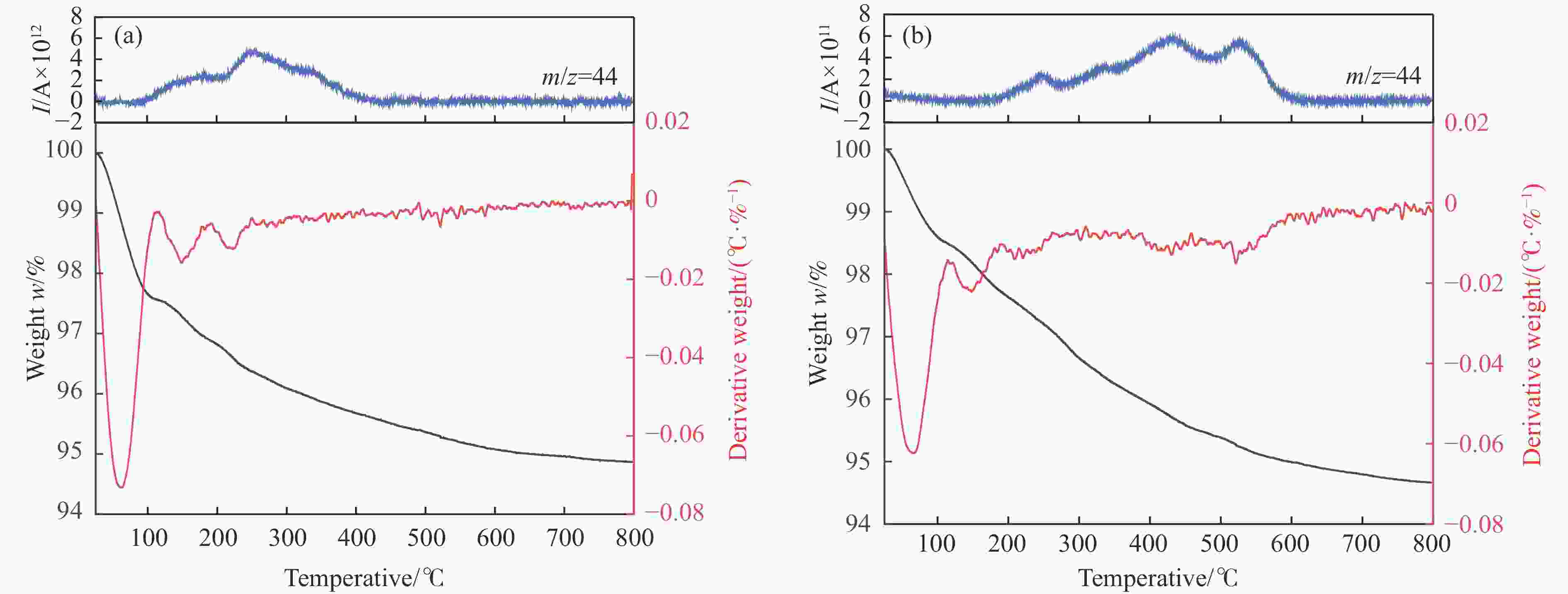
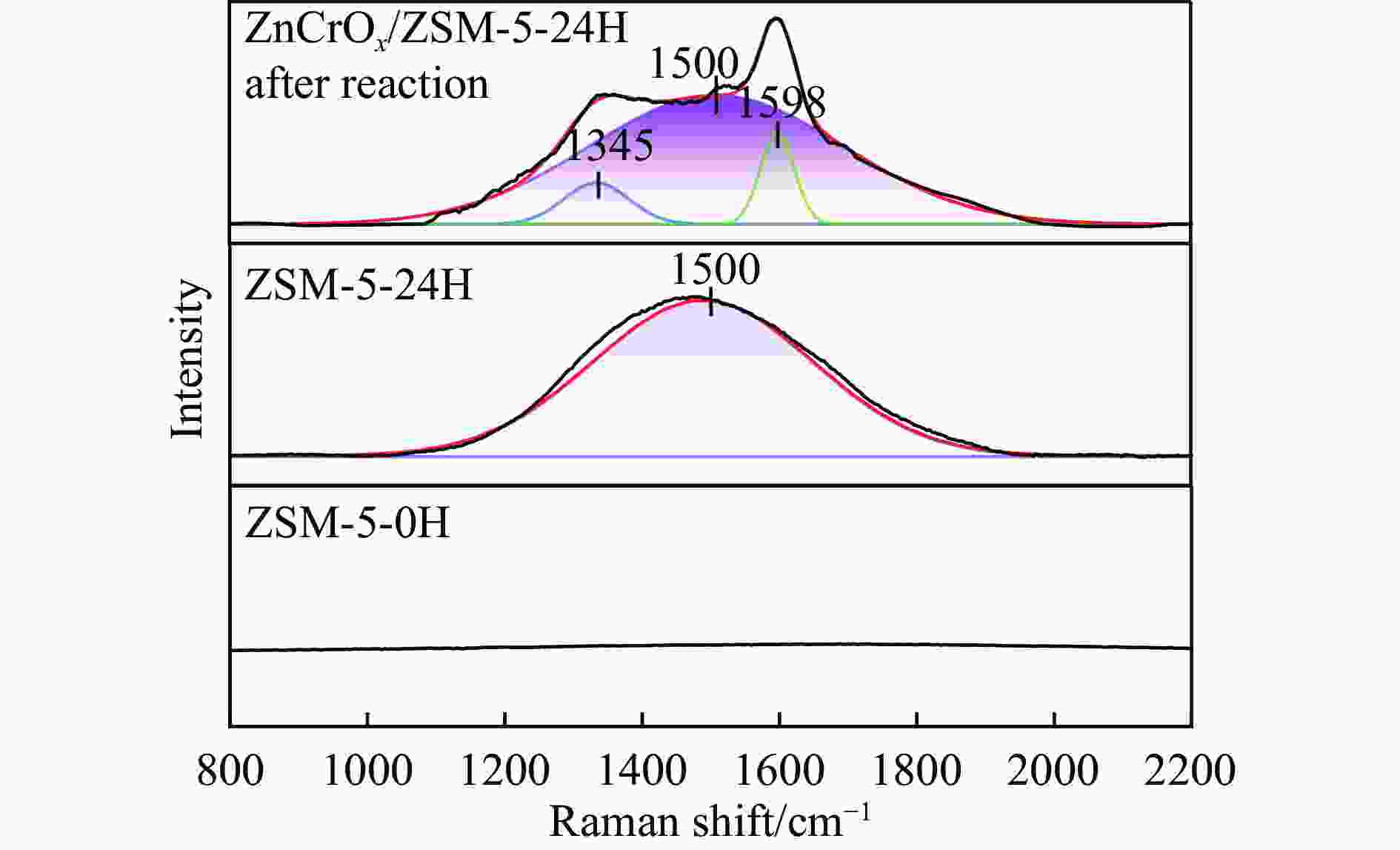
Study of pre-coking modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve and its benzene and syngas alkylation properties
-
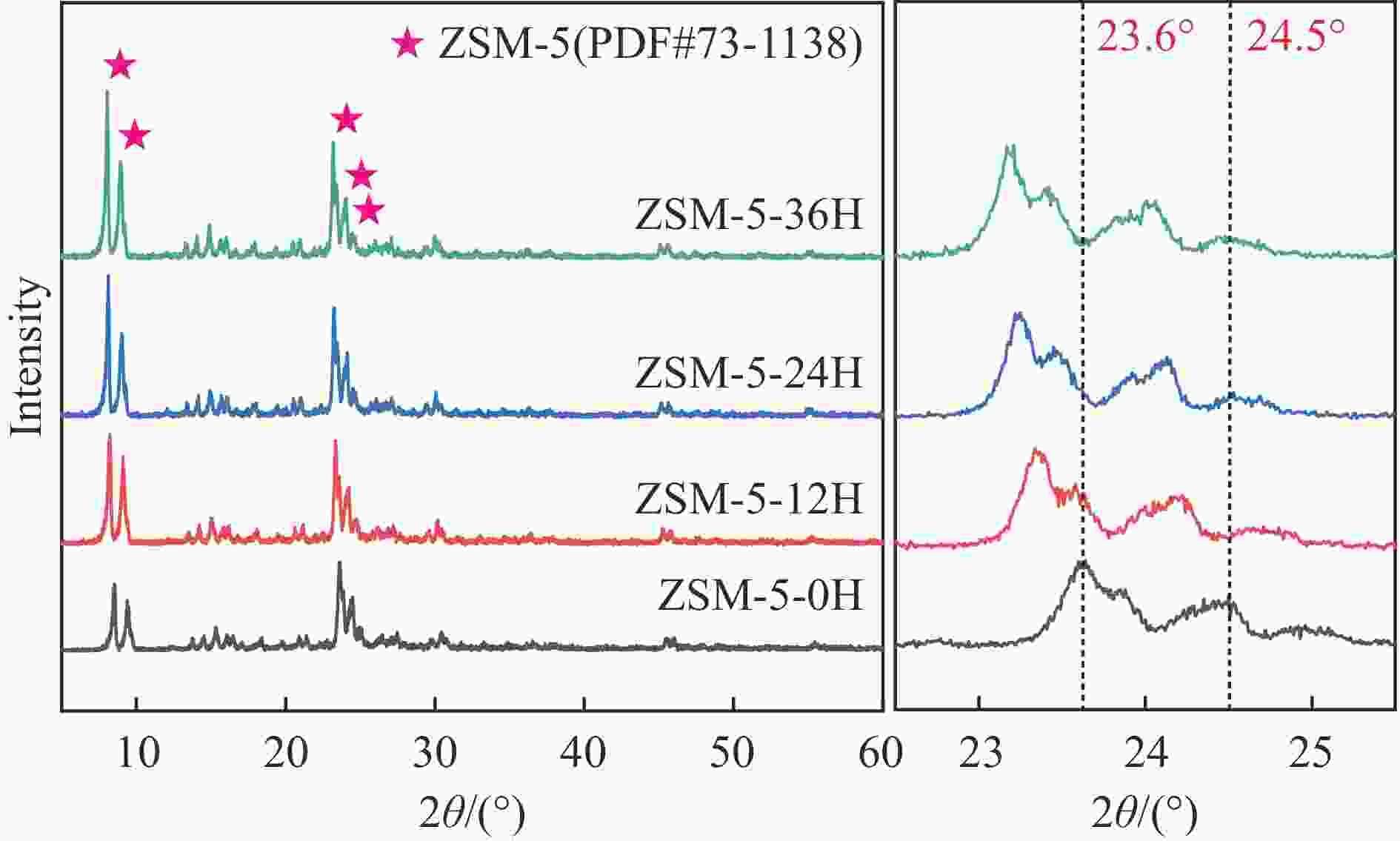
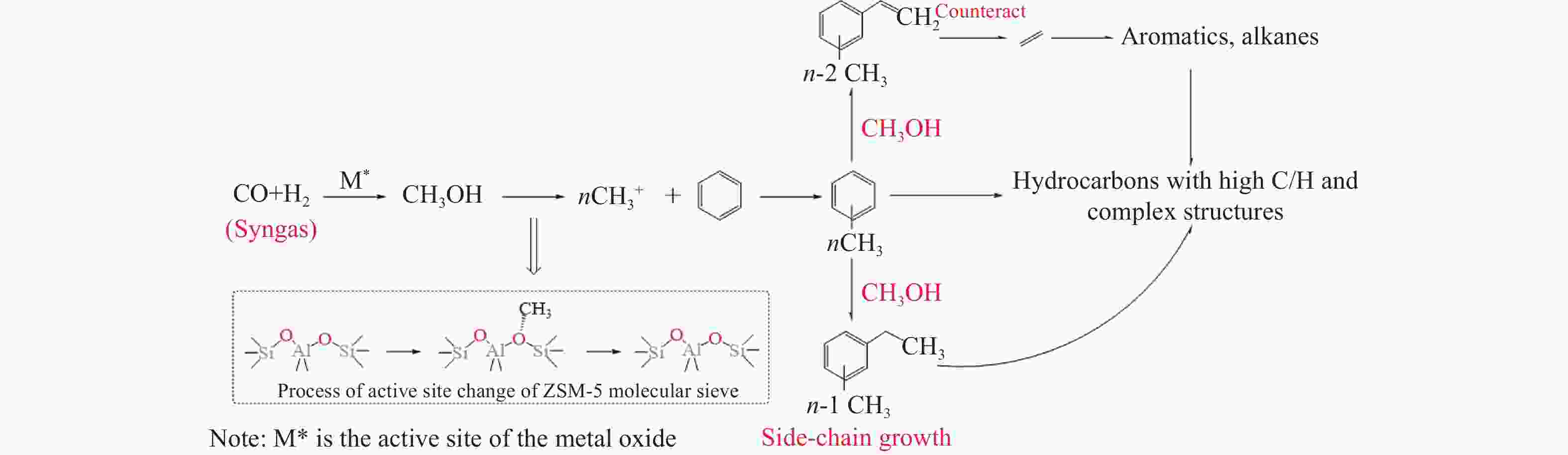
摘要: 苯与合成气的烷基化反应旨在利用非石油资源生产甲苯、二甲苯等烷基苯,本工作采用甲醇蒸汽预积炭制备一系列的ZSM-5分子筛,并与ZnCrOx复合形成双功能催化剂,探索对苯和合成气烷基化制烷基苯的影响。通过对预积炭时间的考察,发现适当的预积炭能显著提高ZSM-5分子筛的催化性能。在450 ℃、4.0 MPa的反应条件下,预积炭改性24 h的催化剂苯转化率达到20.18%。对预积炭改性的ZSM-5分子筛和反应后的复合催化剂进行分析,表明预积炭改变了分子筛的酸性。预积炭覆盖了ZSM-5分子筛上的一些B酸位点,降低了B酸/L酸比,从而提高苯的转化率。最后,通过烃池机理对苯与合成气烷基化反应的失活机理进行合理推测。Abstract: Toluene, xylene and other alkylbenzenes are important basic chemical raw materials, which mainly come from the petrochemical industry. With the increasing foreign dependence of petroleum resources in China, the development of coal-to-aromatics technology can not only alleviate the problem of shortage of petroleum resources in China, but also promote the transformation and upgrading of consumption in the traditional coal chemical industry and promote the clean and efficient use of coal. In this paper, methanol-modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves were used and mechanically milled with ZnCrOx in a mass ratio of 3∶1 as a composite catalyst, so as to investigate the catalytic effect of pre-preg carbon modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves. Under the reaction conditions of 450 ℃ and 4.0 MPa, the catalytic performance of the catalyst modified with pre-built carbon for 24 h was the best, in which the conversion of benzene reached 20.18% and that of CO reached 46.55%. It was found that the catalytic performance of the pre-built carbon modified ZSM-5 sieve was mainly affected by the B acid/L acid ratio, and the pre-built carbon covered some B acid sites on the ZSM-5 sieve, which reduced the B acid/L acid ratio and led to an increase in the benzene conversion, while the crystalline and pore structures of the pre-built carbon modified ZSM-5 sieve did not undergo significant changes. changed significantly. In order to better understand the deactivation mechanism of the carbon-modified ZSM-5 catalyst, TG-MS, Raman and GC-MS were used to further analyze the carbon species, and it was found that the carbon species of the carbon-modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves were mainly low-temperature carbon, which was mainly due to the fact that the strong acid was partially covered by the carbon-modified composite catalyst with the reduced amount of acid, and the carbon species were alkanes, olefins, aromatics and other oligomers mainly. Soluble carbon, high-temperature carbon and graphitic carbon are less, so as to avoid the reduction of catalyst activity caused by excessive carbonisation, while the carbon species on the composite catalyst after the reaction are mainly high-temperature carbon, which is mainly because the carbon species after the reaction of the composite catalyst are mainly large-molecule aromatic hydrocarbons and olefins, and even insoluble carbon such as graphitic carbon. In addition, the deactivation mechanism of ZSM-5 molecular sieve in the alkylation reaction of benzene and syngas was speculated based on the hydrocarbon pool mechanism: in the alkylation reaction of benzene and syngas syngas syngas firstly forms methanol in the active site of metal oxides, and then the methanol migrates in the acidic site of the molecular sieve to generate alkylbenzene with benzene, but as the reaction proceeds, the alkylbenzene will be alkylated deeply in the molecular sieve to form heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or graphitic However, as the reaction proceeds, alkylbenzene will be deeply alkylated on the molecular sieve, forming heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or graphite carbon, etc. Such substances are not easy to diffuse in the pores and will continuously cover the acid centre and pores of the molecular sieve, which will ultimately lead to catalyst deactivation.
-
Key words:
- ZSM-5 /
- pre-accumulation of carbon /
- B acid/L acid ratio /
- phenylalkylation
-
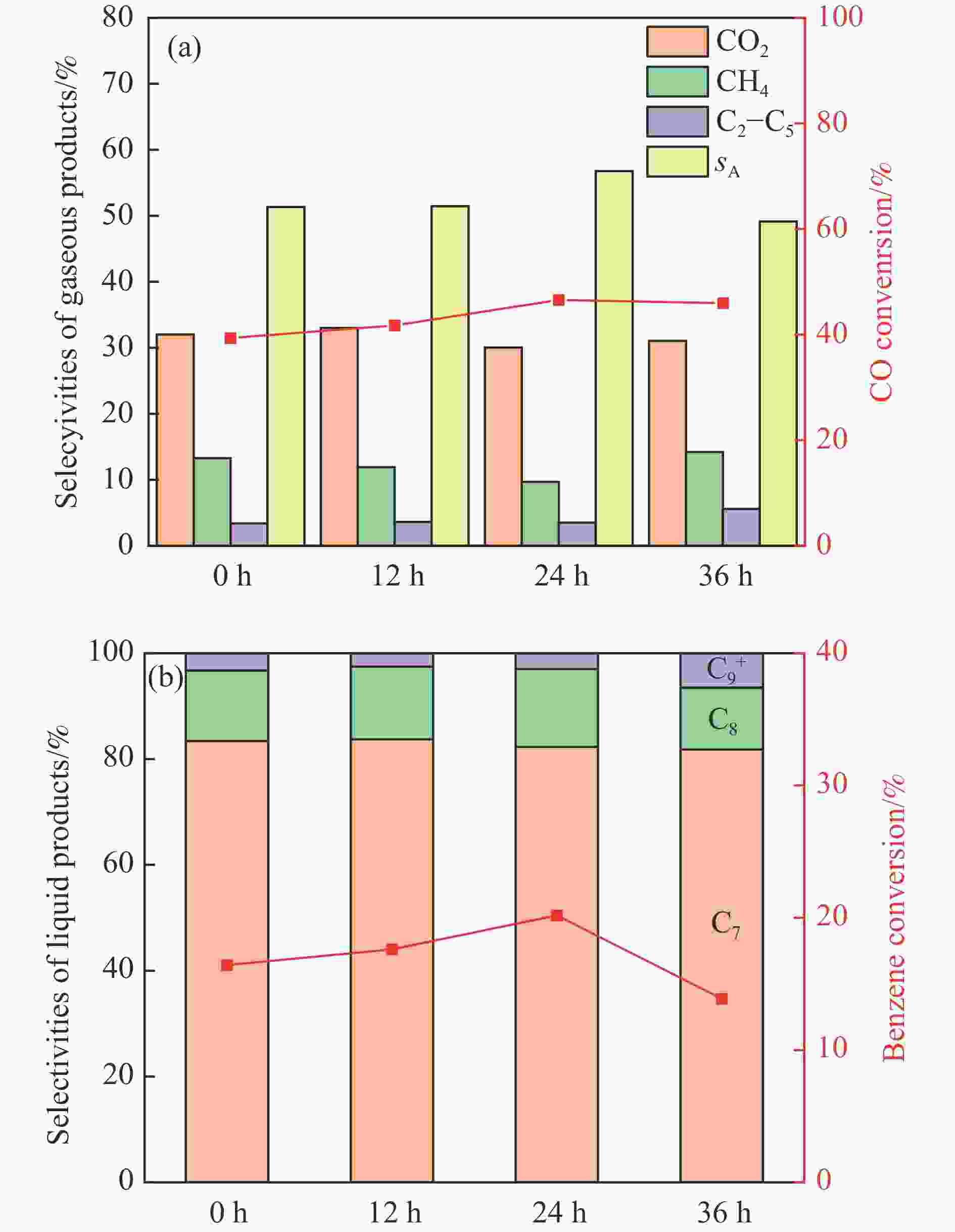
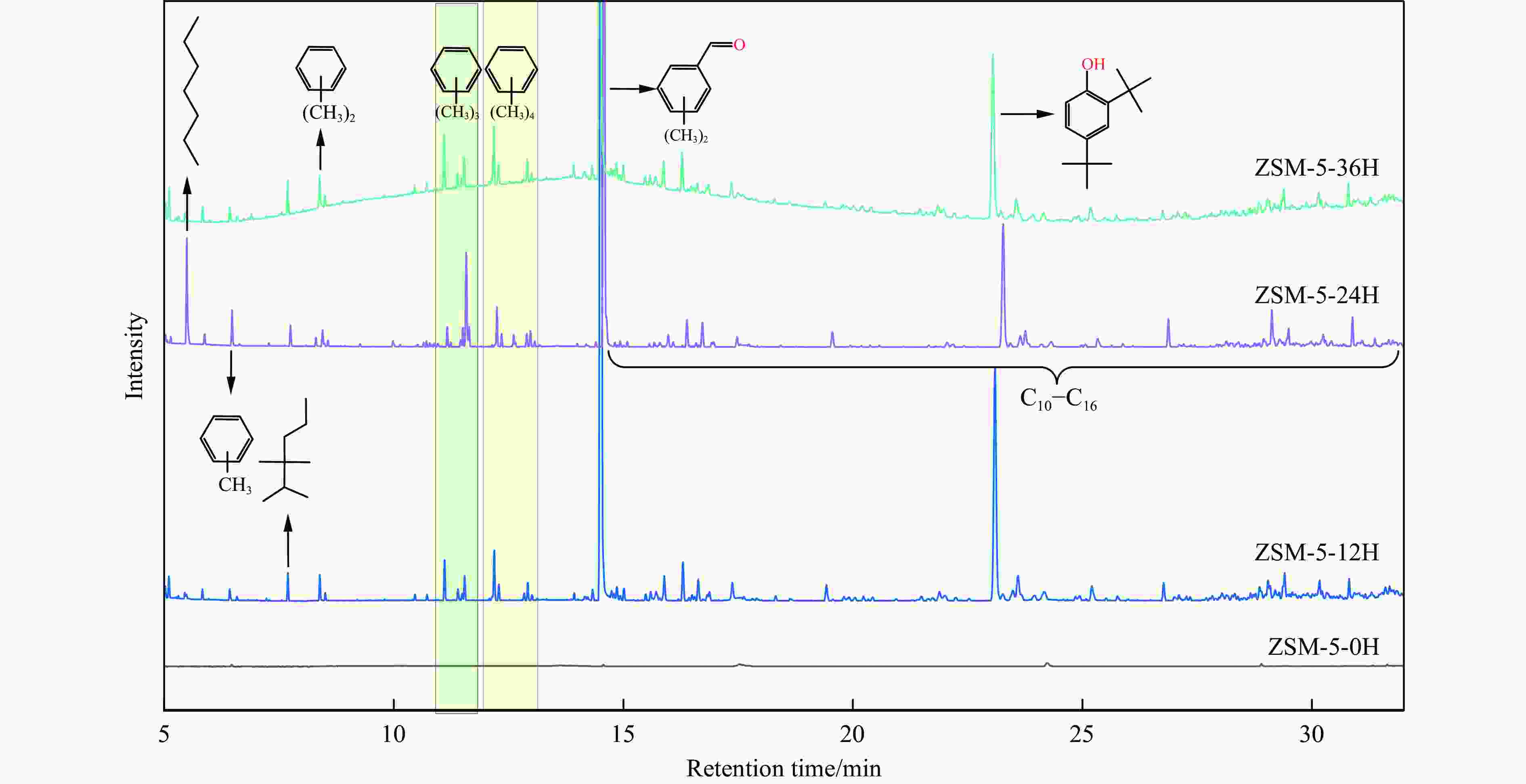
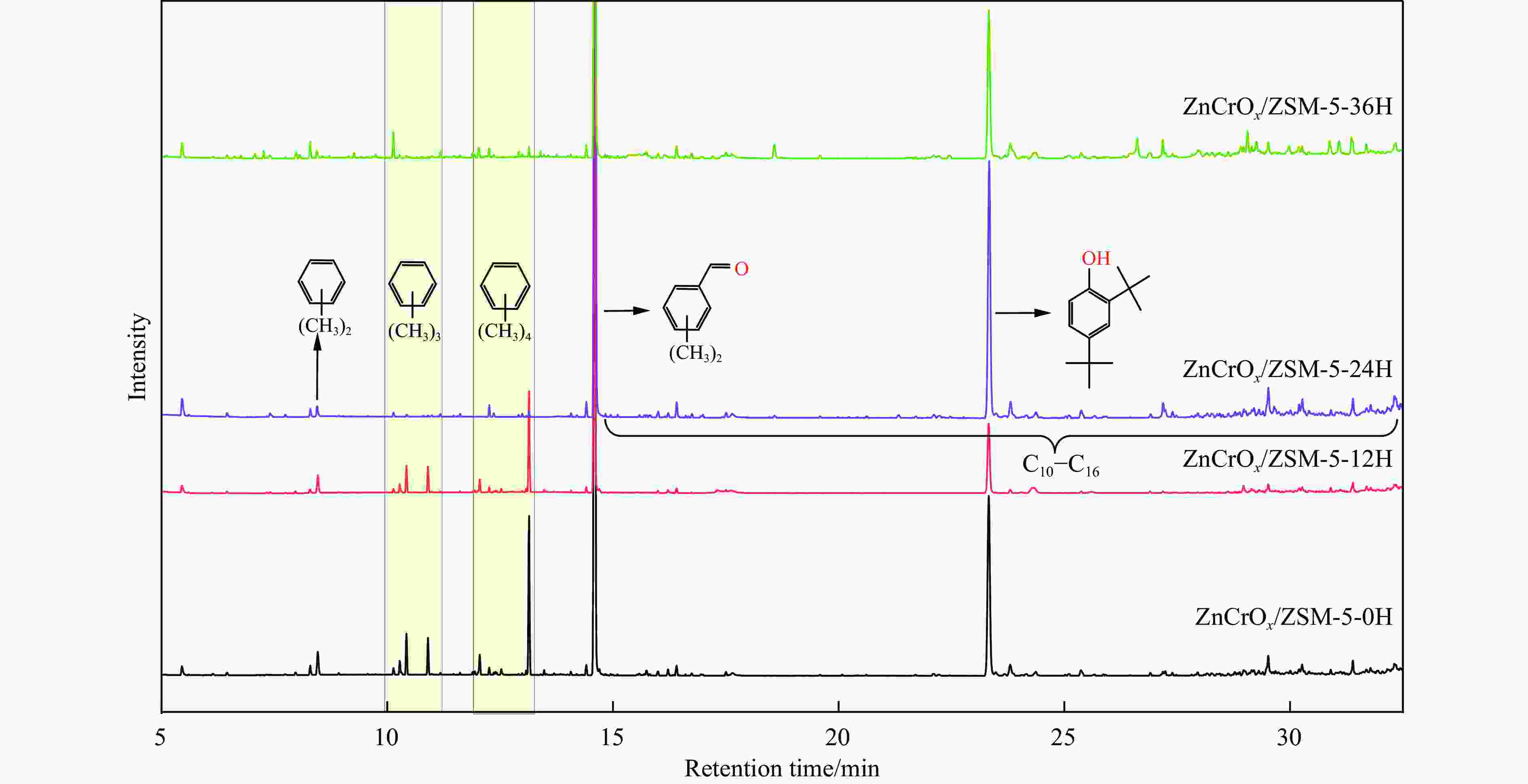
图 5 不同预积炭改性ZSM-5分子筛和ZnCrOx复合催化剂上苯与合成气烷基化反应性能
Figure 5 Reaction performance of benzene with syngas alkylation over different preaccumulated carbon modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves and ZnCrOx composite catalysts. (a) CO conversion and selectivity of gas phase products, (b) benzene conversion and selectivity of liquid phase products
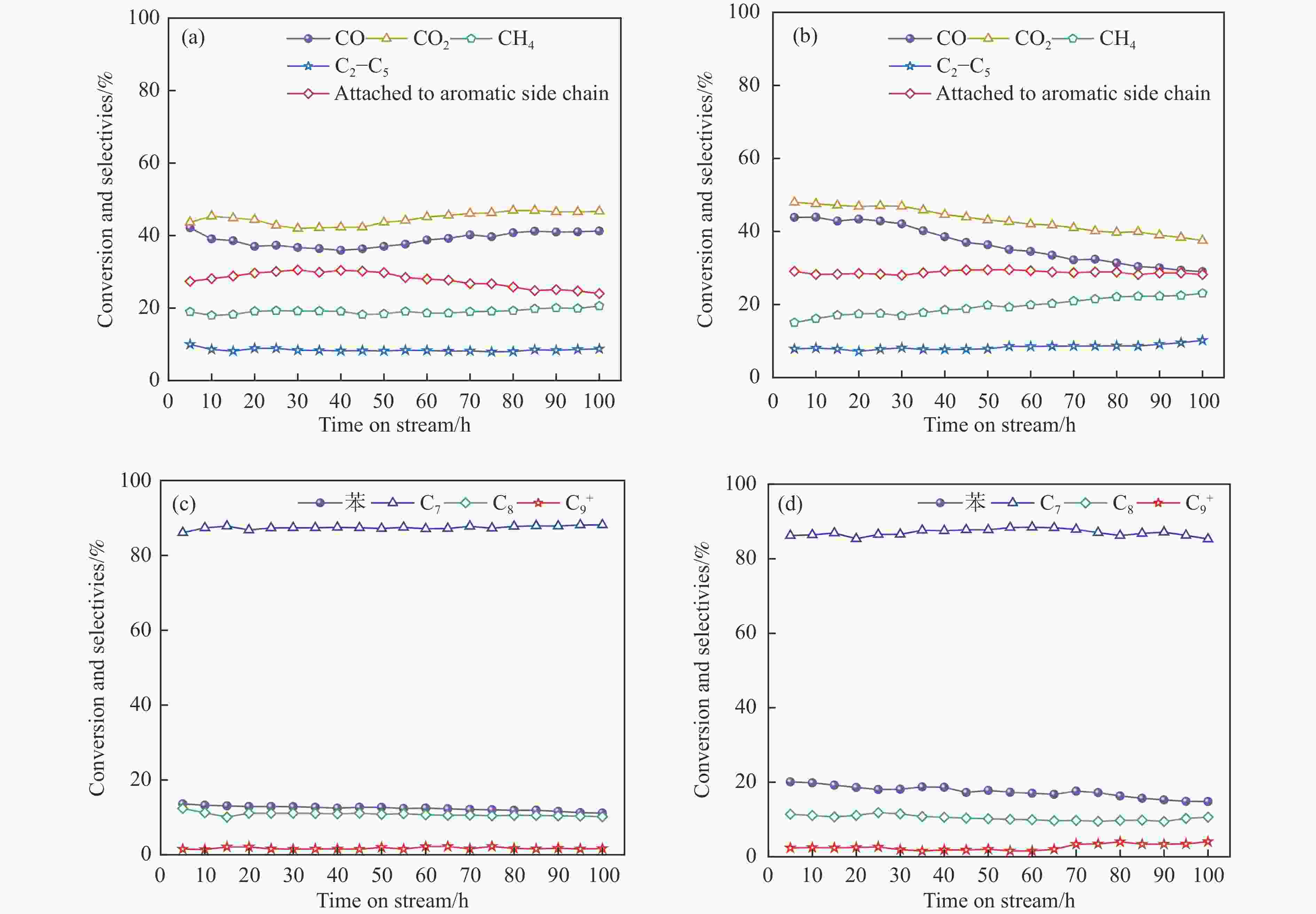
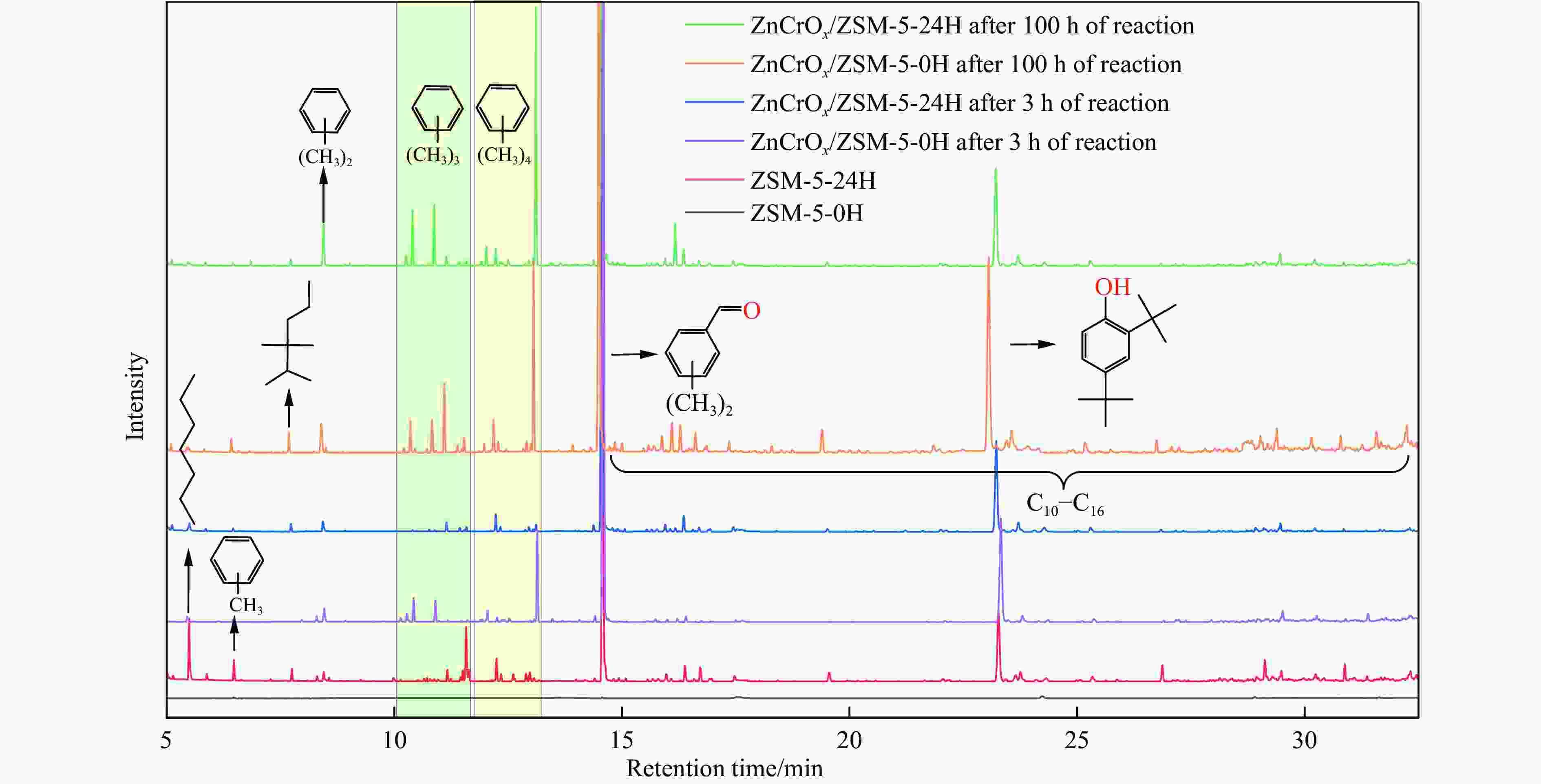
图 6 在100 h内ZnCrOx/ZSM-5-0H的CO转化率及气相产物选择性(a)和苯转化率及液相选择性(c);ZnCrOx/ZSM-5-24H的CO转化率及气相产物选择(b)和苯转化率及液相选择性(d)
Figure 6 CO conversion and gas-phase product selectivity (a) and benzene conversion and liquid-phase selectivity (c) of ZnCrOx/ZSM-5-0H over 100 h; CO conversion and gas phase product selectivity (b) and benzene conversion and liquid phase selectivity (d) of ZnCrOx/ZSM-5-24H over 100 h
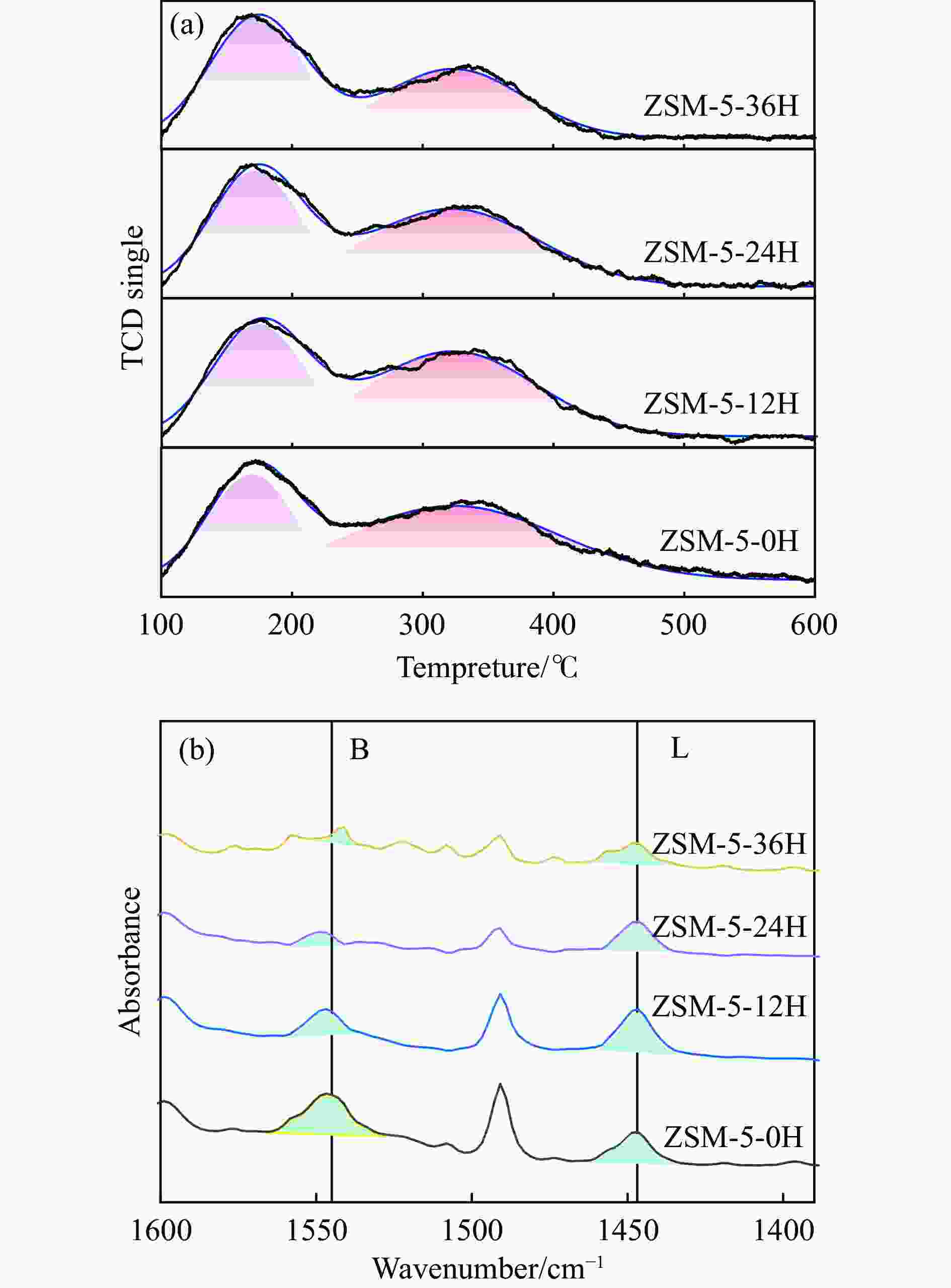
表 1 不同预积炭时间改性ZSM-5分子筛的酸性
Table 1 Acidity of modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves with different pre-carbon build-up times
Sample NH3-TPD/(μmol·g−1) Py-FTIR/(μmol·g−1) weak medium and strong total brønsted lewis B/L ZSM-5-0H 126 154 280 113 75 1.54 ZSM-5-12H 123 146 269 64 94 0.68 ZSM-5-24H 125 118 243 33 64 0.51 ZSM-5-36H 126 103 229 20 50 0.40 表 2 不同预积炭时间改性ZSM-5 分子筛的孔道参数
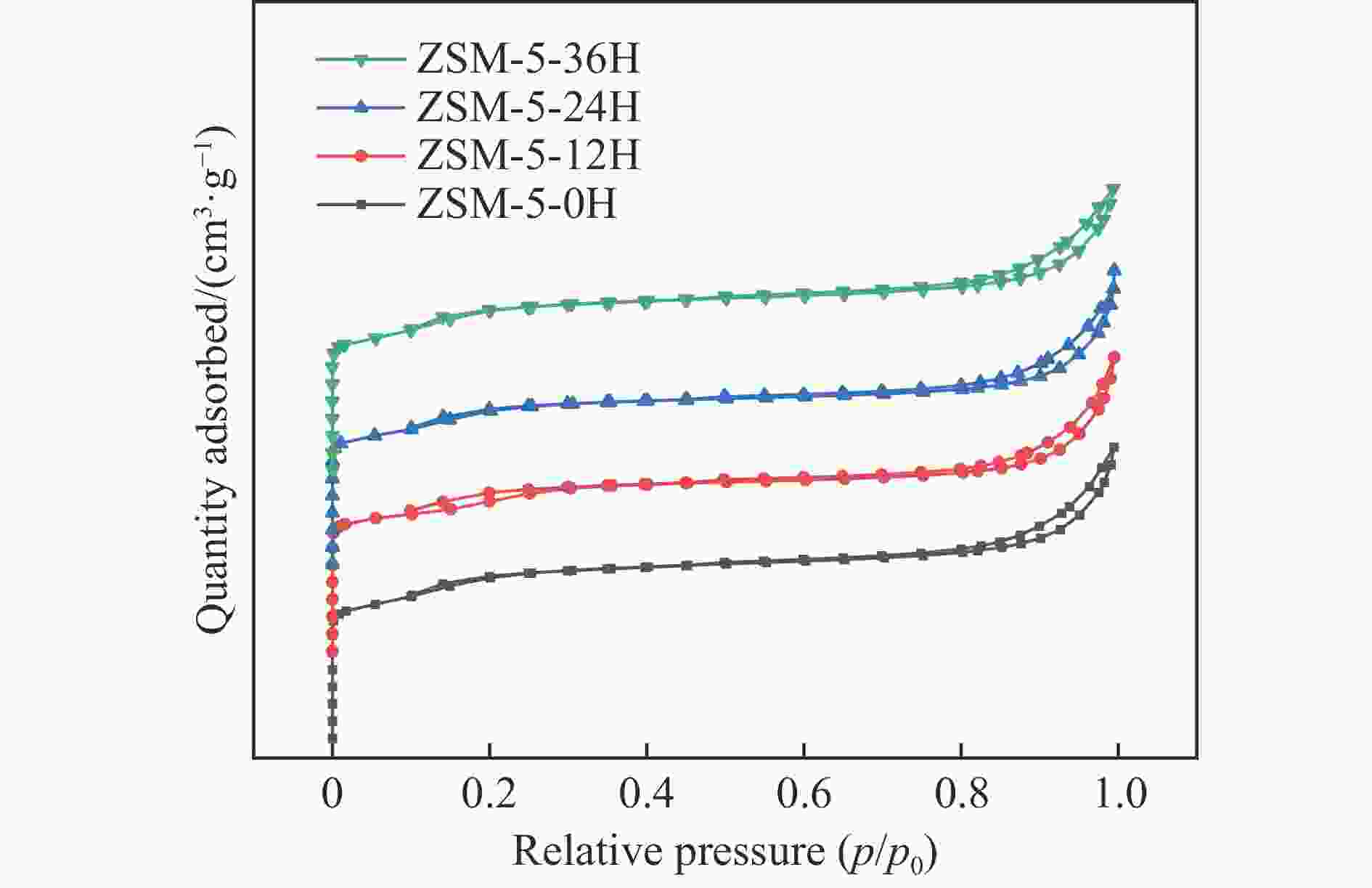
Table 2 Pore parameters of modified ZSM-5 molecular sieves with different pre-accumulation times
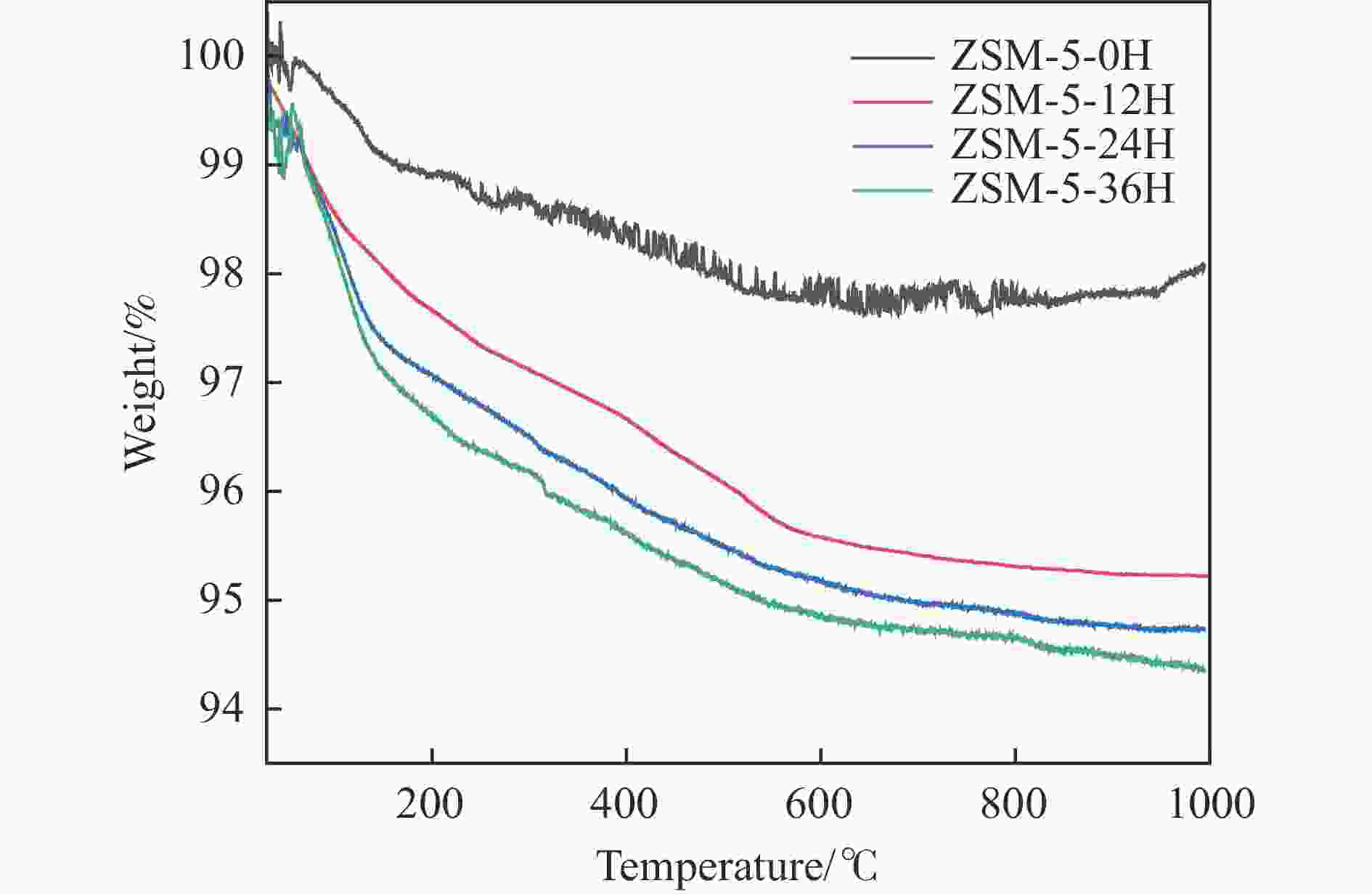
Sample $S_{{\mathrm{BET}}}^{\mathrm{a}} $/(m2·g−1) $S_{{\mathrm{meso}}}^{\mathrm{b}} $/(m2·g−1) $S_{\mathrm{micro}}^{\mathrm{c}} $/(m2·g−1) $v_{\mathrm{total}}^{\mathrm{d}} $/(cm3·g−1) $v_{\mathrm{micro}}^{\mathrm{c}} $/(cm3·g−1) ZSM-5 313.9 187.5 126. 4 0.354 0.162 ZSM-5-12H 296.8 171.3 125.5 0.352 0.162 ZSM-5-24H 300.6 184.5 116.1 0.345 0.157 ZSM-5-36H 291.6 177.2 114.4 0.334 0.151 a: BET method; b: Smeso=SBET-Smicro; c: t-plot method; d: Volume adsorbed at p/p0=0.99. -
[1] 张一成, 王洪学, 章序文, 等. 甲醇制芳烃反应的催化研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2016,35(3):801−806.ZHANG Yicheng, WANG Hongxue, ZHANG Xuwen, et al. Advances in the catalysis of methanol to aromatics reaction[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2016,35(3):801−806. [2] Cheng K, Zhou W, Kang J, et al. Bifunctional Catalysts for One-Step Conversion of Syngas into Aromatics with Excellent Selectivity and Stability[J]. Chem,2017,3(2):334−347. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2017.05.007 [3] Settle A E, Berstis L, Rorrer N A, et al. Heterogeneous Diels–Alder catalysis for biomass-derived aromatic compounds[J]. Green Chem,2017,19(15):3468−3492. doi: 10.1039/C7GC00992E [4] Yang F, Zhong J, Liu X, et al. A novel catalytic alkylation process of syngas with benzene over the cerium modified platinum supported on HZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Appl Energy,2018,226:22−30. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.05.093 [5] Gao B, Ding C, Wang J, et al. Construction of a tandem HZSM-5 with CuZnAl catalyst for alkylation of benzene with syngas[J]. New J Chem,2020,44(6):2471−2478. doi: 10.1039/C9NJ05273A [6] Shen K, Qian W, Wang N, et al. Centrifugation-free and high yield synthesis of nanosized H-ZSM-5 and its structure-guided aromatization of methanol to 1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene[J]. J Mater Chem A,2014,2(46):19797−19808. doi: 10.1039/C4TA04444D [7] Tukur N M, Al-Khattaf S. Comparison studies of xylene isomerization and disproportionation reactions between SSZ-33, TNU-9, mordenite and ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts[J]. Chem Eng J,2011,166(1):348−357. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.004 [8] Schmidt F, Hoffmann C, Giordanino F, et al. Coke location in microporous and hierarchical ZSM-5 and the impact on the MTH reaction[J]. J Catal,2013,307:238−245. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.07.020 [9] Adebajo M O, Howe R F, Long M A. Methylation of benzene with methanol over zeolite catalysts in a low pressure flow reactor[J]. Catal Today,2000,63(2):471−478. [10] 翟岩亮, 张少龙, 张络明, 等. 不同B, Al分布对ZSM-5分子筛的甲醇制丙烯反应性能的影响[J]. 物理化学学报,2019,35(11):1248−1258.ZHAI Yanliang, ZHANG Shaolong, ZHANG Luoming, et al. Effect of B and Al Distribution in ZSM-5 Zeolite on Methanol to Propylene Reaction Performance[J]. Acta Phys Chim Sin,2019,35(11):1248−1258. [11] Li N, Zhang Y Y, Chen L, et al. Synthesis and application of HZSM-5@silicalite-1 core–shell composites for the generation of light olefins from CH3Br[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2016,227:76−80. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.02.017 [12] Bauer F, Chen W H, Ernst H, et al. Selectivity improvement in xylene isomerization[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2004,72(1):81−89. [13] Wang L, Qi J, Jiao H, et al. The guiding role of pre-coking on the coke deposition over ZSM-5 in methanol to propylene[J]. R Soc Open Sci,2019,6(9):190218. doi: 10.1098/rsos.190218 [14] Liu J, Xu H, Dong J, et al. Alkylbenzene synthesis from benzene and syngas over a ZnCrO x/beta bifunctional catalyst[J]. React Chem Eng,2022,7(6):1447−1460. doi: 10.1039/D2RE00026A [15] Guisnet M. “Coke” molecules trapped in the micropores of zeolites as active species in hydrocarbon transformations[J]. J Mol Catal A: Chem,2002,182-183:367−382. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1169(01)00511-8 [16] Bauer F, Chen W H, Bilz E, et al. Surface modification of nano-sized HZSM-5 and HFER by pre-coking and silanization[J]. J Catal,2007,251(2):258−270. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2007.08.009 [17] Kubo K, Iida H, Namba S, et al. Effect of steaming on acidity and catalytic performance of H-ZSM-5 and P/H-ZSM-5 as naphtha to olefin catalysts[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2014,188:23−29. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.01.002 [18] Gołąbek K, Tarach K A, Góra-Marek K. Xylenes transformation over zeolites ZSM-5 ruled by acidic properties[J]. Spectrochim Acta, Part A,2018,192:361−367. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2017.11.028 [19] Lu Y, Wang D, Yang P, et al. Coupling ZnxCd1−xS nanoparticles with graphene-like MoS2: superior interfacial contact, low overpotential and enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation[J]. Catal Sci Technol,2014,4(8):2650−2657. doi: 10.1039/C4CY00331D [20] Fyfe C A, Kennedy Gordon J, De Schutter C T, et al. Sorbate-induced structural changes in ZSM-5 (silicalite)[J]. J Chem Soc, Chem Commun,1984,(8):541. doi: 10.1039/c39840000541 [21] Wu H, Liu F, Yi Y, et al. Catalytic and deactivated behavior of SAPO-34/ZSM-5 composite molecular sieve synthesized by in-situ two-step method[J]. J Mater Res Technol,2021,15:1844−1853. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.017 [22] Bibby D M, Milestone N B, Patterson J E, et al. Coke formation in zeolite ZSM-5[J]. Journal of Catalysis,1986,97(2):493−502. doi: 10.1016/0021-9517(86)90020-5 [23] Bauer F, Kanazirev V, Vlaev L, et al. Coke formation on ZSM-5 catalysts. Koksbildung in ZSM-5-Katalysatoren[J]. Germany: N. p,1989,41:7. [24] 蒋云涛. ZSM-5分子筛催化剂上甲醇制丙烯反应—失活路径研究及其工艺设计[D]. 浙江大学, 2017.JIANG Yuntao. Research on the reaction and deactivation pathways and process design of methanol to propylene on ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst[D]. Zhejiang, Zhejiang University, 2016) [25] Han T, Xu H, Liu J, et al. One-Pass Conversion of Benzene and Syngas to Alkylbenzenes by Cu–ZnO–Al2O3 and ZSM-5 Relay[J]. Catal Lett,2022,152(2):467−479. doi: 10.1007/s10562-021-03617-5 [26] Okkel L G, Fenelonov V B, Romannikov V N, et al. Coke distribution in high zeolites of the ZSM-5 type[J]. Kinet. Catal , 1992. [27] Pradhan A R, Lin T S, Chen W H, et al. EPR and NMR Studies of Coke Induced Selectivation over H–ZSM-5 Zeolite during Ethylbenzene Disproportionation Reaction[J]. J Catal,1999,184(1):29−38. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2431 [28] Hassan F, Wang J, Chigada P I, et al. Deactivation during 1-Hexene Isomerization over Zeolite Y and ZSM5 Catalysts under Supercritical Conditions[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem Res,2011,50(12):7161−7171. doi: 10.1021/ie101876f [29] Chua Y T, Stair P C. An ultraviolet Raman spectroscopic study of coke formation in methanol to hydrocarbons conversion over zeolite H-MFI[J]. J Catal,2003,213(1):39−46. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9517(02)00026-X [30] Peng C, Zhai Y, Hornung A, et al. Promoting effect of ZSM-5 catalyst on carbonization via hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2018,6(7):9461−9469. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02012 [31] Arstad B, Nicholas J B, Haw J F. Theoretical study of the methylbenzene side-chain hydrocarbon pool mechanism in methanol to olefin catalysis[J]. J Am Chem Soc,2004,126(9):2991−3001. doi: 10.1021/ja035923j [32] Hwang A, Bhan A. Deactivation of zeolites and zeotypes in methanol-to-hydrocarbons catalysis: Mechanisms and circumvention[J]. Acc Chem Res,2019,52(9):2647−2656. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00204 -




 下载:
下载: