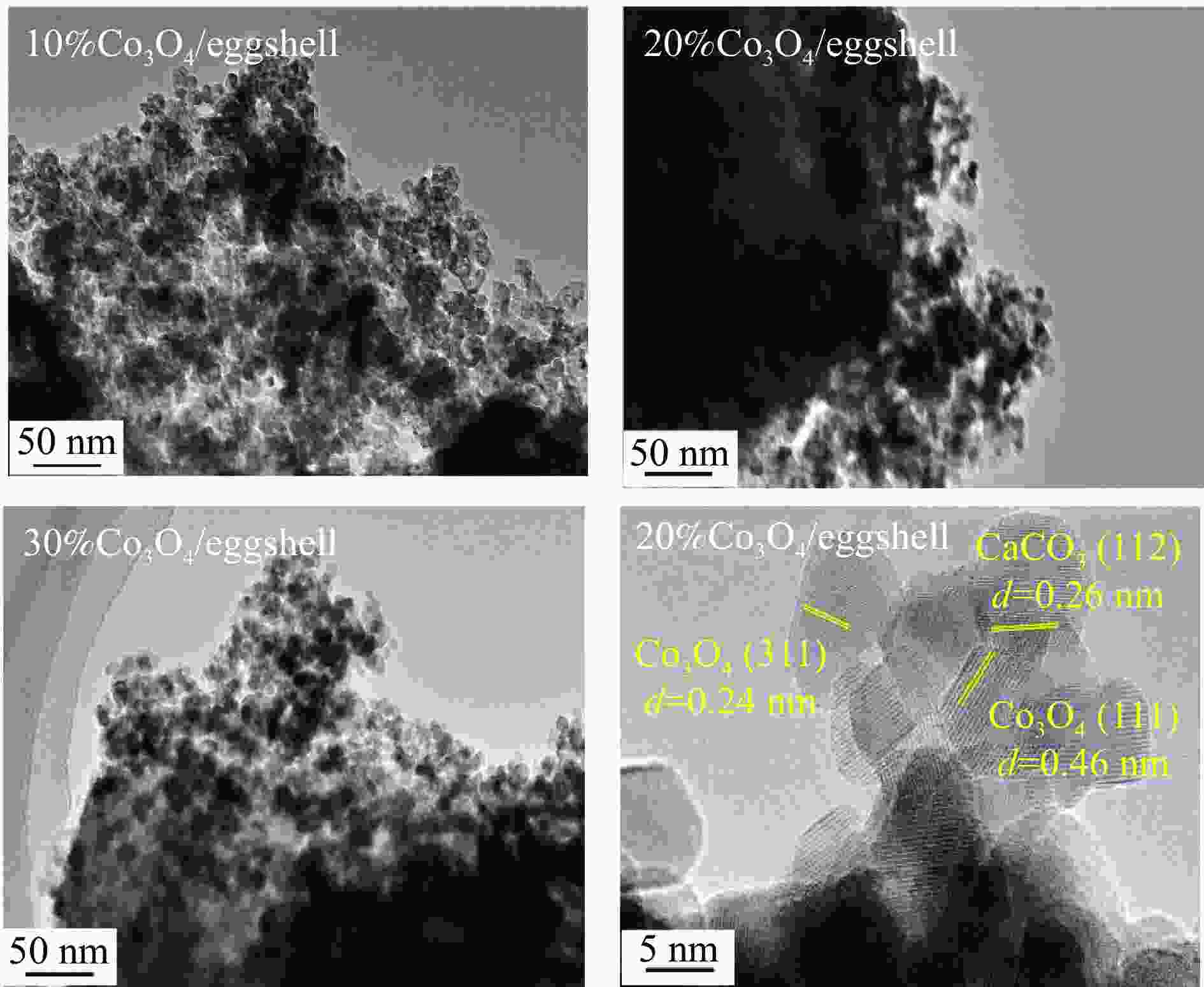
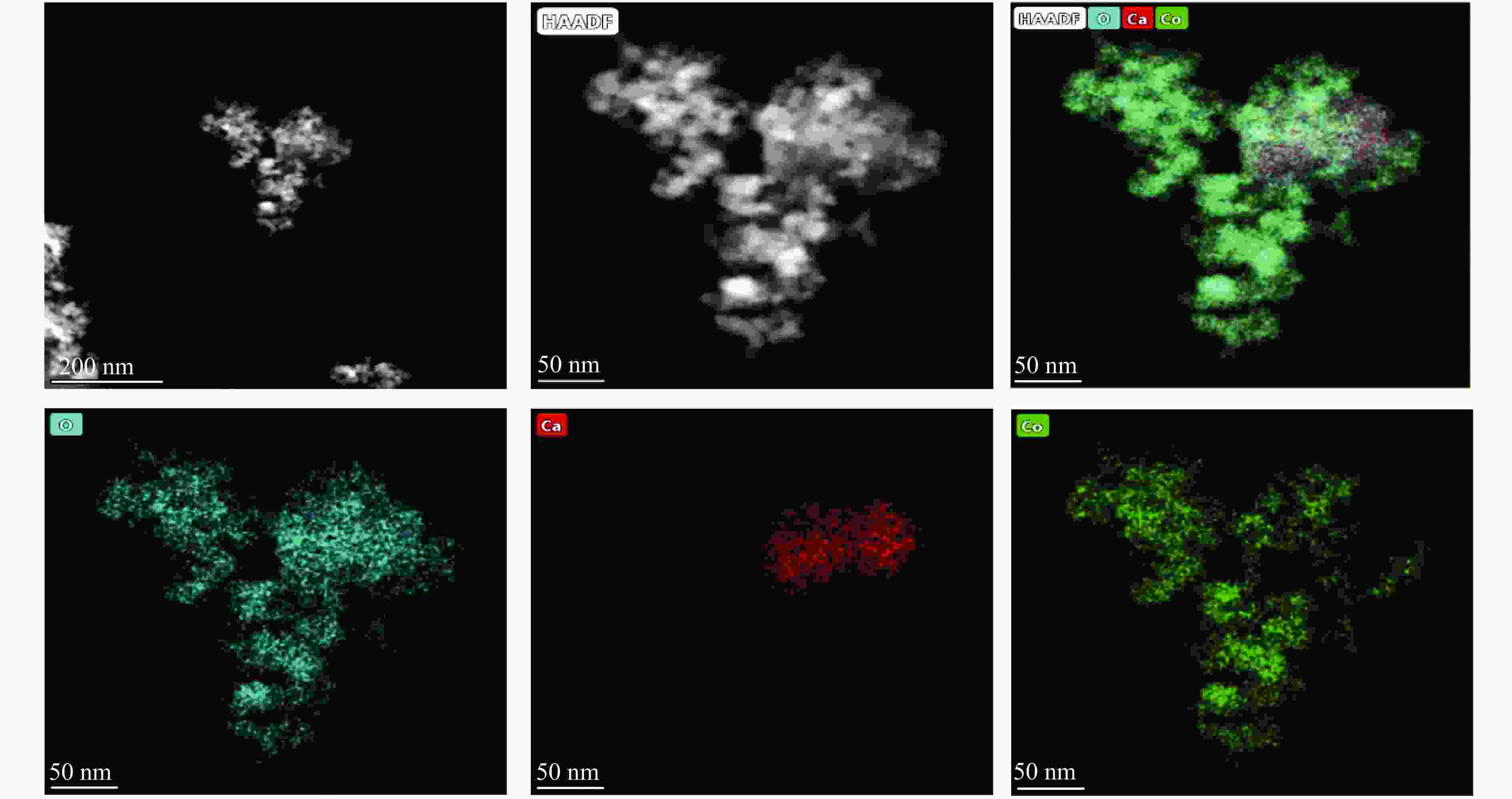
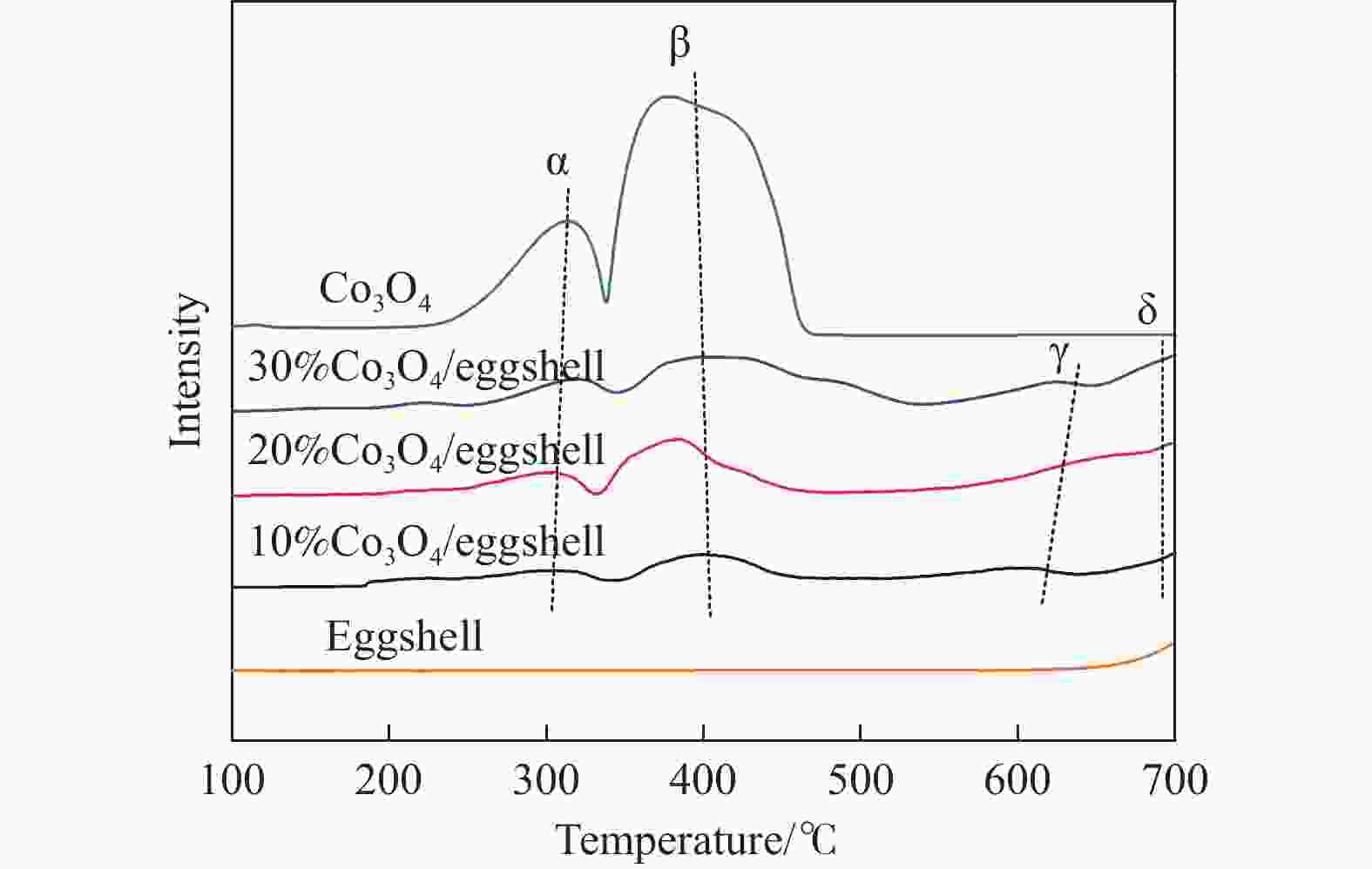
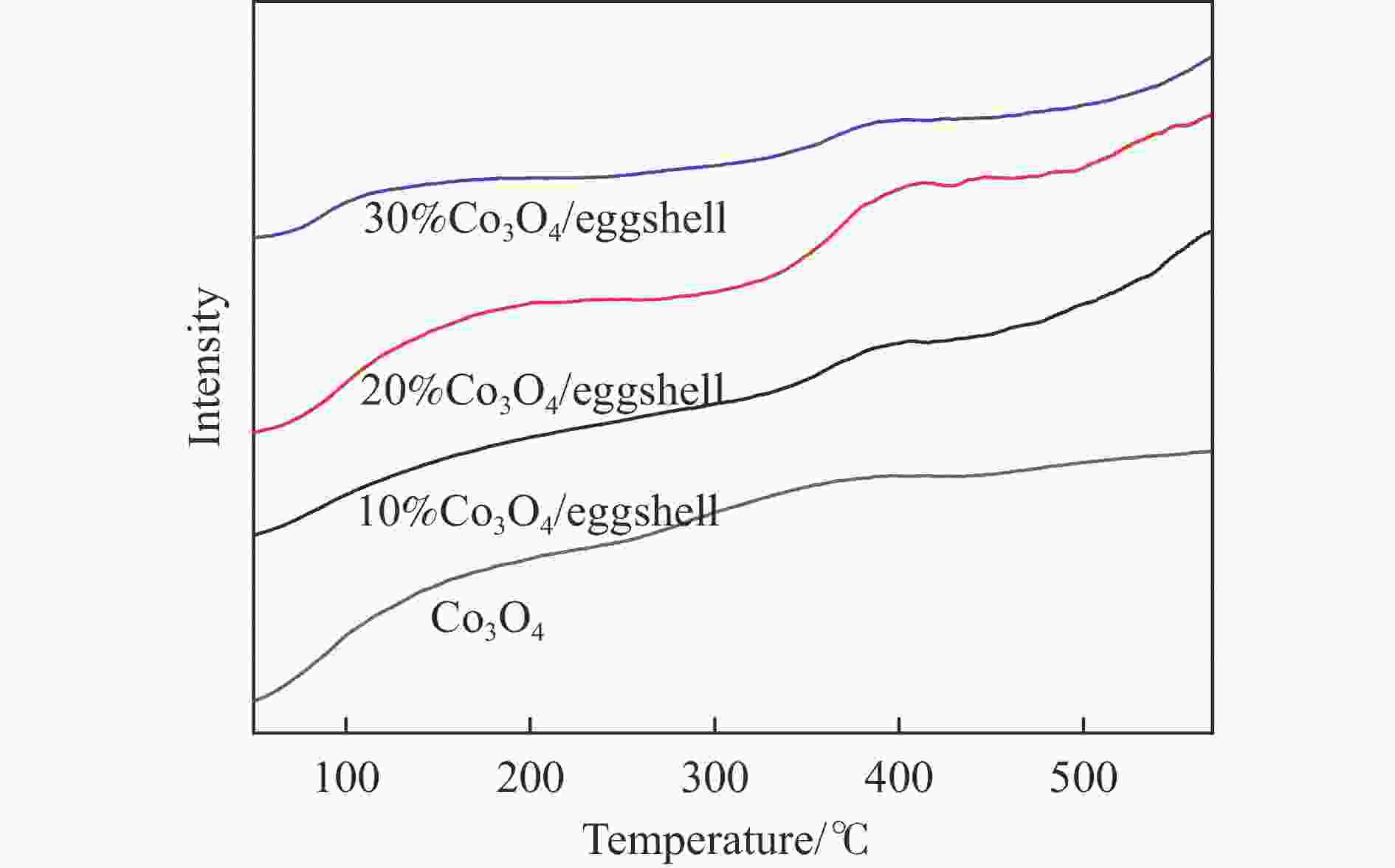
Preparation of eggshell supported Co3O4 catalyst and tested for N2O decomposition
-
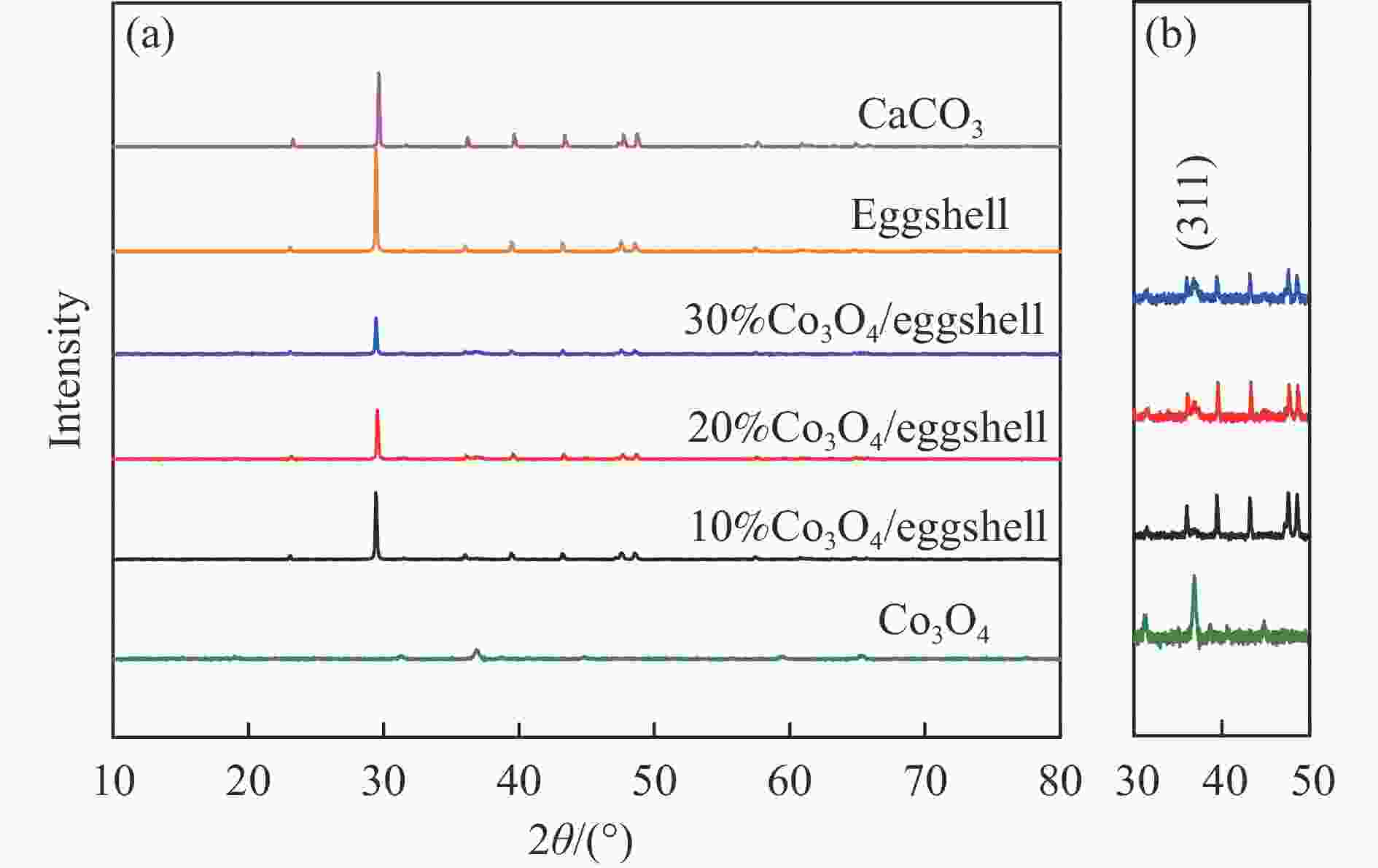
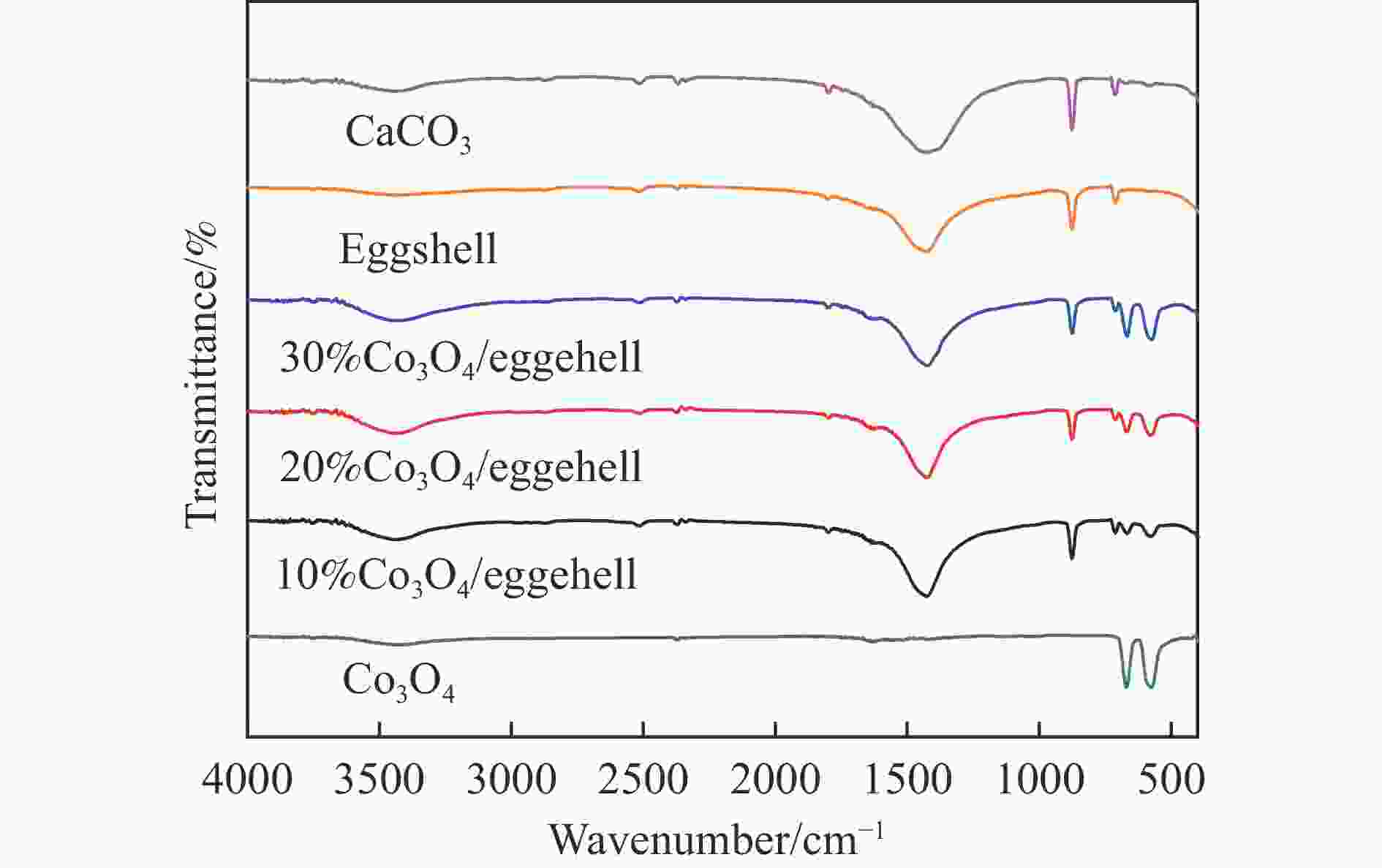
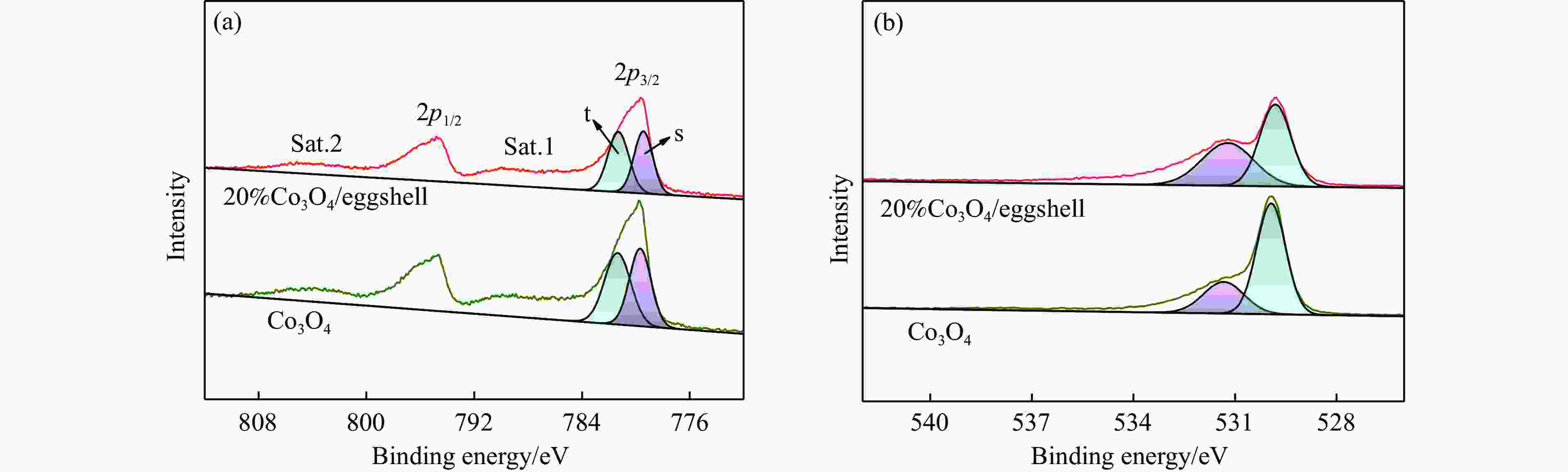
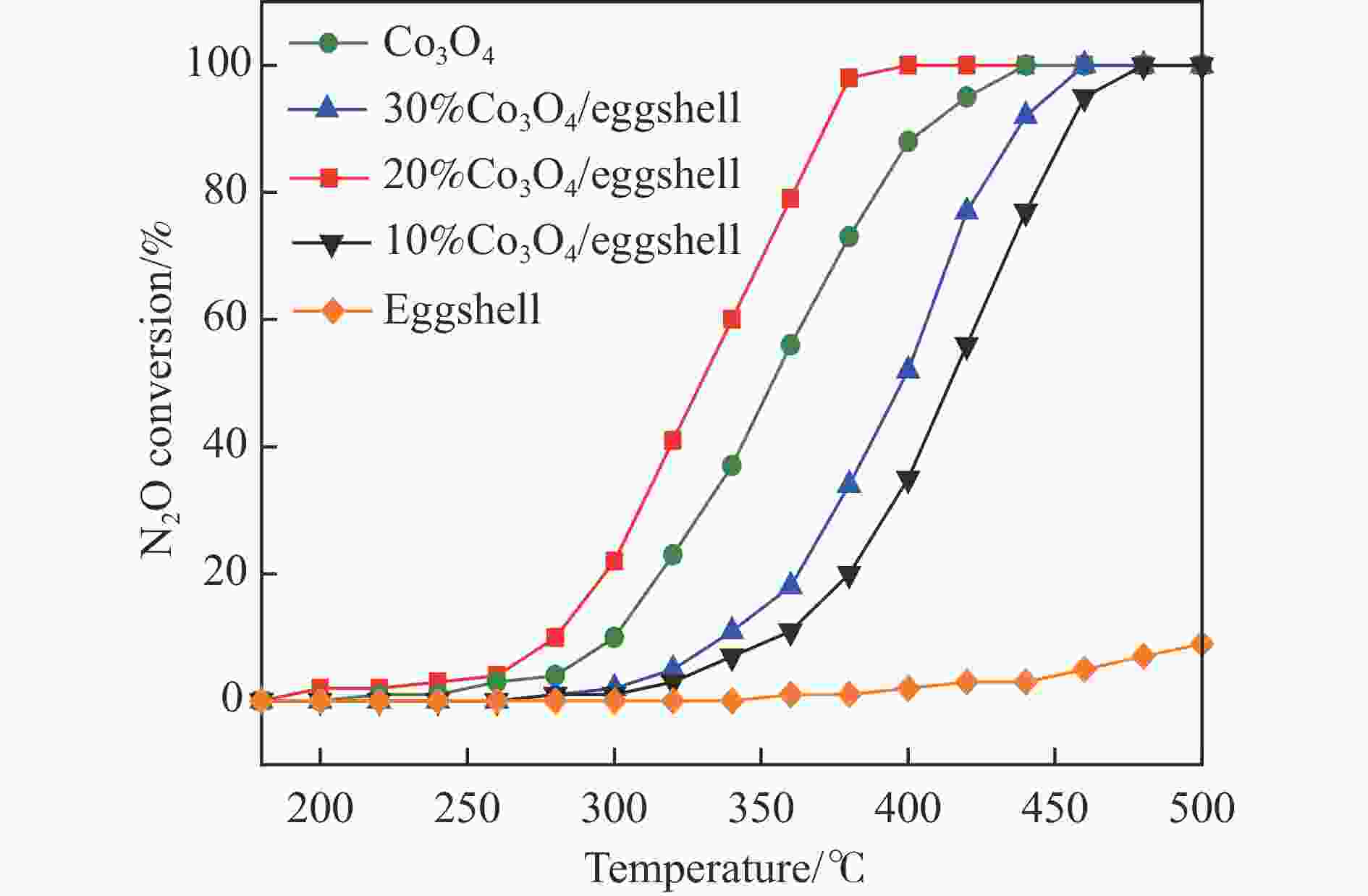
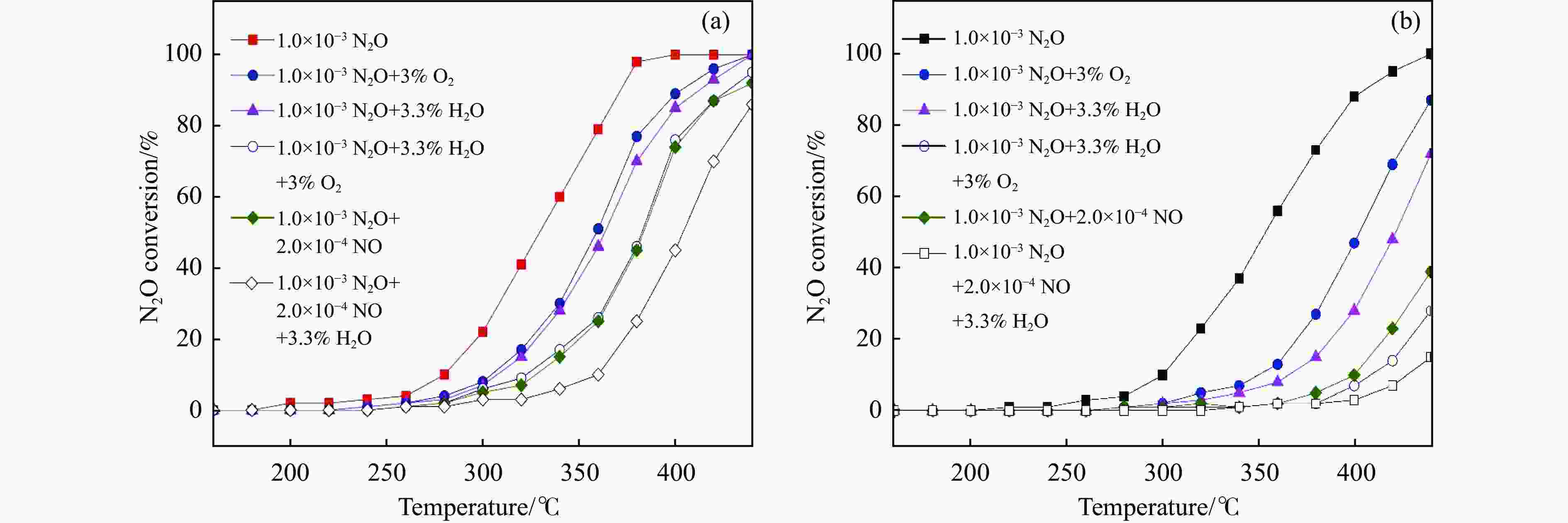
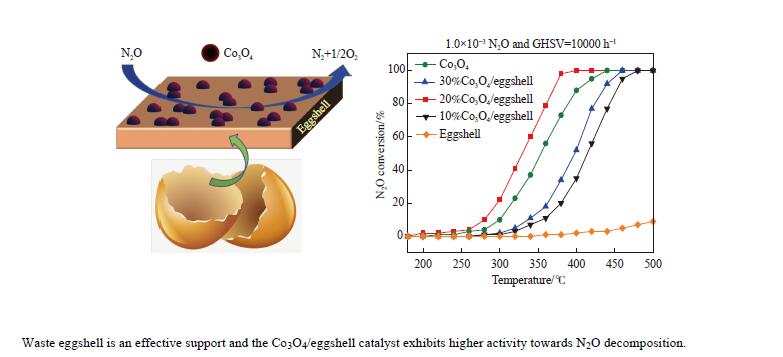
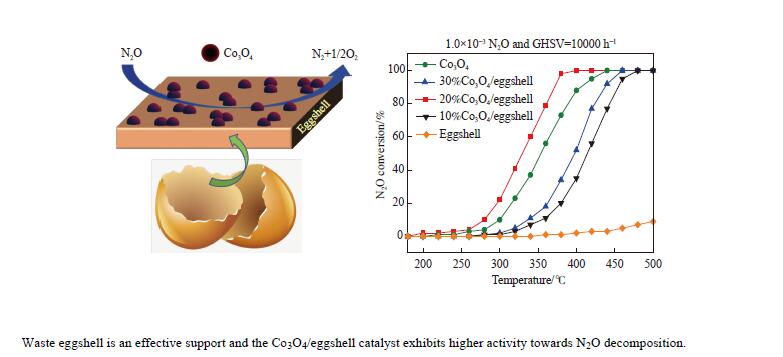
摘要: 采用废弃的鸡蛋壳作载体,沉积沉淀法制备了一系列不同Co3O4含量Co3O4/鸡蛋壳催化剂,并在连续流动微反装置上考察了N2O分解性能。结果表明,当Co3O4质量分数为20%时,催化剂表现出优异的N2O分解性能。在空速10000 h−1和N2O含量0.1%的条件下,400 ℃可实现N2O完全转化;其比活性约为Co3O4催化剂的4.3倍(反应温度为440 ℃);同时,该催化剂对原料气中3% O2、3.3% H2O和/或2.0×10−4 NO表现出较强的耐受性和较高的稳定性。分析催化剂的多种表征结果发现,CaCO3作为鸡蛋壳的主要成分,与活性组分Co3O4紧密结合,两者的强相互作用导致20%Co3O4/鸡蛋壳催化剂中产生更多的氧空位和Co3+;Co3O4氧化还原性能得到提高,Co−O键被有效削弱;此外,该强相互作用可提高20%Co3O4/鸡蛋壳催化剂表面碱性位点的强度,增大碱性位点数量,更易于转移电子而促进N2O分解。Abstract: A series of Co3O4/eggshell catalysts with different Co3O4 contents were prepared by the deposition-precipitation method using discarded eggshells as supports, and tested for the catalytic reaction of N2O decomposition on a fixed-bed continuous flow micro-reactor. The activity test results show that the catalyst exhibits higher activity towards N2O decomposition when the mass fraction of Co3O4 is 20%, with a specific activity of 4.3 times to that of pure Co3O4 (reaction temperature 440 ℃). At the same time, it shows strong resistance to 3% O2, 3.3% H2O and/or 2.0×10−4 NO in feed. Various characterization results indicate that the predominant composition of eggshell is CaCO3, which has a close incorporation with Co3O4. The strong interaction between CaCO3 and Co3O4 contributes to producing more oxygen vacancies and Co3+ in the 20% Co3O4/eggshell catalyst. The redox performance of Co3O4 is improved, and the Co−O bond is effectively weakened. In addition, it helps to increase the strength and amount of basic sites on the catalyst surface, making it easily transfer electrons and promote N2O decomposition.
-
Key words:
- eggshell /
- CaCO3 /
- Co3O4 /
- N2O /
- catalytic decomposition
-
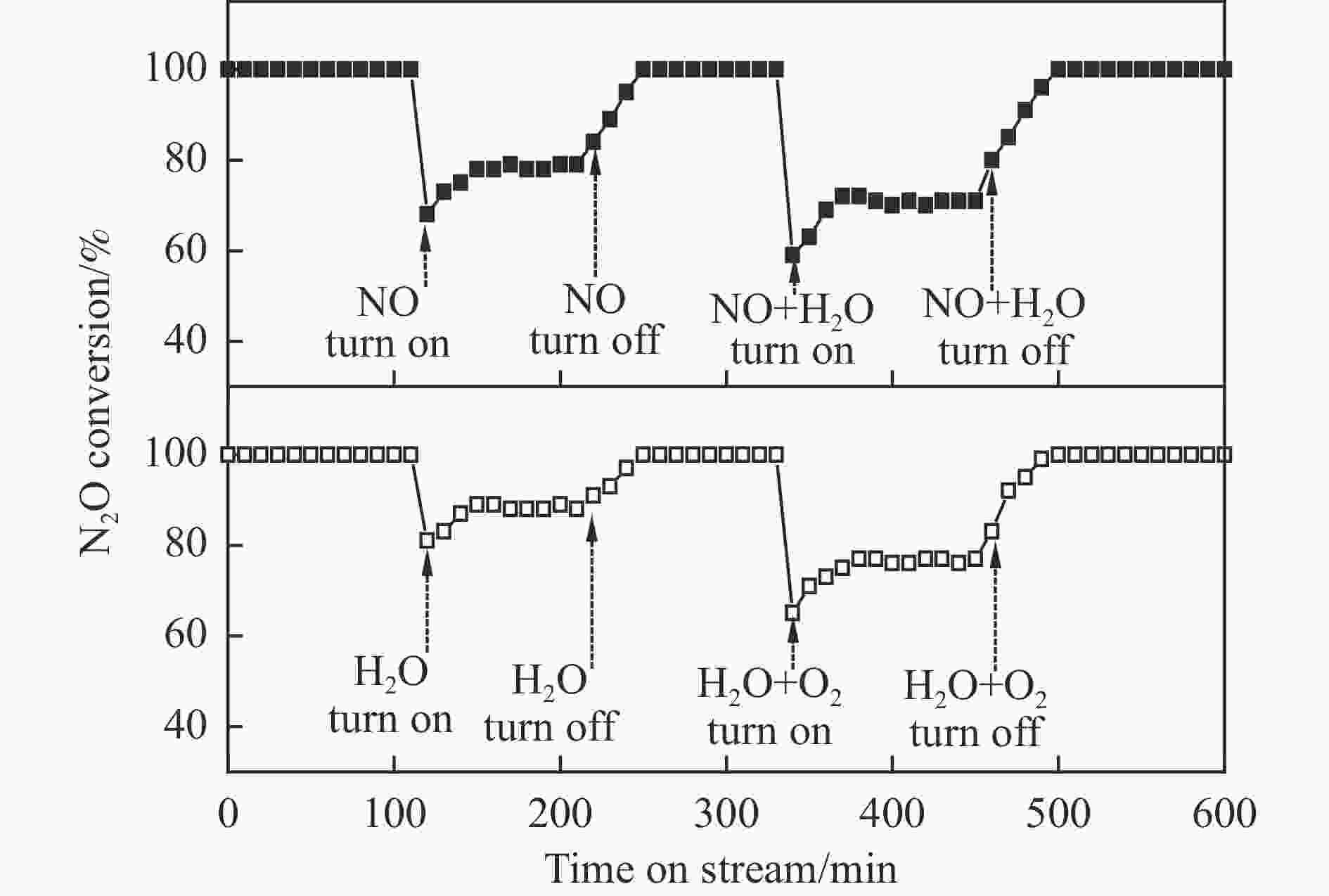
图 12 400 ℃时原料气中周期切换杂质气体3% O2, 3.3% H2O和2.0×10−4 NO,20%Co3O4/eggshell催化剂N2O转化率
Figure 12 N2O conversion over 20%Co3O4/eggshell at 400 ℃ changed with time on stream when impurity gases (3% O2, 3.3% H2O, 2.0×10−4 NO) were injected in or cut off from the feed stream
Reaction condition: GHSV=10000 h−1, 1 atm.
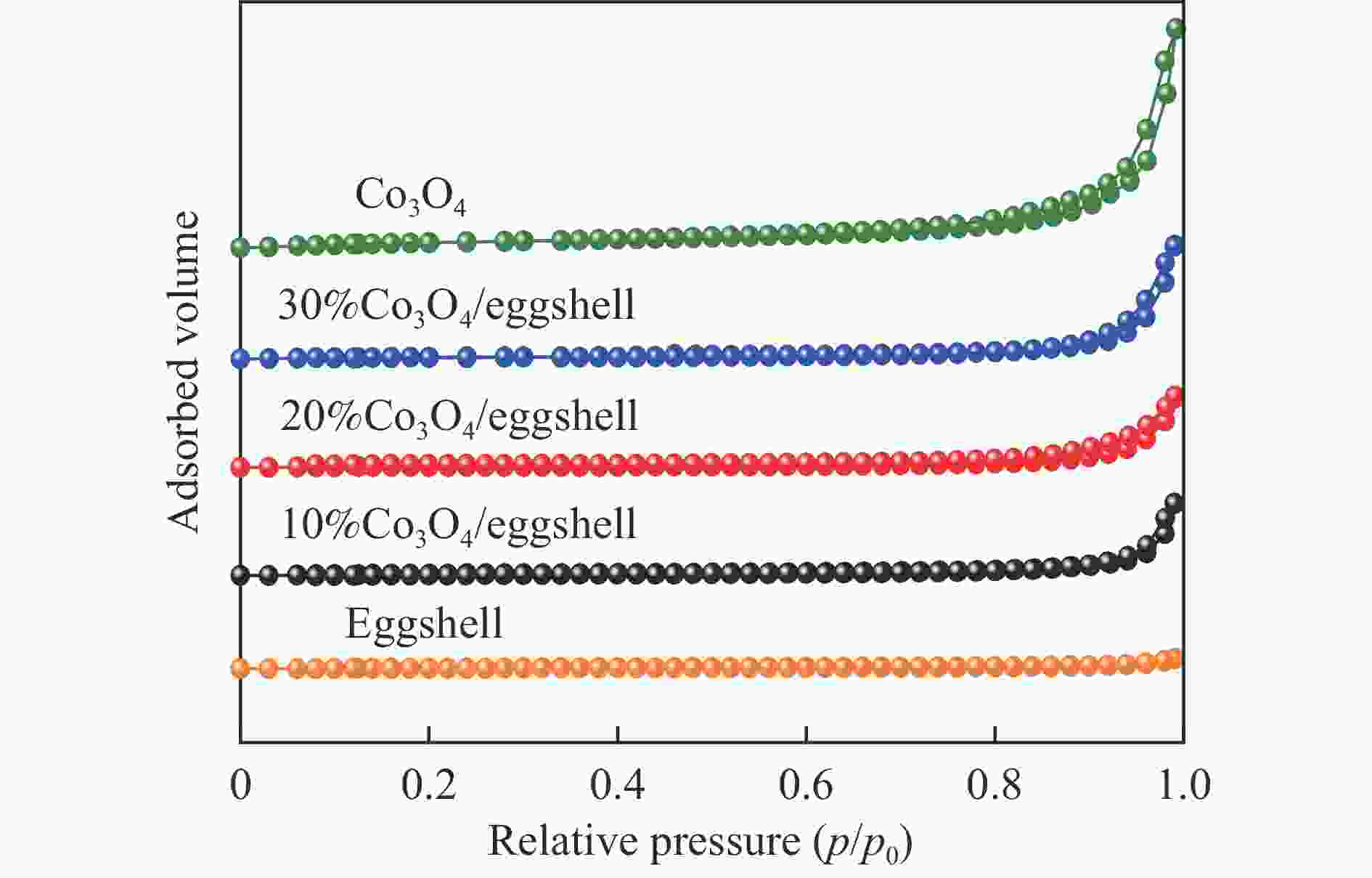
表 1 材料的织构参数
Table 1 The textural parameters for the materials
Material BET
surface
area/
(m2·g−1)Total
pore
volume/
(cm3·g−1)Average
pore
diameter/
nmCaCO3 4.3 0.017 8.7 Eggshell 4.5 0.017 8.8 10%Co3O4/eggshell 9.4 0.034 12.6 20%Co3O4/eggshell 14.5 0.051 14.2 30%Co3O4/eggshell 22.8 0.071 17.1 Co3O4 34.8 0.158 19.7 表 2 催化剂不同碱性位点吸附CO2数量
Table 2 The desorption amount of CO2 for different basic sites on the catalysts
Catalyst Weak
strength
basic
sites/
(μmol·g−1)Strong
strength
basic
sites/
(μmol·g−1)Total
basic
sites/
(μmol·g−1)10%Co3O4/eggshell 17.4 16.2 33.6 20%Co3O4/eggshell 56.6 48.5 105.1 30%Co3O4/eggshell 23.5 21.3 44.8 Co3O4 39.8 25.1 64.9 表 3 催化剂不同氧物种脱附O2数量
Table 3 The desorption amount of O2 for different oxygen species on the catalysts
Catalyst Surface oxygen species/(μmol·g−1) Lattice oxygen species/(μmol·g−1) Total oxygen species/(μmol·g−1) 10%Co3O4/eggshell 23.2 27.8 51.0 20%Co3O4/eggshell 47.2 36.1 83.3 30%Co3O4/eggshell 25.3 34.9 60.2 Co3O4 36.4 11.7 48.1 -
[1] KLEGOVA A, PACULTOVA K, KISKA T. Washcoated open-cell foam cobalt spinel catalysts for N2O decomposition[J]. Mol Catal,2022,533:112754. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2022.112754 [2] ZHAO F L, WANG C Z, WANG D D, et al. Efficient catalytic decomposition of N2O over Cd-doped NiO in the presence of O2[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2023,649:118946. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118946 [3] BOZORGI B, KARIMI-SABET J, KHADIV-PARSI P. The removal of N2O from gas stream by catalytic decomposition over Pt-alkali metal/SiO2[J]. Environ Technol Innovation,2022,26:102344. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2022.102344 [4] KONSOLAKIS M. Recent advances on nitrous oxide (N2O) decomposition over non-noble-metal oxide catalysts: Catalytic performance, mechanistic considerations, and surface chemistry aspects[J]. ACS Catal,2015,5(11):6397−6421. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b01605 [5] 赵天琪, 高强, 廖卫平, 等. 掺加Nd和K改性对Co3O4催化分解N2O活性的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2019,47(9):1120−1128. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(19)30046-5ZHAO Tianqi, GAO Qiang, LIAO Weiping, et al. Effect of Nd-incorporation and K-modification on catalytic performance of Co3O4 for N2O decomposition[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2019,47(9):1120−1128. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(19)30046-5 [6] RICHARDS N, CARTER J H, NOWICKA E, et al. Structure-sensitivity of alumina supported palladium catalysts for N2O decomposition[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2020,264:118501. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118501 [7] XIONG Y, ZHAO Y M, QI X K, et al. Strong structural modification of Gd to Co3O4 for catalyzing N2O decomposition under simulated real tail gases[J]. Environ Sci Technol,2021,55(19):13335−13344. [8] 郑珂, 王永钊, 胡晓波, 等. 还原-氧化预处理对Co3O4催化分解N2O性能的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2019,47(4):455−463.ZHENG Ke, WANG Yongzhao, HU Xiaobo, et al. Effect of reduction-oxidation pretreatment on the catalytic performance of Co3O4 catalyst in N2O decomposition[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2019,47(4):455−463. [9] LIANG X L, TANG H L, YANG F F, et al. Ammonia-steam treated FeZSM-5 for direct N2O decomposition[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2019,290:109655. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109655 [10] LIN F, ANDANA T, WU Y Q, et al. Catalytic site requirements for N2O decomposition on Cu-, Co-, and Fe-SSZ-13 zeolites[J]. J Catal,2021,401:70−80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2021.07.012 [11] WANG Y Z, ZHENG K, HU X B, et al. Y2O3 promoted Co3O4 catalyst for catalytic decomposition of N2O[J]. Mol Catal,2019,470:104−111. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2019.04.002 [12] KIM M J, LEE S J, RYU I S, et al. Catalytic decomposition of N2O over cobalt based spinel oxides: The role of additives[J]. Mol Catal,2017,442:202−207. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.05.029 [13] ZHANG Q L, TANG X S, NING P, et al. Enhancement of N2O catalytic decomposition over Ca modified Co3O4 catalyst[J]. RSC Adv,2015,5(63):51263−51270. doi: 10.1039/C5RA04062K [14] IVANOVA Y A, SUTORMINA E F, ISUPOVA L A, et al. Effect of the composition of NixCo3–xO4 (x=0–0.9) oxides on their catalytic activity in the low-temperature reaction of N2O decomposition[J]. Kinet Catal,2018,59(3):357−362. doi: 10.1134/S0023158418030072 [15] WANG Y Z, HU X B, ZHENG K, et al. Effect of SnO2 on the structure and catalytic performance of Co3O4 for N2O decomposition[J]. Catal Commun,2018,111:70−74. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.04.004 [16] HU X B, WANG Y Z, WU R F, et al. Effects of zirconia crystal phases on the catalytic decomposition of N2O over Co3O4/ZrO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2020,514:145892. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145892 [17] GRZYBEK G, STELMACHOWSKI P, GUDYKA S, et al. Strong dispersion effect of cobalt spinel active phase spread over ceria for catalytic N2O decomposition: The role of the interface periphery[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2016,180:622−629. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.07.027 [18] KLEGOVÁ A, PACULTOVÁ K, FRIDRICHOVÁ D, et al. Cobalt oxide catalysts on commercial supports for N2O decomposition[J]. Chem Eng Technol,2017,40:981−990. doi: 10.1002/ceat.201600628 [19] YU H B, WANG X P, LI Y. Strong impact of cobalt distribution on the activity for Co3O4/CaCO3 catalyzing N2O decomposition[J]. Catal Today,2020,339:274−280. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.10.036 [20] HU X B, WANG Y Z, WU R F, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride-supported cobalt oxides as a potential catalyst for decomposition of N2O[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2021,538:148157. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148157 [21] LACA A, LACA A, DÍAZ M. Eggshell waste as catalyst: A review[J]. J Environ Manage,2017,197:351−359. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.088 [22] YUSUFF A S, ADENIYI O D, AZEEZ S O, et al. Synthesis and characterization of anthill-eggshell-Ni-Co mixed oxides composite catalyst for biodiesel production from waste frying oil[J]. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin,2019,13(1):37−47. doi: 10.1002/bbb.1914 [23] GUO Y L, YANG D P, LIU M H, et al. Enhanced catalytic benzene oxidation over a novel waste-derived Ag/eggshell catalyst[J]. J Mater Chem A,2019,7(15):8832−8844. doi: 10.1039/C8TA10822F [24] LI Z H, YANG D P, CHEN Y S, et al. Waste eggshells to valuable Co3O4/CaCO3 materials as efficient catalysts for VOCs oxidation[J]. Mol Catal,2020,483:110766. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2020.110766 [25] 郑丽, 李和健, 徐秀峰. 碳球为模板水热合成Mg-Co复合氧化物及其催化分解N2O[J]. 燃料化学学报(中英文),2018,46(5):569−577. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(18)30024-0ZHENG Li, LI Hejian, XU Xiufeng. Catalytic decomposition of N2O over Mg-Co composite oxides hydrothermally prepared by using carbon sphere as template[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2018,46(5):569−577. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(18)30024-0 [26] SUN J R, SONG A L, TIAN Y, et al. Unravelling the effect of alkali metal deposition on Co3O4 for catalytic decomposition of N2O[J]. ChemCatChem,2023,15:1−10. [27] 李和健, 郑丽, 赵天琪, 等. 水热合成Co3O4的制备参数调变及其催化分解N2O性能[J]. 燃料化学学报,2018,46(6):717−724. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(18)30031-8LI Hejian, ZHENG Li, ZHAO Tianqi, et al. Effect of preparation parameters on the catalytic performance of hydrothermally synthesized Co3O4 in the decomposition of N2O[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2018,46(6):717−724. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(18)30031-8 [28] YU H B, WANG X P, WU, X X, et al. Promotion of Ag for Co3O4 catalyzing N2O decomposition under simulated real reaction conditions[J]. Chem Eng J,2018,334:800−806. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.079 [29] 刘晓丽, 王永钊, 赵永祥. Sr掺杂羟基磷灰石负载Co3O4催化N2O分解[J]. 燃料化学学报,2021,49(8):1190−1200.LIU Xiaoli, WANG Yongzhao, ZHAO Yongxiang. Co3O4 supported on Sr doped hydroxyapatite as catalysts for N2O catalytic decomposition[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2021,49(8):1190−1200. [30] DONG N, CHEN M Y, YE Q, et al. Promotional effect of cobalt doping on catalytic performance of cryptomelane-type manganese oxide in toluene oxidation[J]. J Environ Sci,2023,126:263−274. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2022.03.024 [31] ZHANG C, ZHANG Z P, SUI C, et al. Catalytic decomposition of N2O over Co-Ti oxide catalysts: Interaction between Co and Ti oxide[J]. ChemCatChem,2016,8(12):2155−2164. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201600231 [32] HU X B, WANG Y Z, WU R F, et al. N-doped Co3O4 catalyst with a high efficiency for the catalytic decomposition of N2O[J]. Mol Catal,2021,509:111656. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111656 [33] 窦喆, 张海杰, 潘燕飞, 等. N2O在钾改性Cu-Co尖晶石型复合氧化物上的催化分解[J]. 燃料化学学报,2014,42(2):238−245. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(14)60016-5DOU Zhe, ZHANG Haijie, PAN Yanfei, et al. Catalytic decomposition of N2O over potassium-modified Cu-Co spinel oxides[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2014,42(2):238−245. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(14)60016-5 [34] 赵婉君, 李潇, 党慧, 等. 负载型Pd-Cu催化剂的制备及富氢气氛下CO优先氧化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报(中英文),2022,43(3):20210754.ZHAO Wanjun, LI Xiao, Dang Hui, et al. Preparation of supported Pd-Cu catalyst and its preferential oxidation of CO under hydrogen-rich atmosphere[J]. Chem J Chin Univ,2022,43(3):20210754. -




 下载:
下载: