Effect of alkali metal occurrence on the pyrolysis behavior of rice straw
-
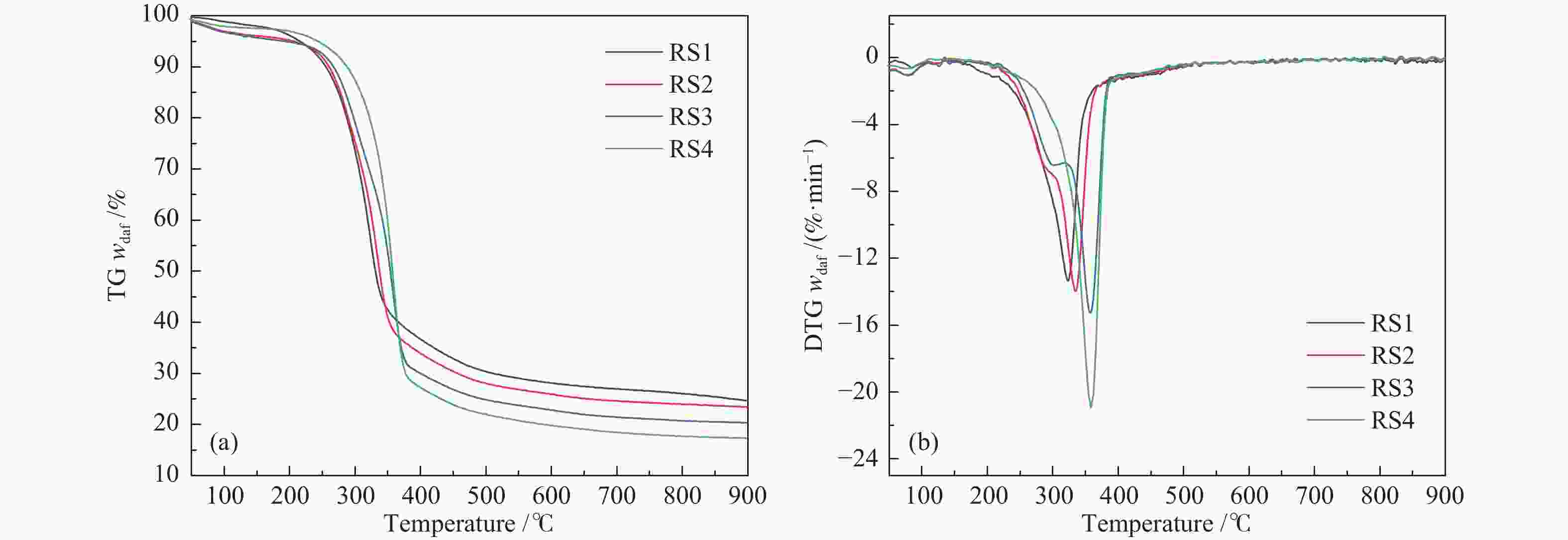
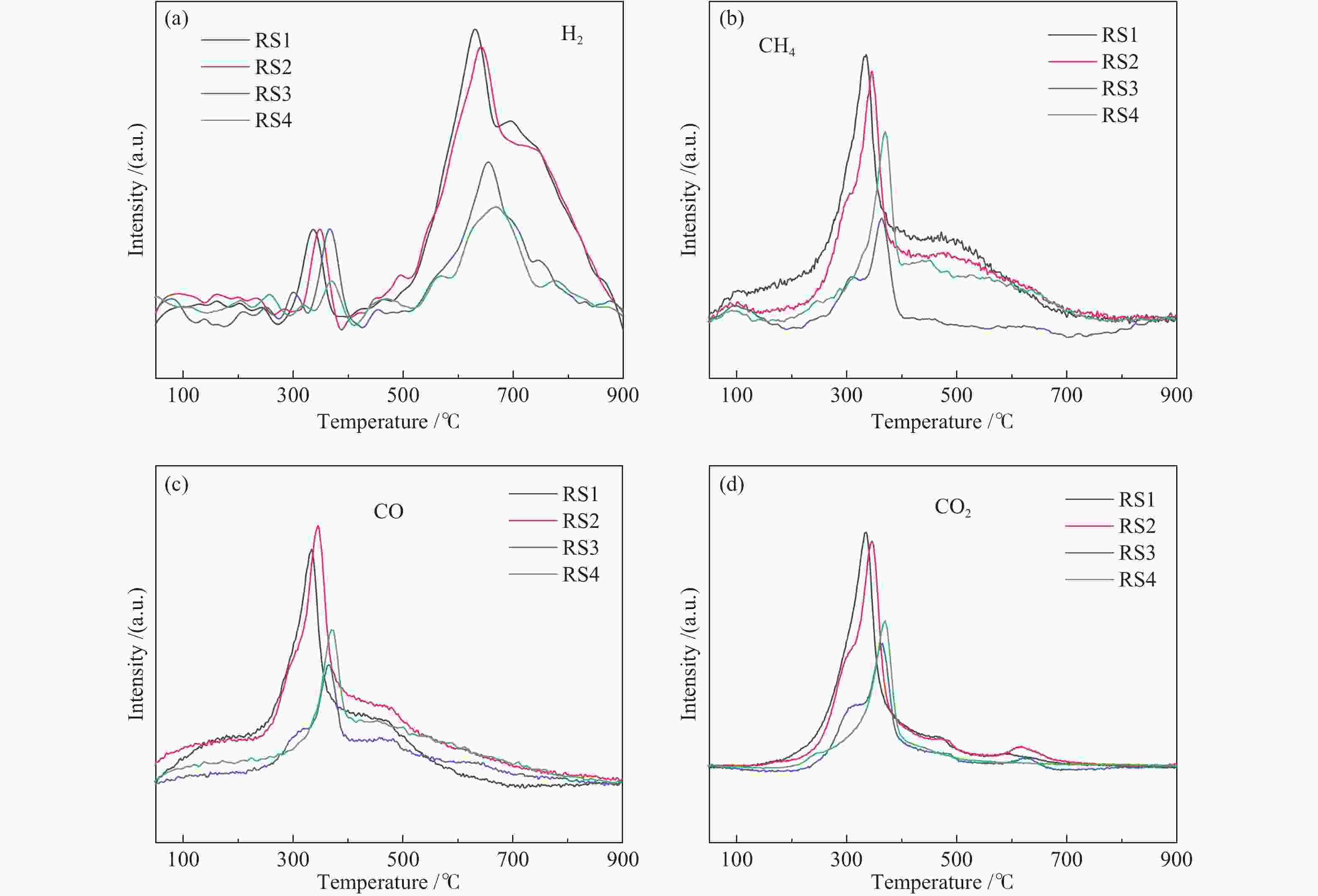
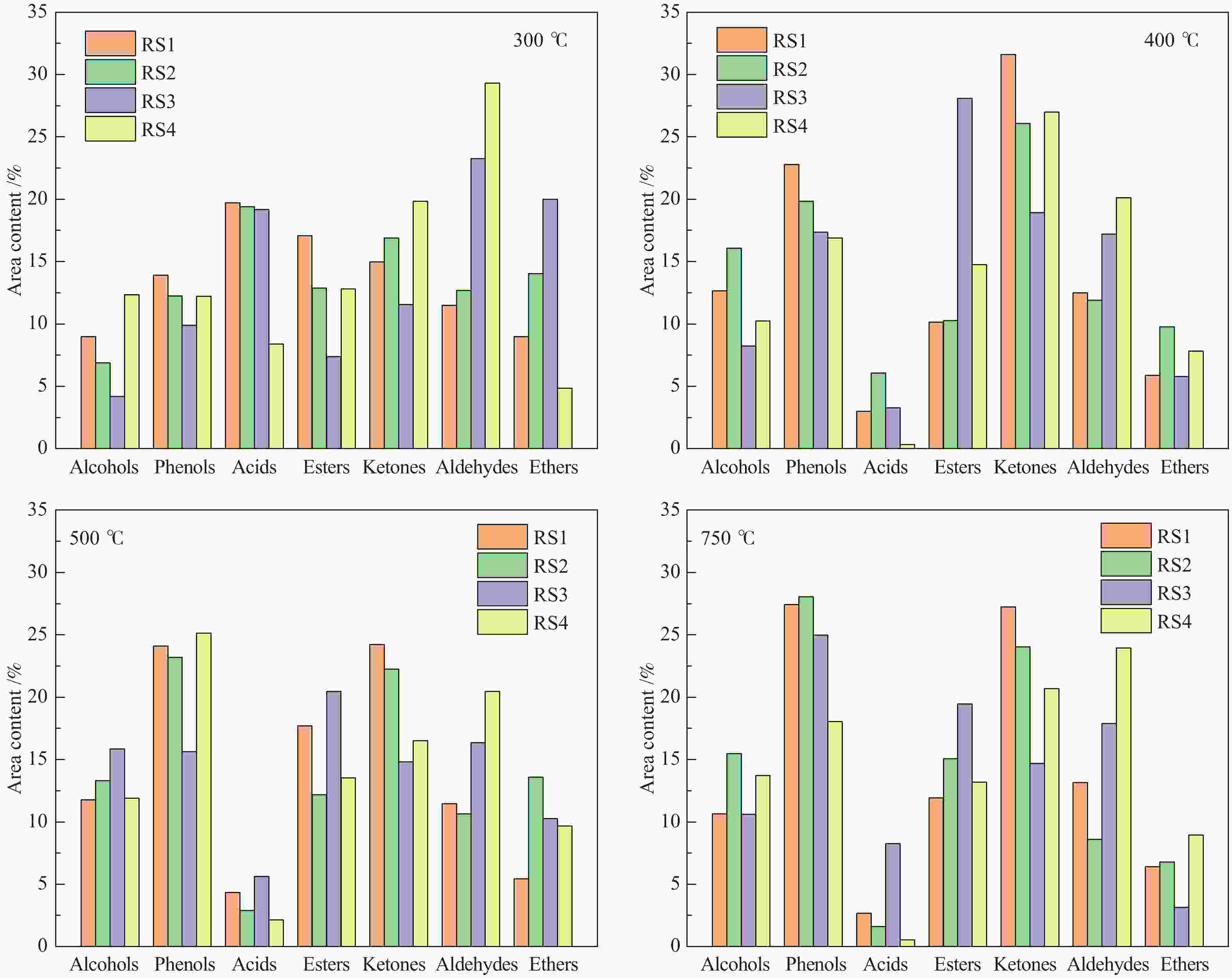
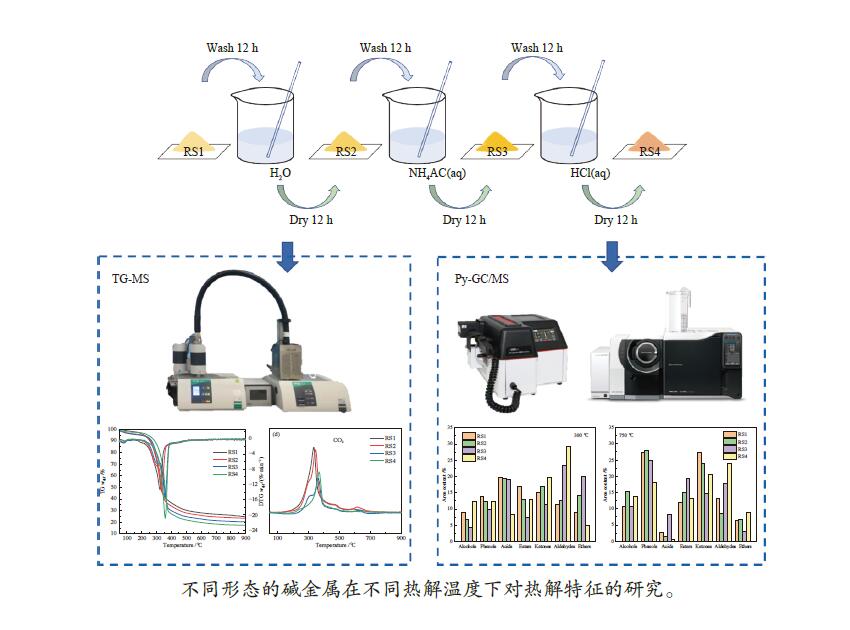
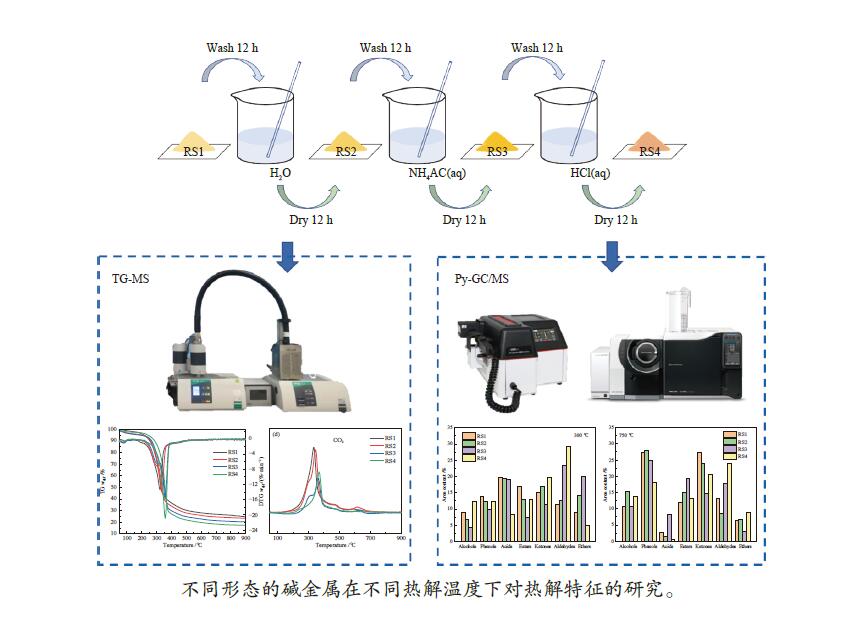
摘要: 碱金属是生物质热解过程的重要影响因素。本研究以含不同赋存形态碱金属的水稻秸秆(RS)为研究对象,采用热重-质谱联用仪(TG-MS)和热裂解-气质联用仪(Py-GC/MS)研究其热解特性、小分子气体的释放规律及原位热解焦油组成变化规律,以揭示不同赋存形态碱金属在热解过程中的作用机理。结果表明,随水稻秸秆碱金属脱除程度的提高,热解过程中小分子释放温度向高温区域偏移,碱金属对小分子逸出过程存在催化作用。而不同赋存形态的碱金属对焦油组分的影响不同。水溶性碱金属抑制了醇类物质的产生而促进酮类和醛类的生成。离子交换态碱金属在不同温度下对油品组成的影响不同,在300 ℃热解时抑制了醛类和醚类的产生,促进了酯类和酮类的生成,而热解温度高于400 ℃后则相反。动力学分析表明,水溶性碱金属离子和交换态碱金属均会降低生物质热解活化能。Abstract: Alkali metals are important factors affecting the process of biomass pyrolysis. In this paper, rice straw (RS) with different occurrence forms of alkali metals was used as the research object. The heat decomposition characteristics, the release law of small molecule gases and the change law of in-situ pyrolysis tar composition were investigated by the thermal mass spectrometer (TG-MS) and thermal pyrolysis-GC/MS (Py-GC/MS) to reveal the action mechanism of different occurrence forms of alkali metals in the pyrolysis process. The results showed that with the increase of the removal degree of alkali metal from rice straw, the release temperature of small molecules during the pyrolysis shifted to the high temperature region, due to the catalytic effect of alkali metals on the escape of small molecules. The different occurrence forms of alkali metals had different influences on the tar components. Water-soluble alkali metals inhibited the production of alcohols and promoted the production of ketones and aldehydes. Ion-exchanged alkali metals had different effects on oil composition at different temperatures. At the pyrolysis of 300 ℃, the presence of ion-exchanged alkali metals inhibited the production of aldehydes and ethers, and promoted the production of esters and ketones, but opposite effect was obtained at the temperature higher than 400 ℃. Kinetic analysis showed that both water-soluble alkali metal ions and exchanged alkali metal could reduce the activation energy of biomass pyrolysis.
-
Key words:
- straw /
- pyrolysis /
- alkali metal /
- occurrence form /
- tar
-
表 1 水稻秸秆的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate and ultimate analyses of RS
Sample Proximate analysis wad /% Ultimate analysis wdaf /% M A V FC C H O N S RS1 6.76 9.22 69.16 14.87 44.50 6.24 45.66 1.46 2.15 RS2 7.32 8.33 70.68 13.68 45.31 6.25 43.29 1.62 3.54 RS3 8.38 6.55 74.54 10.53 45.29 6.14 43.61 1.56 3.40 RS4 5.96 9.48 72.90 11.67 46.10 6.23 43.71 1.11 2.85 表 2 水稻秸秆的灰化学组成
Table 2 Ash compositions of rice straw
Compositions w/% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO Na2O K2O MgO others 52.42 0.55 0.47 3.42 0.67 24.56 3.27 14.64 表 3 样品的碱金属及碱土金属元素组成
Table 3 Element composition of main alkali and alkaline earth metals in samples
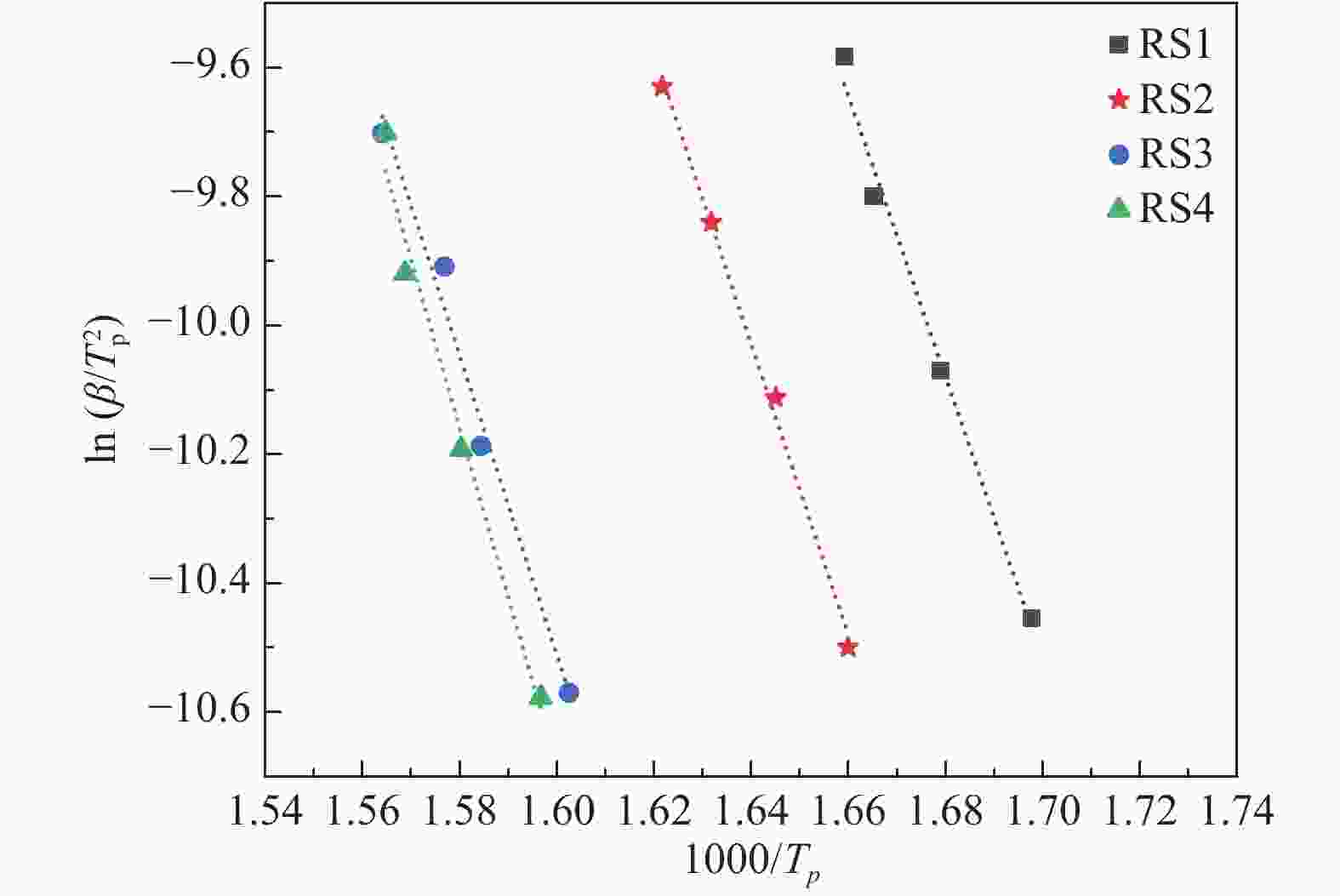
Sample Content wad /% K Na Ca Mg Fe RS1 2.10 0.65 0.37 0.18 0.05 RS2 0.61 0.03 0.40 0.08 0.04 RS3 0.02 0.01 0.34 0.02 0.03 RS4 < 0.01 < 0.01 < 0.01 0.01 0.02 表 4 水稻秸秆热解的活化能
Table 4 Activation energy of rice straw pyrolysis
Sample Linear equations Eα/(kJ·mol−1) R2 RS1 y = −21.84x + 26.62 181.57776 0.990 RS2 y = −22.57x + 26.99 187.64698 0.996 RS3 y = −23.22x + 26.64 193.05108 0.984 RS4 y = −26.15x + 31.16 217.41110 0.982 -
[1] TURSUN Y, XU S P, WANG G Y, WANG C, XIAO Y H. Tar formation during co-gasification of biomass and coal under different gasification condition[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2015,111:191−199. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2014.11.012 [2] MASNADI M S, GRACE J R, BI X T, LIM C J, ELLIS N, LI Y H, WATKINSON A P. From coal towards renewables: Catalytic/synergistic effects during steam co-gasification of switchgrass and coal in a pilot-scale bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Renewable Energy,2015,83:918−930. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2015.05.044 [3] 段会文, 张永奇, 王志青, 李位位, 黄戒介, 赵建涛, 房倚天. 钾和一氧化碳对松木屑快速热解半焦特性的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报,2017,45(7):789−797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.07.003DUAN Hui-wen, ZHANG Yong-qi, WANG Zhi-qing, LI Wei-wei, HUANG Jie-jie, ZHAO Jian-tao, FANG Yi-tian. Effects of potassium and CO atmosphere on properties of biomass chars from flash pyrolysis[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2017,45(7):789−797. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.07.003 [4] 易霜, 何选明, 郑辉, 林红涛, 李翠华, 李冲. 甘蔗渣与褐煤共热解半焦的特性[J]. 化工进展,2016,35(10):3149−3154.YI Shuang, HE Xuan-ming, ZHENG Hui, LIN Hong-tao, LI Cui-hua, LI Chong. Characteristics of co-pyrolysis char of sugarcane bagasse and lignite[J]. Chem Ind Eng Prog,2016,35(10):3149−3154. [5] 朱谢飞, 李凯, 马善为, 朱锡锋. 生物油蒸馏残渣理化性质及热失重研究[J]. 燃料化学学报,2017,45(1):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.01.005ZHU Xie-fei, LI Kai, MA Shan-wei, ZHU Xi-feng. Physicochemical characteristics and TGA of distillation residues from bio-oil[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2017,45(1):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2017.01.005 [6] HU Q, SHEN Y, CHEW J W, GE T, WANG C. Chemical looping gasification of biomass with Fe2O3/CaO as the oxygen carrier for hydrogen-enriched syngas production[J]. Chem Eng J,2020,379:122346. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122346 [7] WANG J L, YIN Y N. Fermentative hydrogen production using various biomass-based materials as feedstock[J]. Renewable Sustuinable Energy Rev,2018,92:284−306. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.033 [8] LIU G C, LIAO Y F, WU Y T, MA X Q. Reactivity of Co-doped Ca2Fe2O5 brownmillerite oxides as oxygen carriers for microalgae chemical looping gasification[J]. Int J Hydrog Energy,2019,44(5):2546−2559. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.232 [9] SONG Y C, LI Q T, LI F Z, WANG L S, HU C C, FENG J, LI W Y. Pathway of biomass-potassium migration in co-gasification of coal and biomass[J]. Fuel,2019,239:365−372. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.11.023 [10] QUYN D M, WU H W, LI C Z. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part I. Volatilisation of Na and Cl from a set of NaCl-loaded samples[J]. Fuel,2002,81(2):143−149. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(01)00127-2 [11] QUYN D M, WU H W, HAYASHI J I, LI C Z. Volatilisation and catalytic effects of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis and gasification of Victorian brown coal. Part Ⅳ. Catalytic effects of NaCl and ion-exchangeable Na in coal on char reactivity[J]. Fuel,2003,82:587−593. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00323-X [12] WU Z Q, YANG W C, CHEN L, MENG H, ZHAO J, WANG S Z. Catalytic effects of the typical alkali metal on gaseous products distribution and char structure during co-pyrolysis of low rank coal and lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,105:102−107. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.286 [13] OKUNO T, SONOYAMA N, HAYASHI J I, LI C Z, SATHE C, CHIBA T. Primary release of alkali and alkaline earth metallic species during the pyrolysis of pulverized biomass[J]. Energy Fuels,2005,19(5):2164−2171. [14] LI X M, ZHANG H, LIU M J, ZHI L F, BAI J, BAI Z Q, LI W. Investigation of coal-biomass interaction during co-pyrolysis by char separation and its effect on coal char structure and gasification reactivity with CO2[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2020,48(8):897−907. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5813(20)30062-1 [15] DI N G, DE J W, SPLIETHOFF H. TG-FTIR characterization of coal and biomass single fuels and blends under slow heating rate conditions: Partitioning of the fuel-bound nitrogen[J]. Fuel Progress Technol,2010,91(1):103−115. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.09.001 [16] ZAMORA F, GONZALEZ M C, DUENAS M T, IRASTORZA A, VELASCO S, IBARBURU I. Thermodegradation and thermal transitions of an exopolysaccharide produced by Pediococcusdamnosus 2.6[J]. J Macromol Sci B,2002,3(41):473−486. [17] 王树荣, 骆仲泱. 生物质组分热裂解[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.WANG Shu-rong, LUO Zhong-yang. Pyrloysis of Biomass Components[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. [18] VAN H K H, HODEK W. Structure and pyrolysis behaviour of different coals and relevant model substances[J]. Fuel,1994,73(6):886−896. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(94)90283-6 [19] ZHU J L, JIN L J, LI J G, BAO Z X, LI Y, HU H Q. Fast pyrolysis behaviors of cedar in an infrared-heated fixed-bed reactor[J]. Bioresource Technol,2019,290:121739. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121739 [20] WANG J F, MA M, BAI Y H, SU W G, SONG X D, YU G S. Effect of CaO additive on co-pyrolysis behavior of bituminous coal and cow dung[J]. Fuel,2020,265:116911. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116911 [21] XIONG Y K, JIN L J, LI Y, ZHU J L, HU H Q. Hydrogen peroxide oxidation degradation of a low-rank Naomaohu coal[J]. Fuel Process Technol,2020,207:106484. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106484 [22] MISHRA R K, LU Q, MOHANTY K. Thermal behaviour, kinetics and fast pyrolysis of Cynodondactylon grass using Py-GC/MS and Py-FTIR analyser[J]. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis,2020,150:104887. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104887 [23] WU Z Q, YANG W C, LI Y W, ZHANG B, YANG B L. On-line analysis on the interaction between organic compounds from co-pyrolysis of microalgae and low-rank coal: Thermal behavior and kinetic characteristics[J]. Bioresource Technol,2018,268:672−676. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.074 -




 下载:
下载: