Study on the role of atomic carbon species in cobalt-based FT synthesis catalyst
-
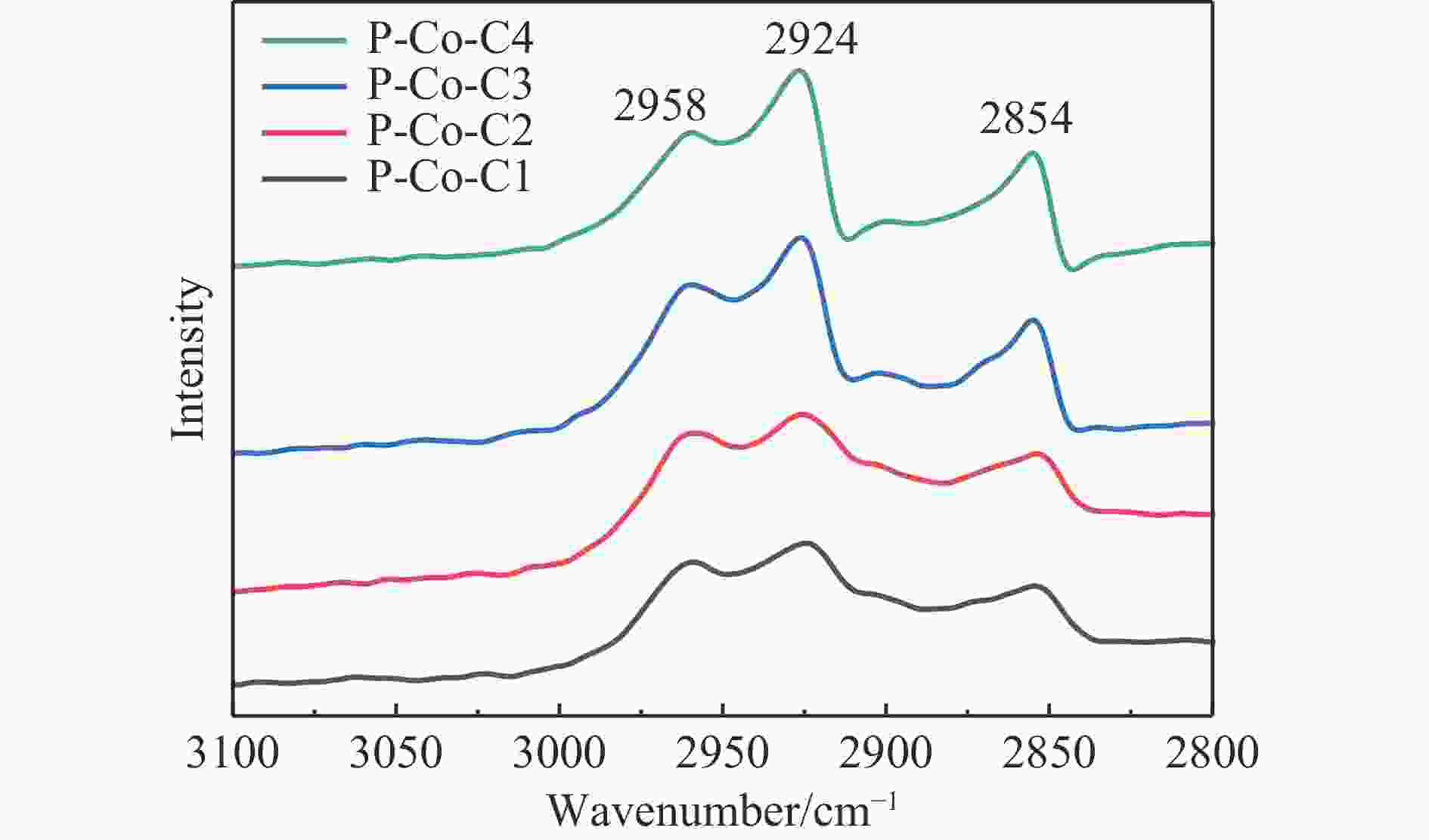
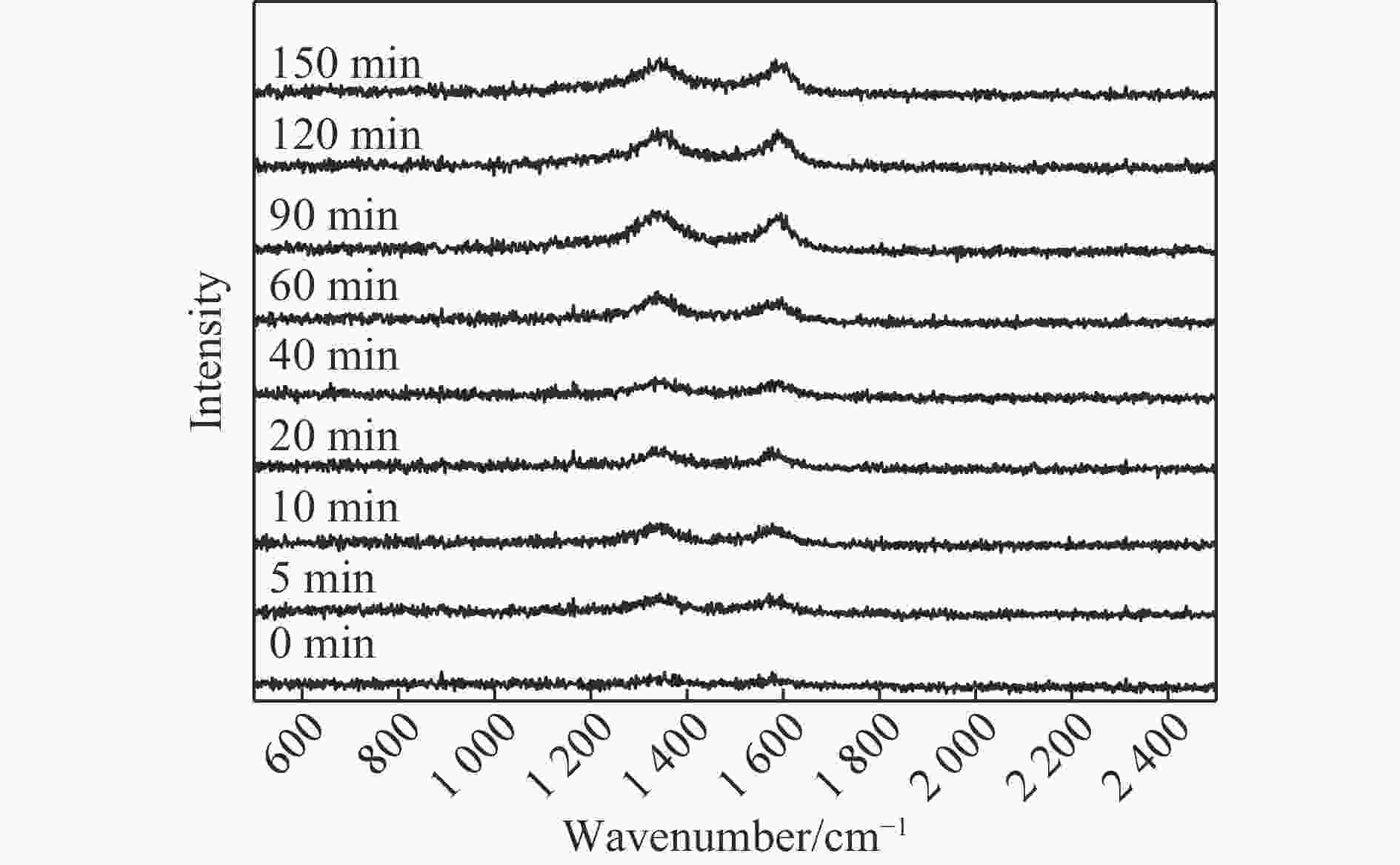
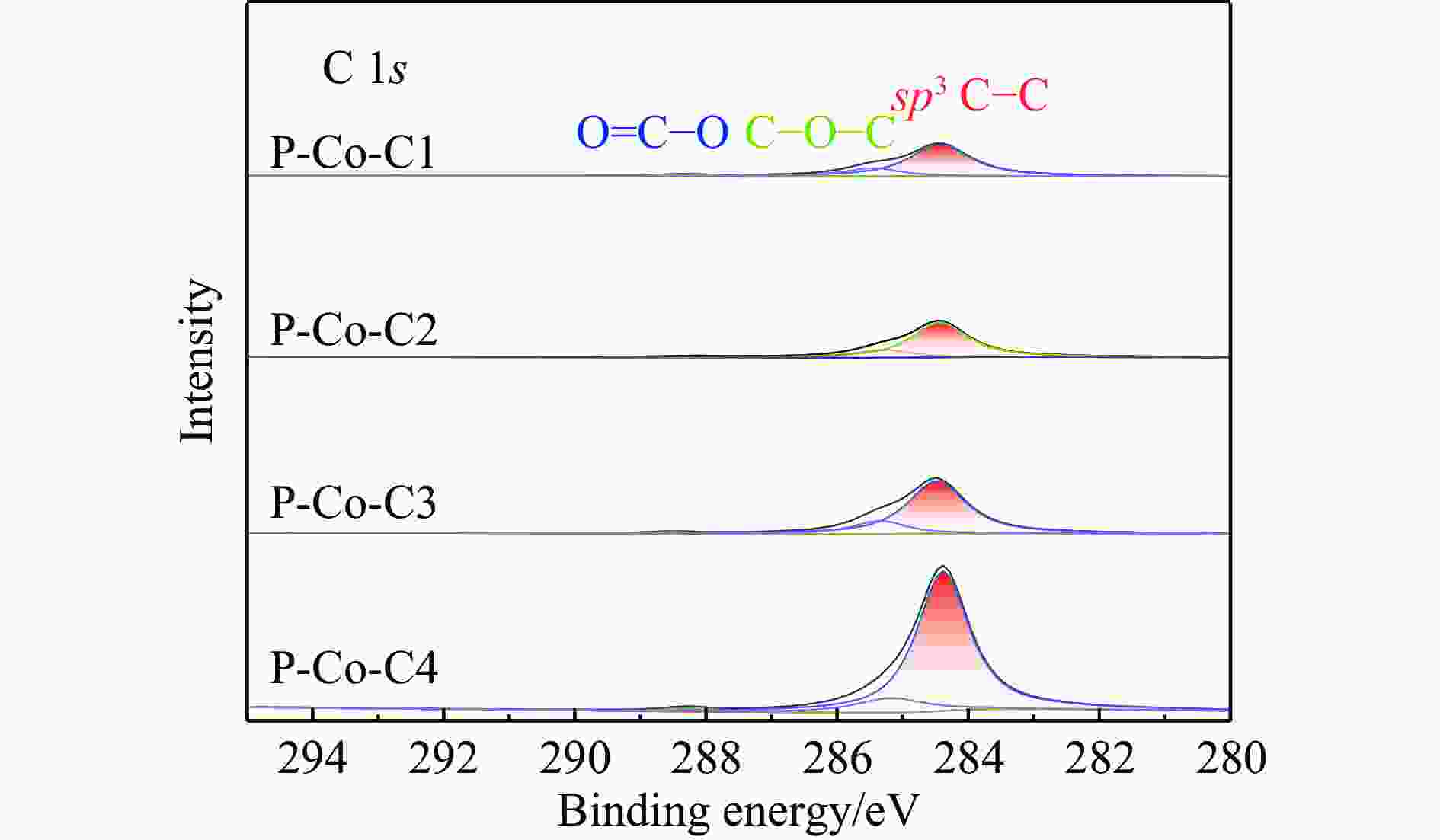
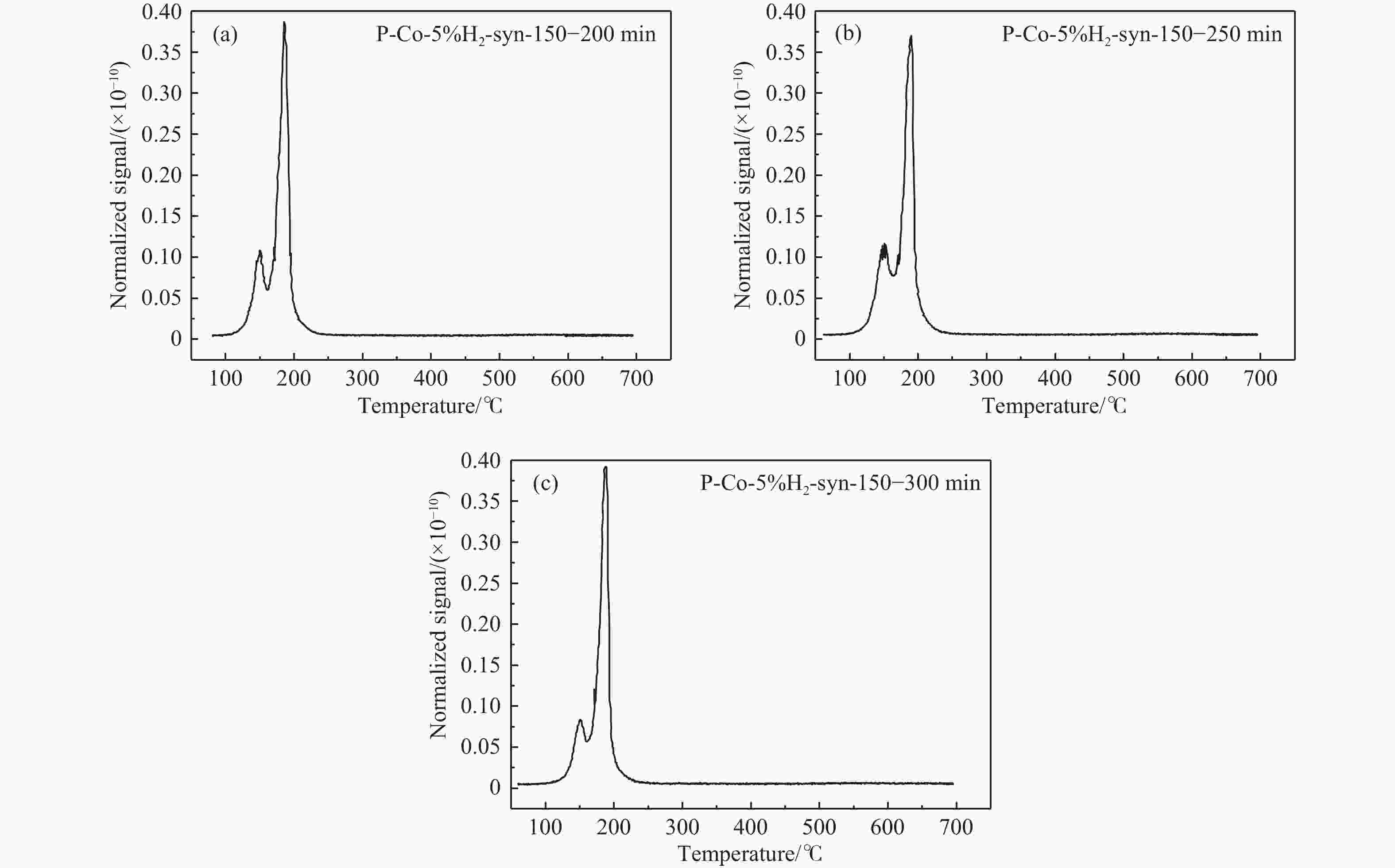
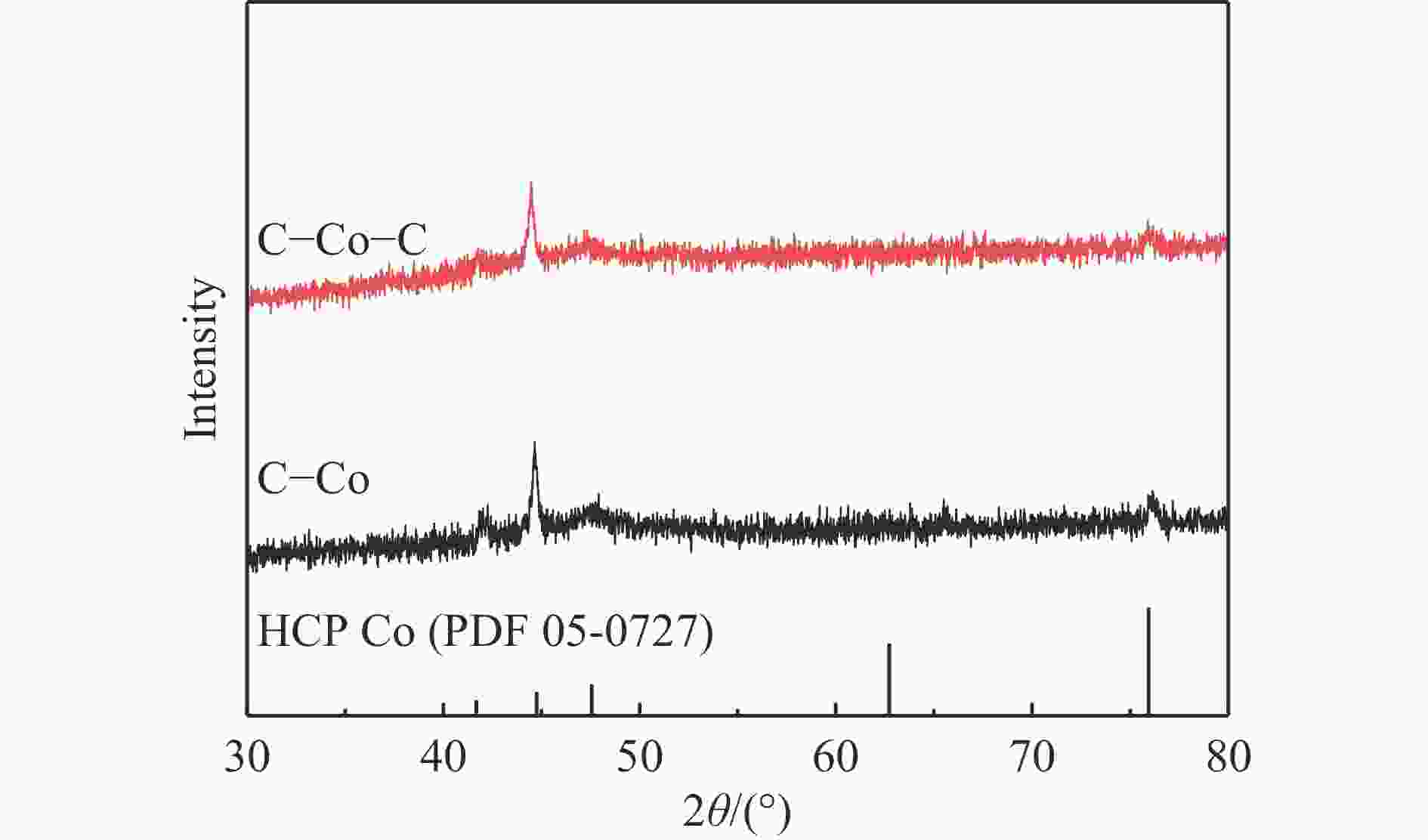
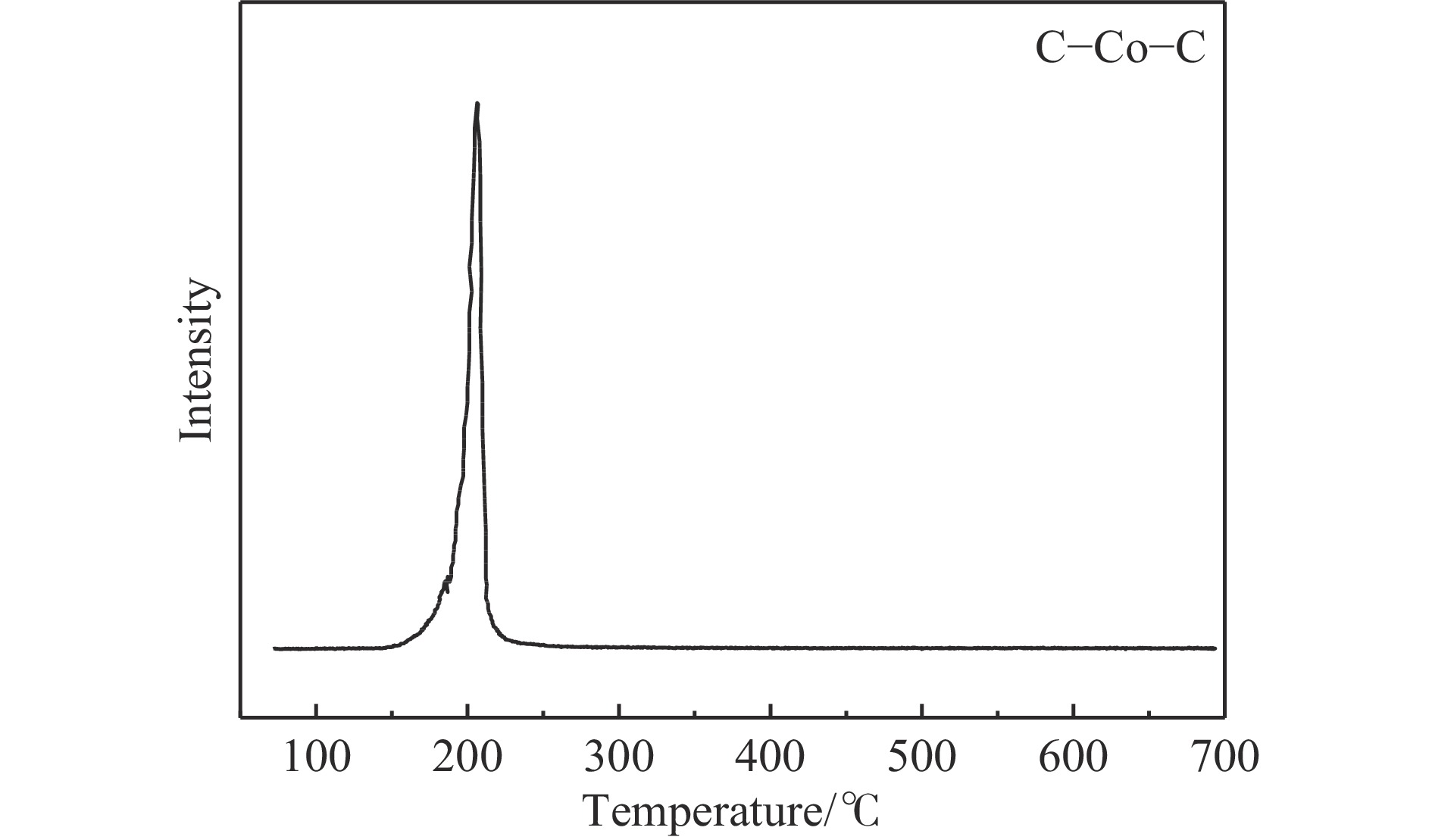
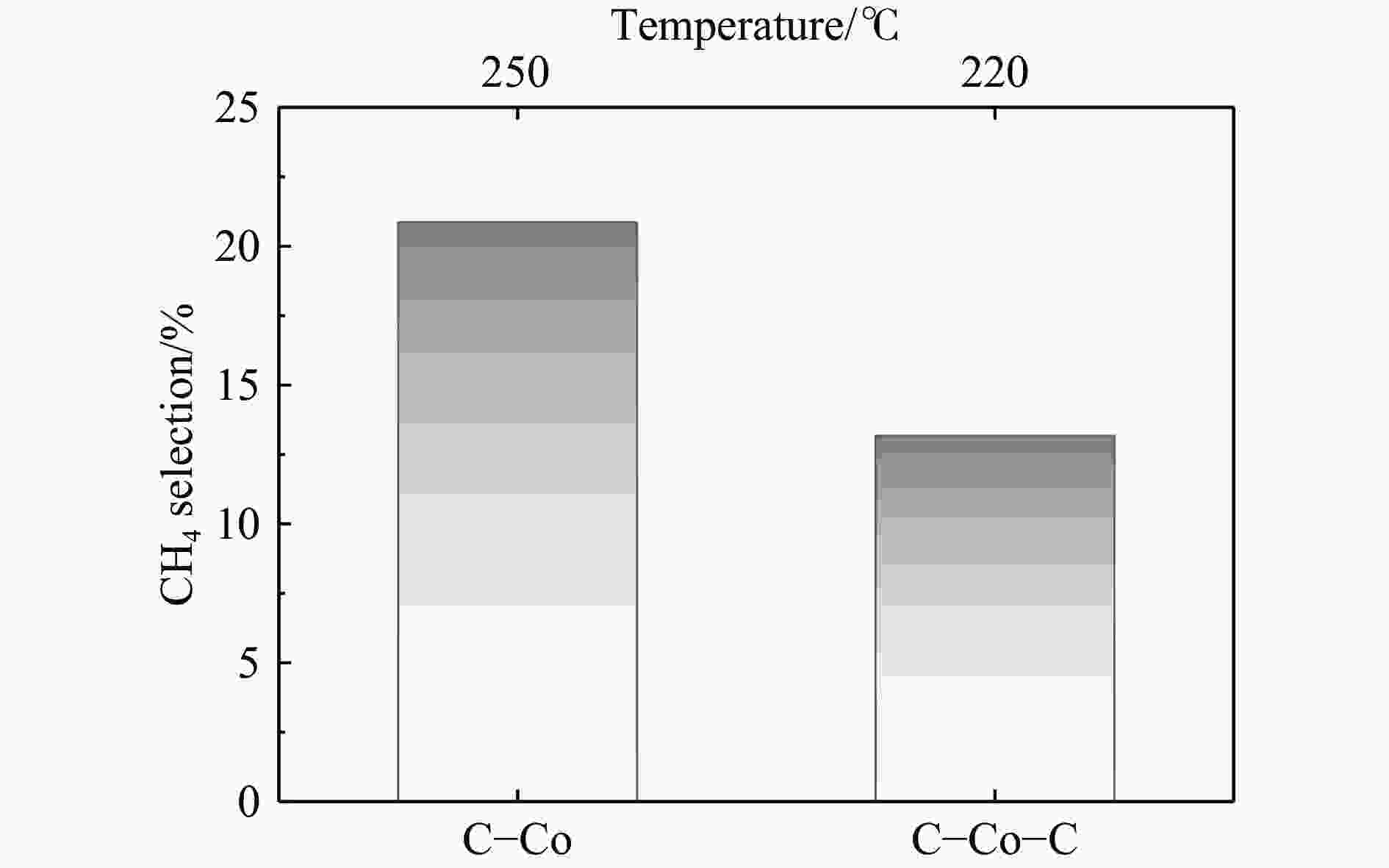
摘要: 费托合成是将合成气催化转化为长链重质烃的工艺过程。在此过程中,CO活化、歧化反应以及烃类脱氢反应都可以在催化剂表面形成碳物种,而碳物种对费托反应的作用一直存在争议。本工作通过对主要暴露面为HCP-Co(10-11)的单晶钴进行不同条件的预处理,成功构建了具有不同含量原子碳物种的模型催化剂,并采用程序升温加氢、拉曼光谱和红外光谱等表征手段对催化剂中的原子碳物种含量和存在形式进行分析。结果表明,在引入原子碳物种后,钴基催化剂的活性和CH4选择性与原子碳物种数量和存在形式密切相关。含碳量为5.72%的P-Co-C3催化剂具有较高的CO转化率,可达72.2%;而含碳量为3.01%的P-Co-C2催化剂具有较低的CH4选择性,仅为4.2%。此外,表征结果进一步证明该原子碳物种是以C(无定形碳)和CxHy两种形式共存,其在反应过程中可能参与了FT反应,进而提升其反应性能。Abstract: The FT synthesis reaction is a process that catalytically converts syngas into long-chain heavy hydrocarbons. The Fischer-Tropsch reaction involves CO activation, disproportionation reactions, and hydrocarbon dehydrogenation reactions that can form carbon species on the catalyst surface. The role of carbon species in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction has been a topic of controversy. This paper reports the successful construction of model catalysts with varying atomic carbon species content. The catalysts were prepared by pretreating single-crystal cobalt with HCP-Co(10-11) as the main exposed surface under different conditions. The carbon species content and existing forms of the catalyst were characterized by temperature programmed hydrogenation, Raman spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy. The study found that the activity and CH4 selectivity of the catalysts were closely related to the number and form of atomic carbon species introduced. With the increase of pretreatment time, the content of atomic carbon species deposited on the catalyst first increased and then decreased, and finally maintained a dynamic equilibrium, indicating that the content of atomic carbon species would remain unchanged with the increase of pretreatment time to a certain extent. The pre-treated catalyst was characterized by XRD, and no characteristic peak of CoO was found. The crystal structure is consistent with that of P-Co catalyst, and the influence of CoO and other crystal structure on the performance of FT synthesis is excluded. The P-Co-C3 catalyst, with a carbon content of 5.72%, achieved a high CO conversion rate of 72.2%, whereas the P-Co-C2 catalyst, with a carbon content of 3.01%, had a low CH4 selectivity of 4.2%. When the carbon content of P-Co-C1 (2.76%) and P-Co-C2 (3.01%) catalysts is low, the atomic carbon species mainly exists in the form of amorphous carbon (C). The presence of amorphous carbon in atomic carbon species covers part of methane generation sites, thus inhibiting methane generation, resulting in a decrease in methane selectivity. As the carbon content of P-Co-C3 (5.72%) and P-Co-C4 (14.12%) catalysts increases, the atomic carbon species in P-Co-C3 and P-Co-C4 catalysts may mainly exist in the form of CxHy, and CxHy species plays a major role in the performance of Fischer-Tropsch reaction. It is speculated that CxHy may exist in the form of low carbon olefins in adsorbed state in the atomic carbon species on the catalyst. According to the olefin readsorption mechanism, olefin readsorption produced on the catalyst surface can be used as chain initiation and chain growth species, resulting in changes in activity. Using the same pretreatment conditions, the carbon deposition on the single crystal cobalt catalyst C−Co, whose main exposed crystal surface is HCP-Co (11-20), and the Fischer-Tropsch reaction performance evaluation. The carbon species on catalyst were analyzed by temperature programmed hydrogenation and infrared characterization, and it was found that atomic carbon species were deposited on catalyst C−Co. The results showed that the deposition of atomic carbon species on the C−Co catalyst inhibited the formation of CH4 and improved the activity of the catalyst. It is further confirmed that the presence of a few atomic carbon species on cobalt-based catalysts has a certain universality to improve the performance of Fischer-Tropsch reaction.
-
Key words:
- atomic carbon species /
- carbon content /
- forms of existence /
- Fischer-Tropsch synthesis
-
表 1 催化剂的费托反应性能
Table 1 FT reaction performance of catalyst
Catalyst C/% Temperature/℃ CO conversion/% Product selectivity/% CH4 C2-C4 C5+ P-Co 0.00 220 28.0 9.8 13.1 77.2 P-Co-C1 2.76 220 36.0 8.1 25.3 66.6 P-Co-C2 3.01 220 45.7 6.0 18.7 75.3 P-Co-C3 5.72 220 72.2 13.0 23.7 63.4 P-Co-C4 14.12 220 29.5 14.7 34.4 50.9 Reaction conditions:H2/CO=2, p=2 MPa, GHSV=1000 h−1, TOS=48 h. -
[1] NAVARRO V, VAN SPRONSEN MA, FRENKEN JWM. In situ observation of self-assembled hydrocarbon Fischer-Tropsch products on a cobalt catalyst[J]. Nat Chem,2016,8:929−934. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2613 [2] KHODAKOV AY, CHU W, FONGARLAND P. Advances in the development of novel cobalt Fischer-Tropsch catalysts for synthesis of long-chain hydrocarbons and clean fuels[J]. Chem Rev,2007,107:1692−1744. doi: 10.1021/cr050972v [3] MOODLEY DJ, VAN DE LOOSDRECHT J, SAIB AM, et al. Carbon deposition as a deactivation mechanism of cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch synthesis catalysts under realistic conditions[J]. Appl Catal A-Gen,2009,354:102−110. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2008.11.015 [4] BAE JW, KIM SM, PARK SJ, et al. Deactivation by filamentous carbon formation on Co/aluminum phosphate during Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2009,48:3228−3233. doi: 10.1021/ie801956t [5] PETERSEN MA, VAN DEN BERG JA, CIOBîCA IM, et al. Revisiting CO activation on Co catalysts: impact sites from dft of step and kink[J]. Acs Catalysis,2017,7:1984−1992. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02843 [6] BöLLER B, DURNER KM, WINTTERLIN J. The active sites of a working Fischer-Tropsch catalyst revealed by operando scanning tunnelling microscopy[J]. Nat Catal,2019,2:1027−1034. doi: 10.1038/s41929-019-0360-1 [7] CHEN W, KIMPEL T F, SONG Y J, et al. Influence of carbon deposits on the cobalt-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch reaction: evidence of a two-site reaction model[J]. acs catalysis,2018,8:1580−1590. [8] HAZEMANN P, DECOTTIGNIES D, MAURY S, et al. Selectivity loss in fischer-tropsch synthesis: The effect of cobalt carbide formation[J]. J Catal,2021,397:1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2021.03.005 [9] TSAKOUMIS NE, RONNING M, BORG O, et al. Deactivation of cobalt based Fischer-Tropsch catalysts: A review[J]. Catal Today,2010,154:162−182. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.02.077 [10] DAI Y Y, YU F, LI Z J, et al. Effect of sodium on the structure-performance relationship of Co/Sio2 for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Chin J Chem,2017,35:918−926. doi: 10.1002/cjoc.201600748 [11] KOCIC S, VALERO M C, SCHWEITZER J M, et al. Surface speciation of co based fischer-tropsch catalyst under reaction conditions: deactivation by coke or by oxidation?[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2020,590:12. [12] SWART JCW, VAN STEEN E, CIOBíCA IM, et al. Interaction of graphene with FCC−Co(111)[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys,2009,11:803−807. doi: 10.1039/B814664K [13] LU WL, WANG JG, MA ZY, et al. Classifying and understanding the role of carbon deposits on cobalt catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Fuel,2023,332:7. [14] QIN C, HOU B, WANG JG, et al. Tailoring carbon deposits on a single-crystal cobalt catalyst for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis without further reduction: the role of surface carbon and penetrating carbon[J]. Acs Catalysis,2023,13:8551−8560. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c01016 [15] QIN C, HOU B, WANG JG, et al. Stabilizing optimal crystalline facet of cobalt catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces,2019,11:33886−33893. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b10174 [16] LIU J X, SU H Y, SUN D P, et al. Crystallographic dependence of co activation on cobalt catalysts: HCP versus FCC[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2013,135:16284−16287. doi: 10.1021/ja408521w [17] GUO J Z, HOU Z Y, GAO J, et al. Drifts study on adsorption and activation of CH4 and CO2 on ni/sio2 catalyst with various ni particle sizes[J]. Chin J Catal,2007,28:22−26. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(07)60009-6 [18] FENG Y, ZHANG Y, WANG J, et al. Promotion of anatase/rutile junction to direct conversion of syngas to ethanol on the Rh/Tio2 catalysts[J]. ACS Catalysis. 2024, 1874−1881. [19] NI ZJ, KANG SF, BAI JR, et al. Uniformity dispersive, anti-coking core@double-shell-structured Co@Sio2@c: effect of graphitic carbon modified interior pore-walls on c5+ selectivity in fischer-tropsch synthesis[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci,2017,505:325−331. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.096 [20] GUAN H, WANG X, CHEN SM, et al. Coaxial Cu-Si@C array electrodes for high-performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Chem Commun,2011,47:12098−12100. doi: 10.1039/c1cc15595d [21] BLUME R, ROSENTHAL D, TESSONNIER JP, et al. Characterizing graphitic carbon with x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: a step-by-step approach[J]. ChemCatChem,2015,7:2871−2881. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201500344 [22] AT , BELL. Catalytic synthesis of hydrocarbons over group-viii metals-a discussion of the reaction-mechanism[J]. Catal Rev-Sci Eng, 1981, 23 : 203−232. [23] DRY ME. Practical and theoretical aspects of the catalytic fischer-tropsch process[J]. Appl Catal A-Gen,1996,138:319−344. doi: 10.1016/0926-860X(95)00306-1 [24] Guan Z, Zhao WT, Li DB, et al. The new role of pivotal intermediate CH x in CO activation and conversion to hydrocarbons on the transition metal catalysts[J]. Fuel,2023,331:15. -





 下载:
下载: