/D2CY00661H [39] DU S, VALLA J, BOLLAS G. Characteristics and origin of char and coke from fast and slow, catalytic and thermal pyrolysis of biomass and relevant model compounds[J]. Green Chem,2013,15(11):3124−3229. [40] BARBERA, K, SORENSEN S, BORDIGA S, et al. Role of internal coke for deactivation of ZSM-5 catalysts after low temperature removal of coke with NO2[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2012,2(6):1196−1206. doi: 10.1039/c2cy00529h -





 下载:
下载: