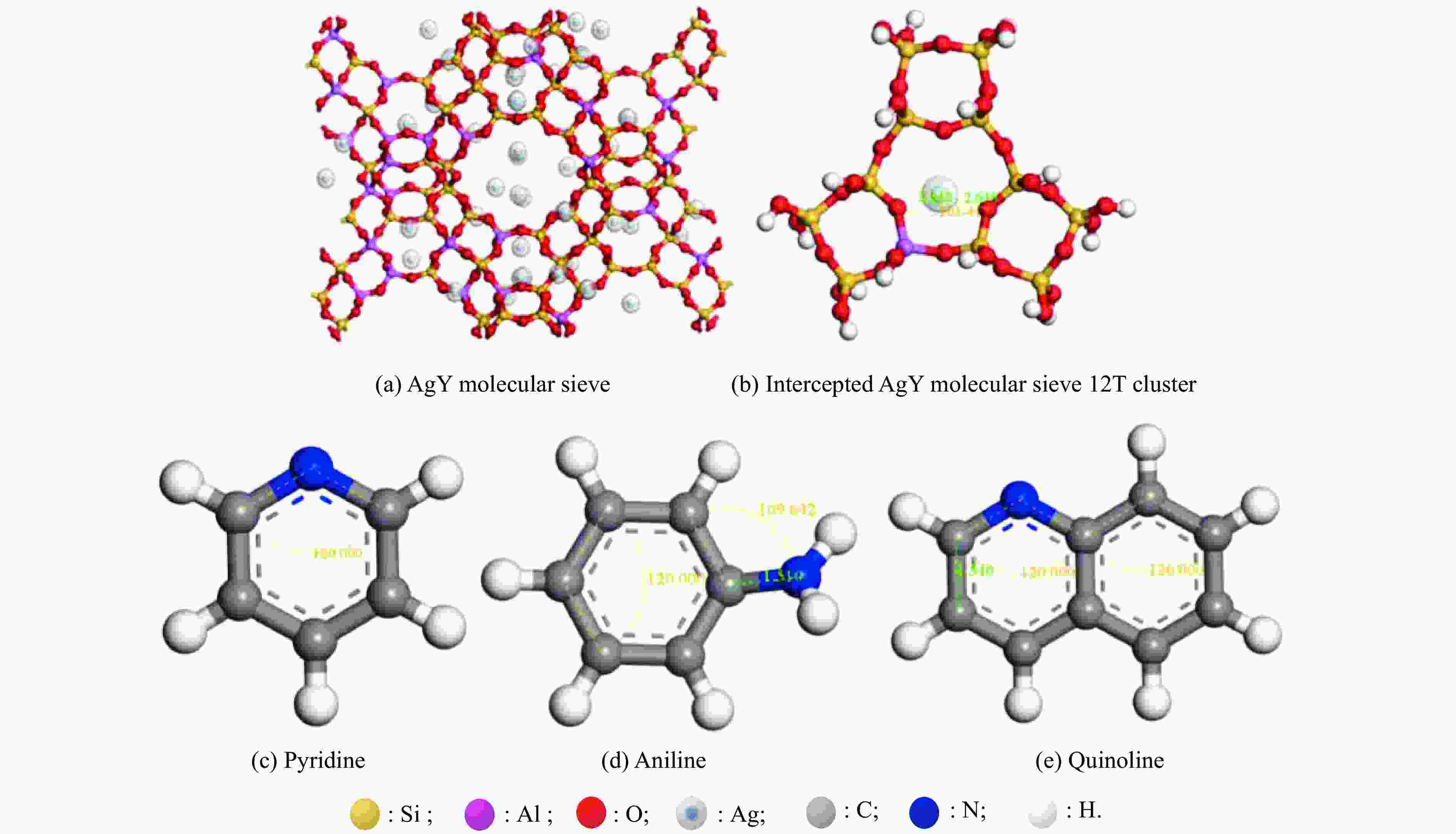
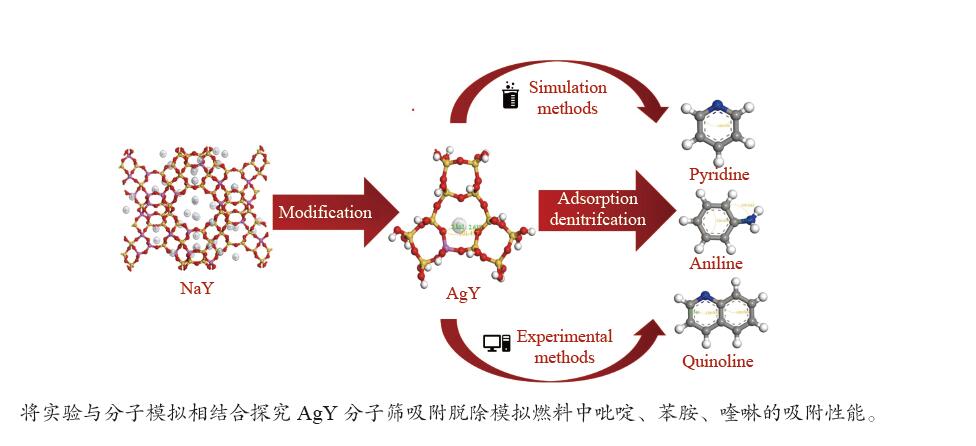
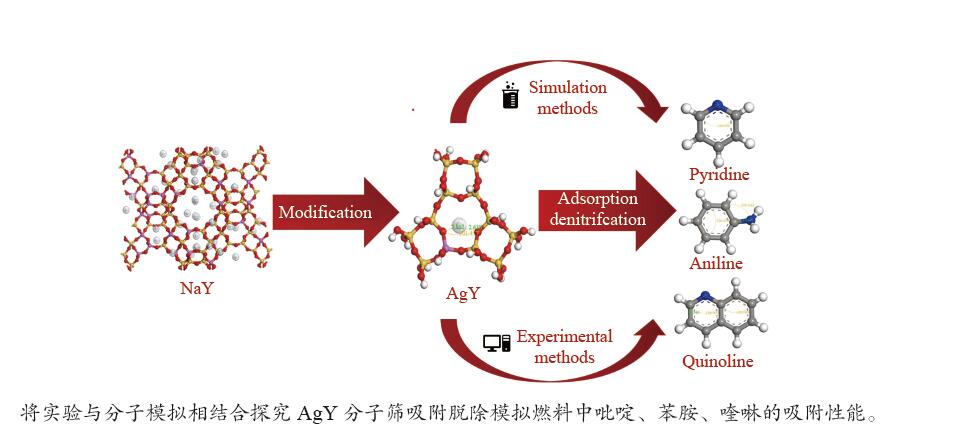
Preparation of Ag+ modified NaY molecular sieve and its adsorption and denitrogenation properties
-
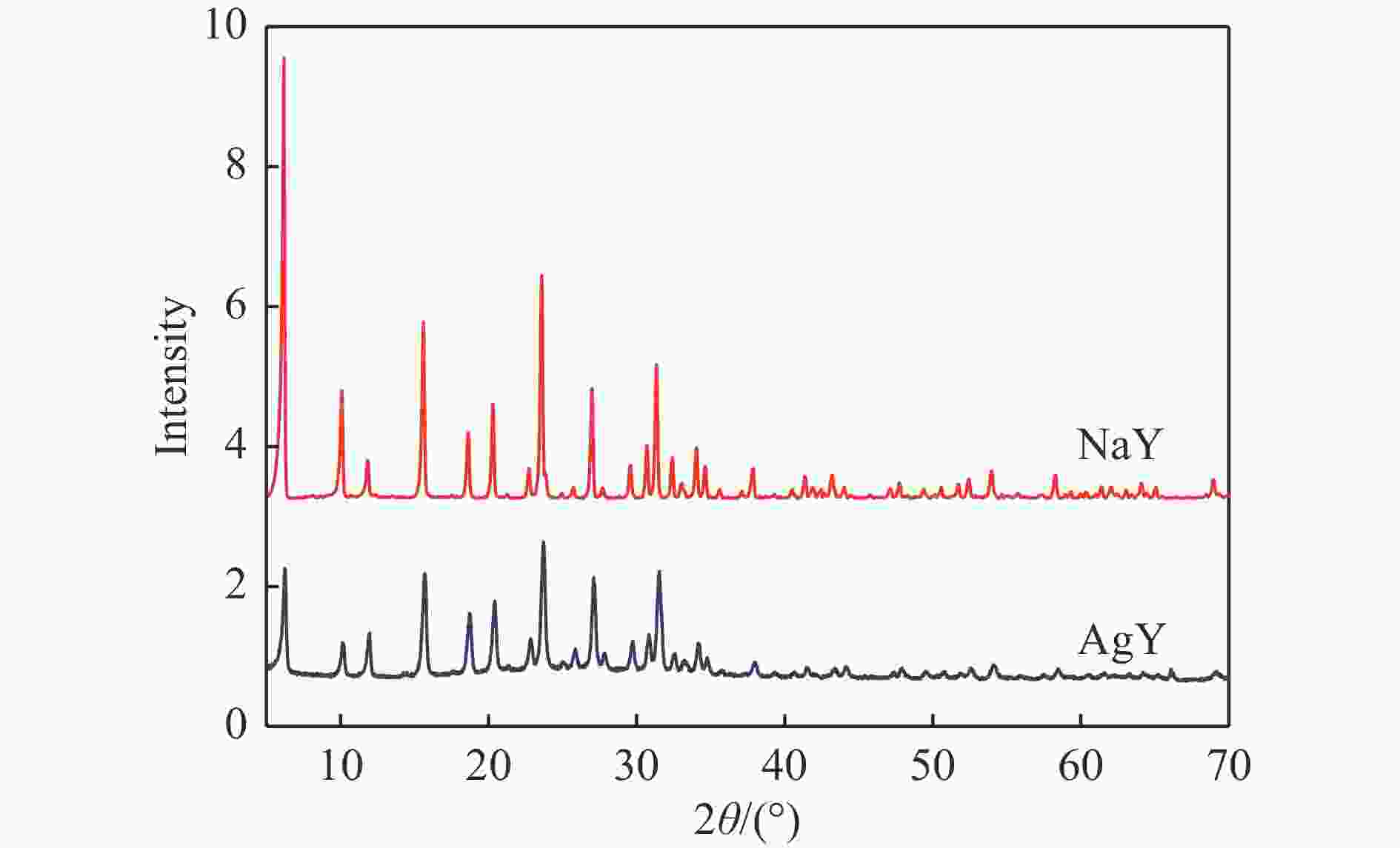
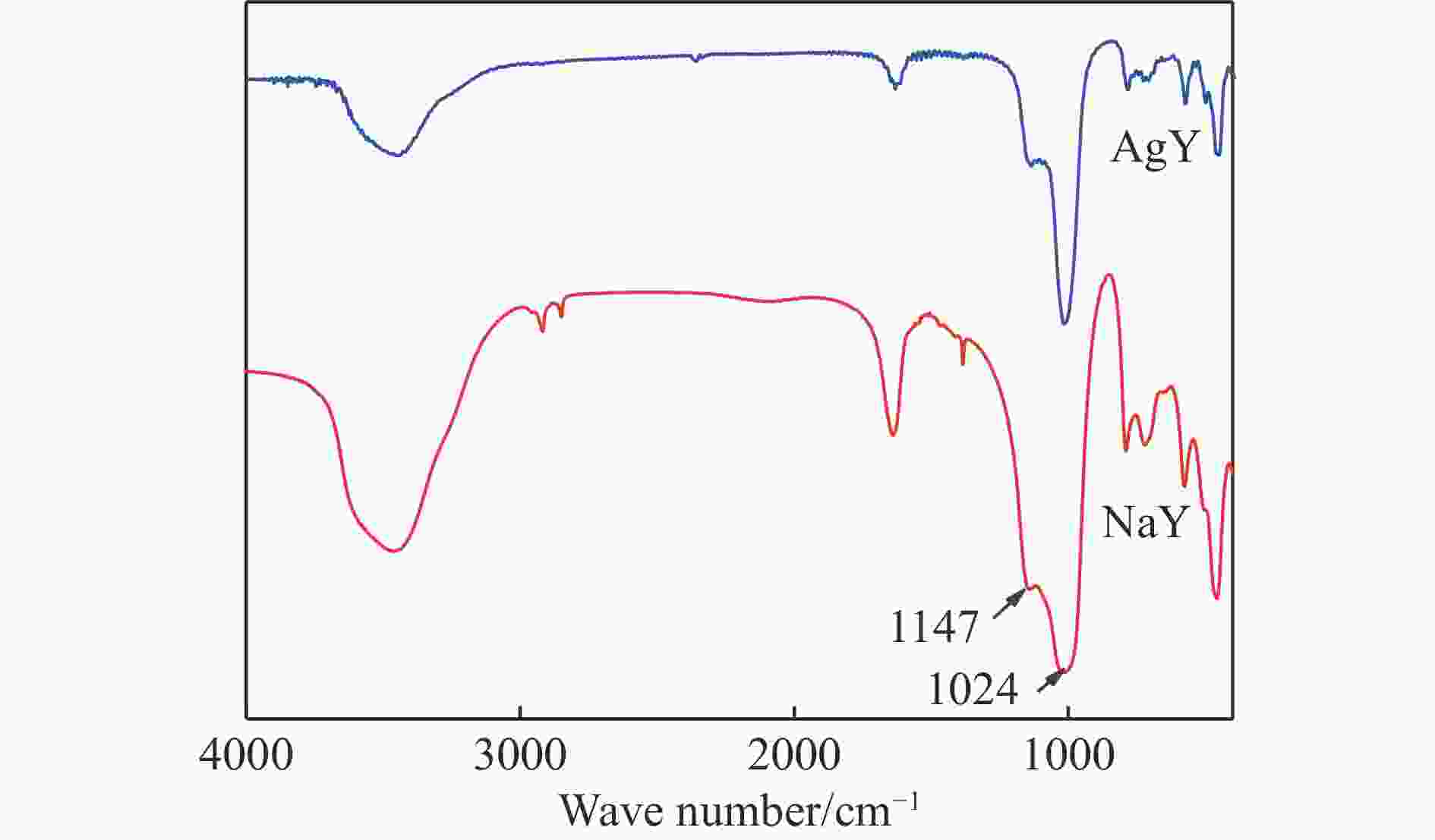
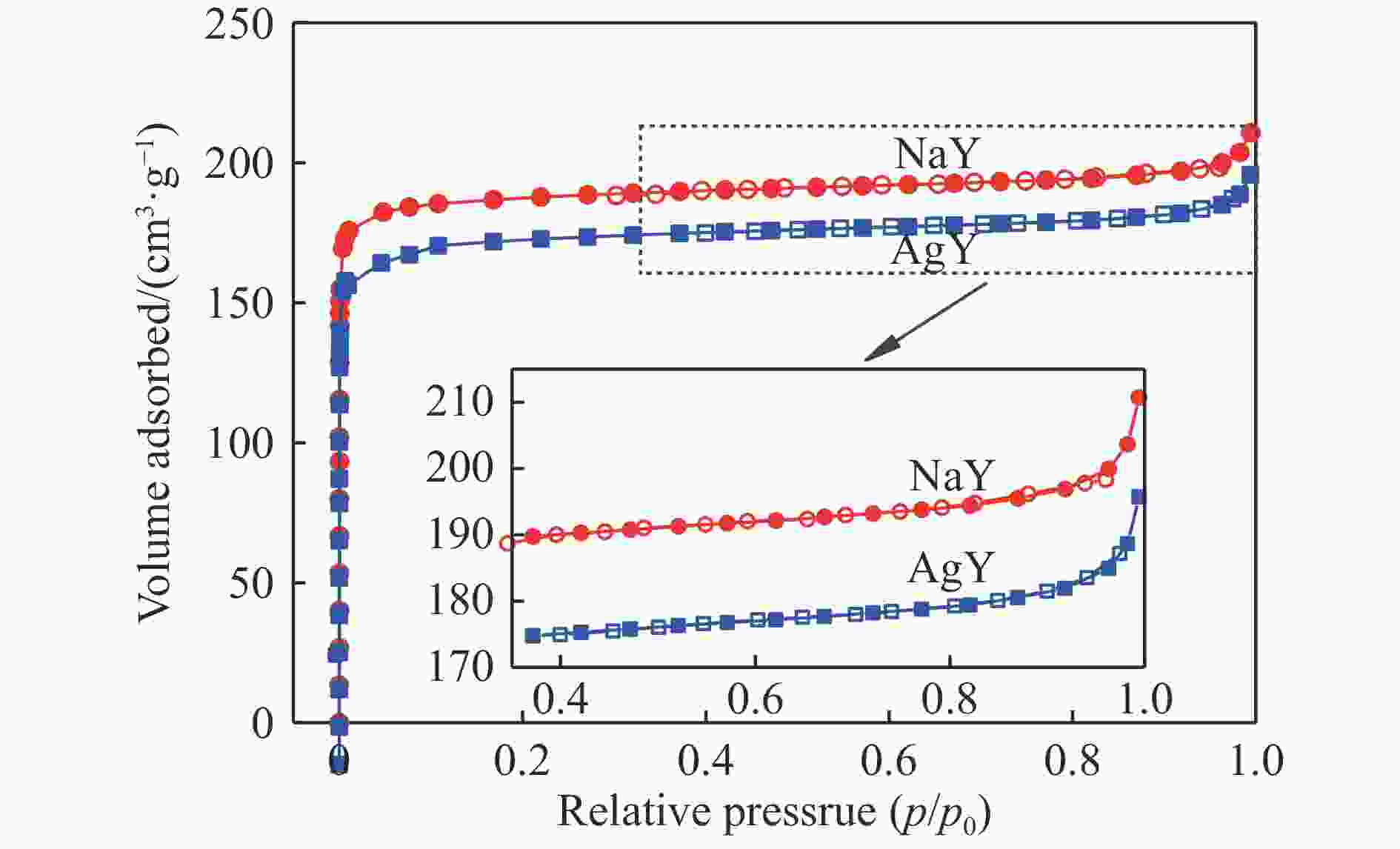
摘要: 采用Ag+改性NaY分子筛成功制备了AgY分子筛,利用XRD射线衍射、FT-IR、N2吸附-脱附对NaY和AgY分子筛进行了表征,并用于吸附脱除模拟燃料中吡啶、苯胺、喹啉碱性氮化物,AgY分子筛的吸附能力明显优于NaY分子筛。考察了吸附温度、吸附时间对AgY分子筛吸附三种氮化物的影响,实验结果表明,吸附能力均为:苯胺>喹啉>吡啶,为了进一步研究其吸附机理,采用Materials Studio软件建立了AgY分子筛12T团簇模型并在303、323、343 K下模拟三种氮化物分子在AgY分子筛上的吸附,计算了吸附能、活性中心与吡啶、苯胺、喹啉分子的距离、前线轨道、等密度分布、径向分布函数等相关参数,计算结果也表明,AgY分子筛对苯胺的吸附优于喹啉,优于吡啶,与实验结果一致,且吸附以化学吸附为主,AgY分子筛S位和W位为主要吸附位。吸附等温线研究结果表明,AgY分子筛对吡啶的吸附符合Langmuir-Freundlich混合吸附模型,对苯胺、喹啉的吸附符合Freundlich吸附模型。吸附动力学和吸附热力学结果表明,AgY分子筛对吡啶的吸附符合准二级动力学模型,对苯胺、喹啉的吸附符合准一级动力学模型,吸附是自发的熵增过程。
-
关键词:
- AgY分子筛 /
- 吸附脱氮 /
- Materials Studio /
- 分子动力学模拟
Abstract: An AgY molecular sieve modified by Ag+ ion was characterized by XRD, FT-IR and N2 adsorption and desorption and used to the adsorption denitrogenation from model fuels containing pyridine, aniline and quinoline basic nitrides. The adsorption capacity for N with the AgY molecular sieve was obviously better than that with the NaY molecular sieve. The effects of adsorption temperature and adsorption time on the adsorption capacity of three kinds of nitrides by AgY molecular sieve were investigated. The experimental results show that the adsorption capacity for N is aniline>quinoline>pyridine. To study the adsorption mechanism of AgY, the 12T cluster model of AgY molecular sieve was established by Materials Studio software and the adsorption of three kinds of nitride molecules on the AgY molecular sieve was simulated at 303 K, 323 K and 343 K. The adsorption energy, the distance between the active center and pyridine, aniline and quinoline molecules, the frontier orbit, the isodensity distribution, the radial distribution function and other relevant parameters were calculated. The calculated results show that the adsorption of aniline by AgY molecular sieve is better than that of quinoline and pyridine, which is consistent with the experimental results. Moreover, the adsorption is mainly the chemical adsorption, and the S and W sites of AgY molecular sieve are the main adsorption sites. The results of isothermal adsorption show that the adsorption of pyridine on the AgY follows the Langmuir-Freundlich mixed adsorption model, and the adsorption of aniline and quinoline follows the Freundlich adsorption model. The results of adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics show that the adsorption of pyridine on the AgY molecular sieve conforms to the quasi-second-order kinetic model, while the adsorption of aniline and quinoline conforms to the quasi-first-order kinetic model, and all adsorption processes are spontaneous entropy increasing process. -
表 1 NaY和AgY吸附脱除模拟燃料中吡啶的脱氮性能
Table 1 Denitrification performance of NaY and AgY molecular sieves for adsorption and removal of pyridine from model fuels
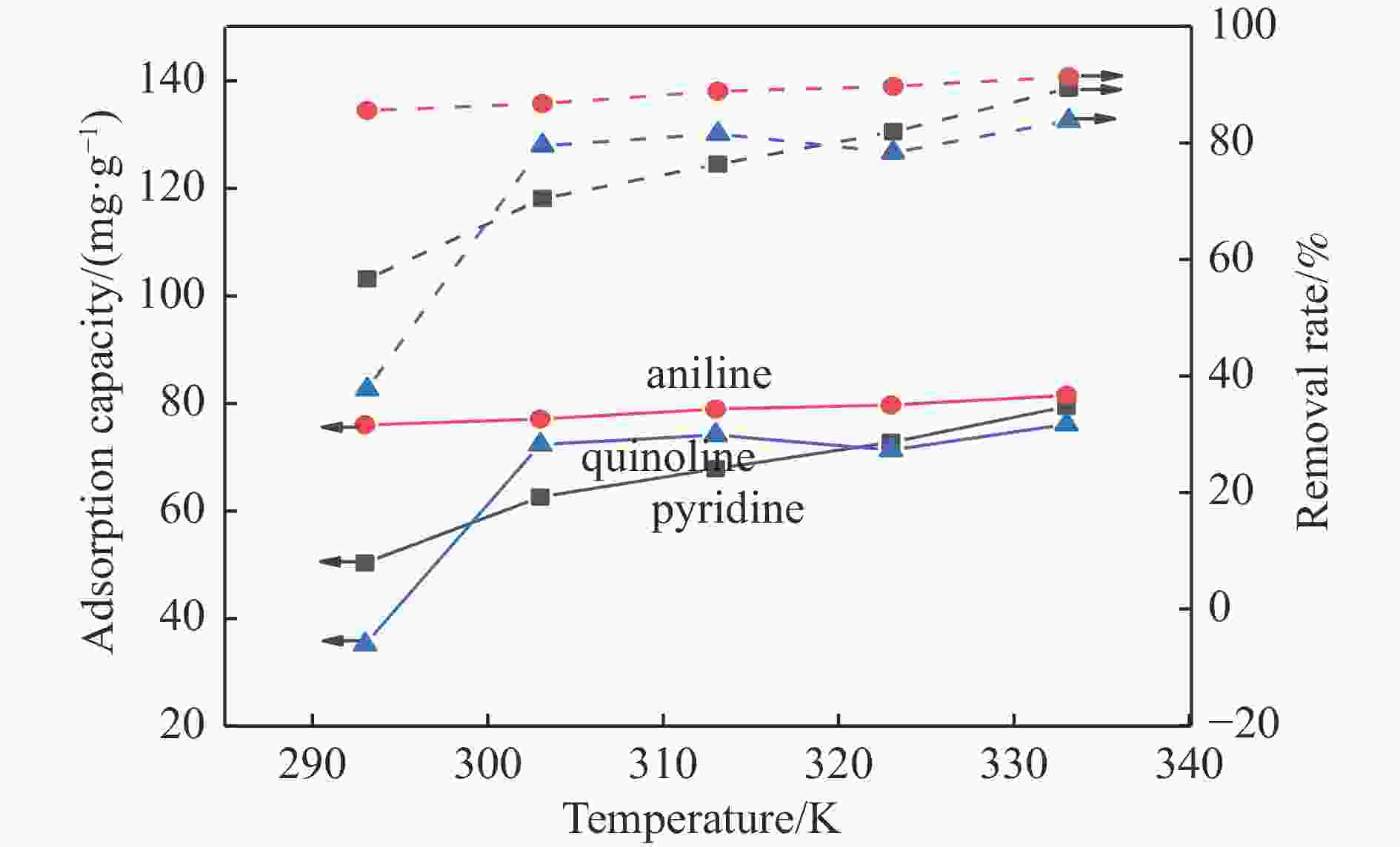
Project NaY AgY Adsorption capacity/(mg·g−1) 51.26 62.60 Removal rate/% 57.69 70.46 表 2 AgY分子筛团簇吸附吡啶、苯胺、喹啉的吸附能
Table 2 Adsorption energy of AgY molecular sieve clusters for aniline, pyridine and quinoline
Project Adsorption complex
energy/eVAdsorbent energy/eV Adsorbed molecule
energy/eVAdsorption energy/eV AgY adsorbed pyridine −172864.913 −166114.168 −6749.488 1.257 AgY adsorbed aniline −310406.903 −302585.559 −7818.546 2.798 AgY adsorbed quinoline −177043.348 −166113.821 −10927.236 2.291 表 3 吡啶、苯胺、喹啉与AgY分子筛活性中心的距离d(Ag-N)和前线轨道能量值
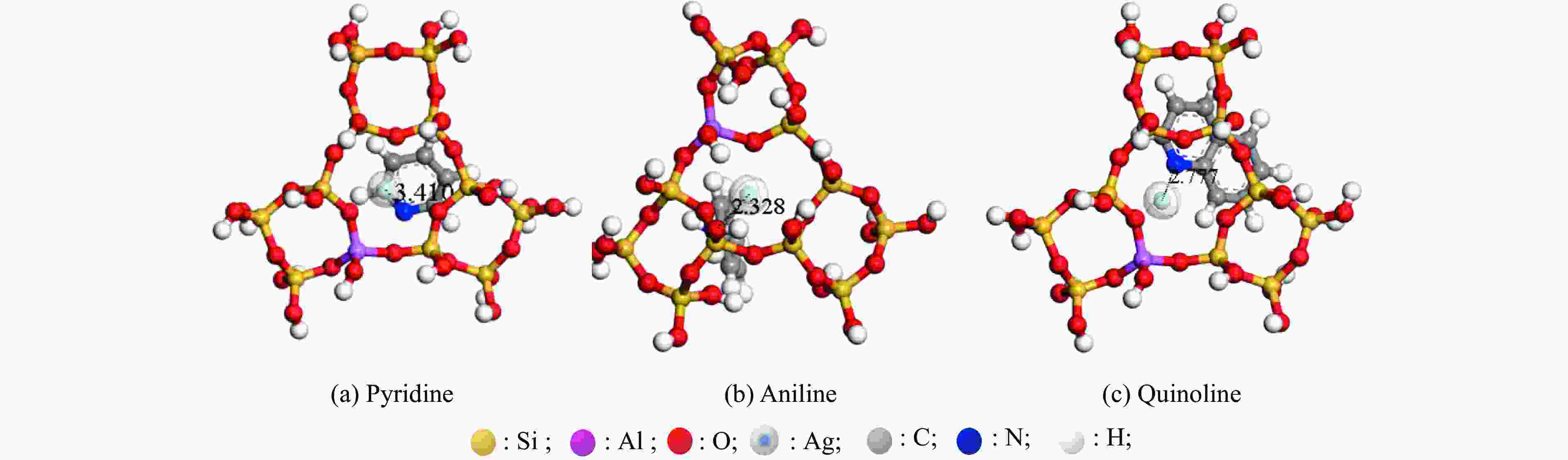
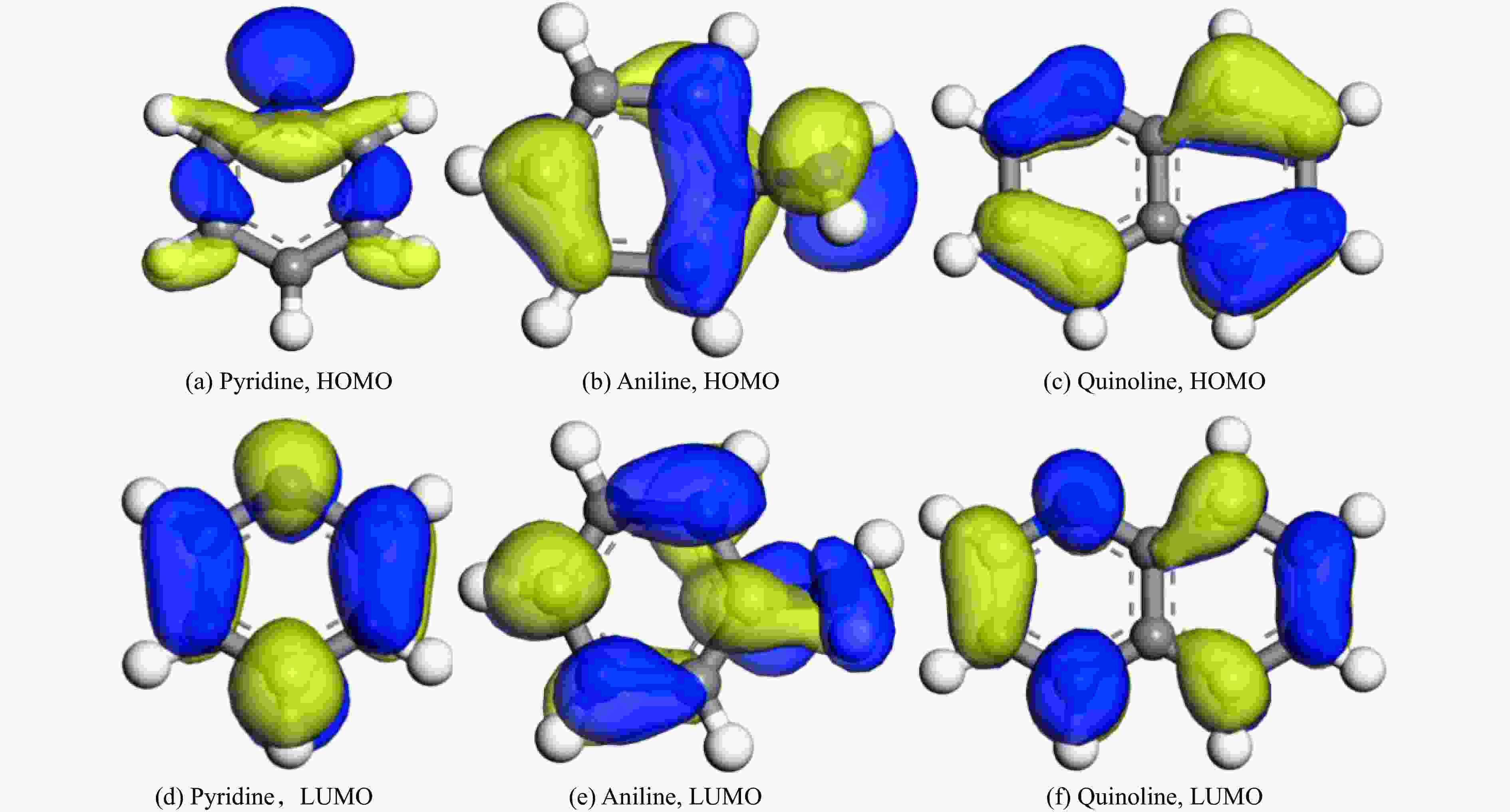
Table 3 Distance d(Ag-N) and frontline orbital energy values of aniline, pyridine, quinoline and AgY molecular sieve active centers
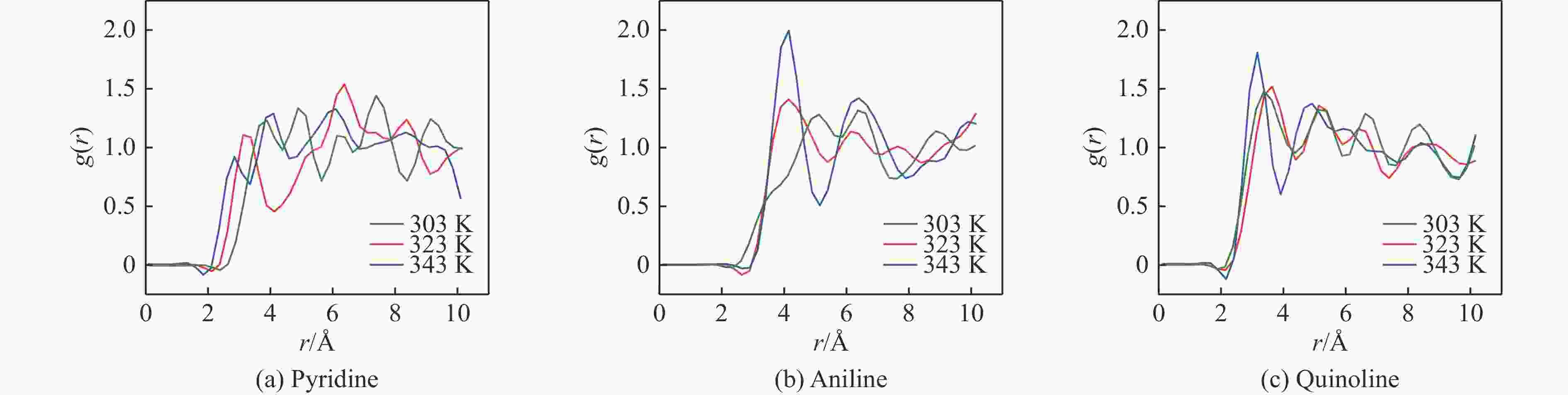
Project HOMO/eV LUMO/eV △E/eV d(Ag-N)/nm AgY adsorbed pyridine −5.960 −2.575 3.385 3.410 AgY adsorbed aniline −4.569 −1.710 2.859 2.328 AgY adsorbed quinoline −7.198 −3.135 4.063 2.777 表 4 三种吸附模型拟合AgY分子筛吸附模吡啶、苯胺、喹啉的相关参数值
Table 4 Model parameter values of the adsorption for pyridine, aniline, and quinoline on the AgY molecular sieve with three adsorption models
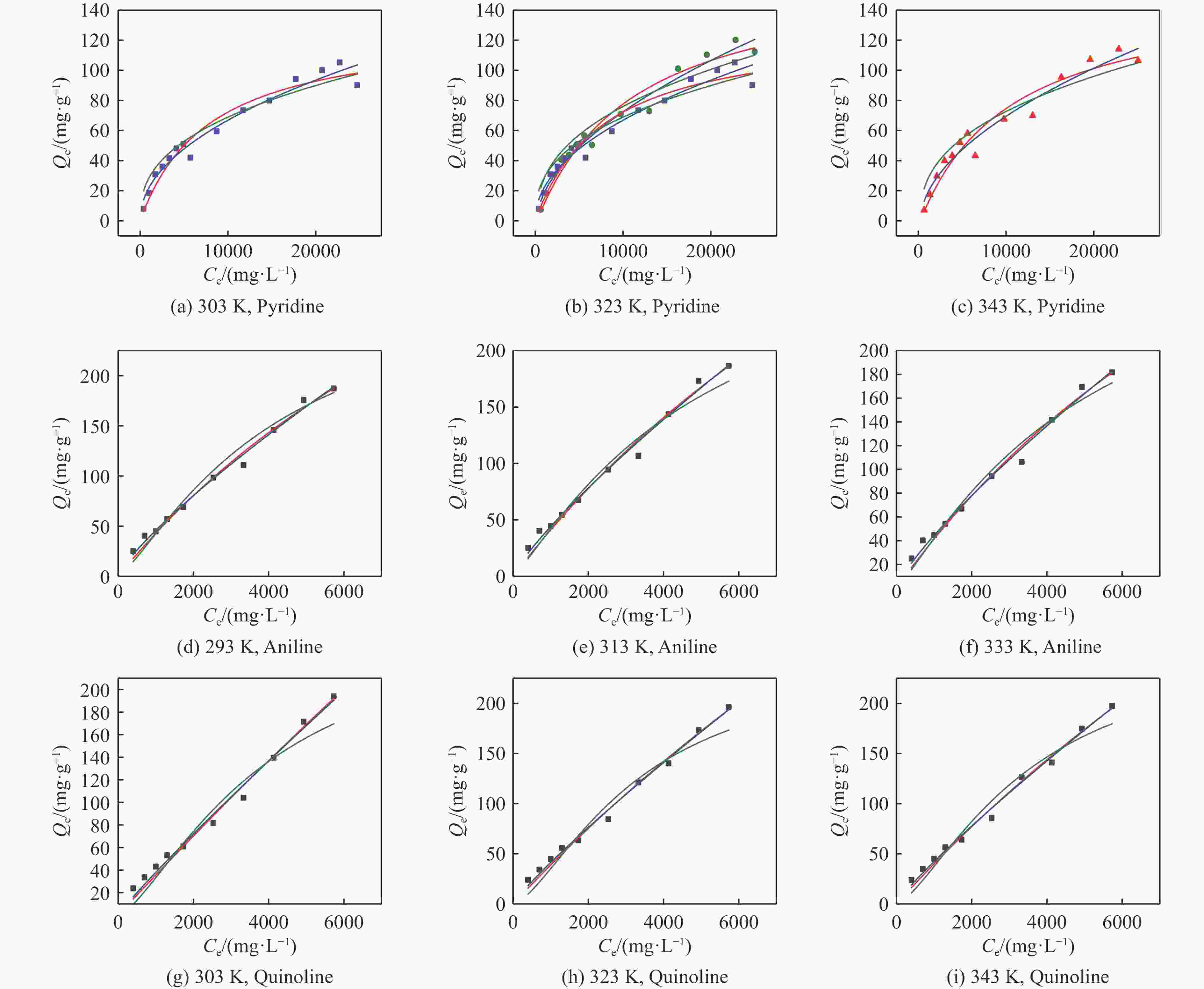
Temperature Langmuir Freundlich Langmuir-Freundlich qm KL × 105 R2 n KF R2 qm Ka × 105 n R2 Pyridine 303 K 142.9 10.788 0.926 0.508 0.639 0.934 291.6 1.769 0.658 0.986 323 K 185.6 8.302 0.925 0.572 0.607 0.935 600.4 0.576 0.652 0.980 343 K 171.2 8.955 0.915 0.559 0.253 0.926 592.3 0.497 0.634 0.982 Aniline 293 K 650.5 7.055 0.985 0.811 0.168 0.991 305 24 1.276 0.972 313 K 733.7 5.929 0.983 0.828 0.144 0.989 320 20 1.172 0.970 333 K 637.5 6.937 0.983 0.811 0.144 0.990 320 20 1.176 0.974 Quinoline 303 K 2770 1.302 0.986 0.923 0.065 0.987 265 26 1.441 0.947 323 K 1223 3.280 0.989 0.885 0.092 0.992 250 30 1.502 0.956 343 K 1092 3.790 0.989 0.877 0.099 0.992 269 28.3 1.445 0.965 表 5 热力学模型拟合的相关参数
Table 5 Relevant parameters for thermodynamic model fitting
Project ΔG/(kJ·mol−1) ∆S/(kJ·mol−1·K−1) ∆H/(kJ·mol−1) Pyridine 303 K −28.76 0.18 28.39 323 K −33.40 343 K −36.04 Aniline 303 K −8.437 0.055 8.228 323 K −9.537 343 K −10.637 Quinoline 293 K −3.273 0.020 2.587 313 K −3.673 333 K −4.073 Note: ΔG is Gibbs free energy; ΔH is enthalpy change; ΔS is entropy change. 表 6 准一级和准二级动力学模型拟合相关参数
Table 6 Parameters fitted with quasi-first-order and quasi-second-order kinetic models
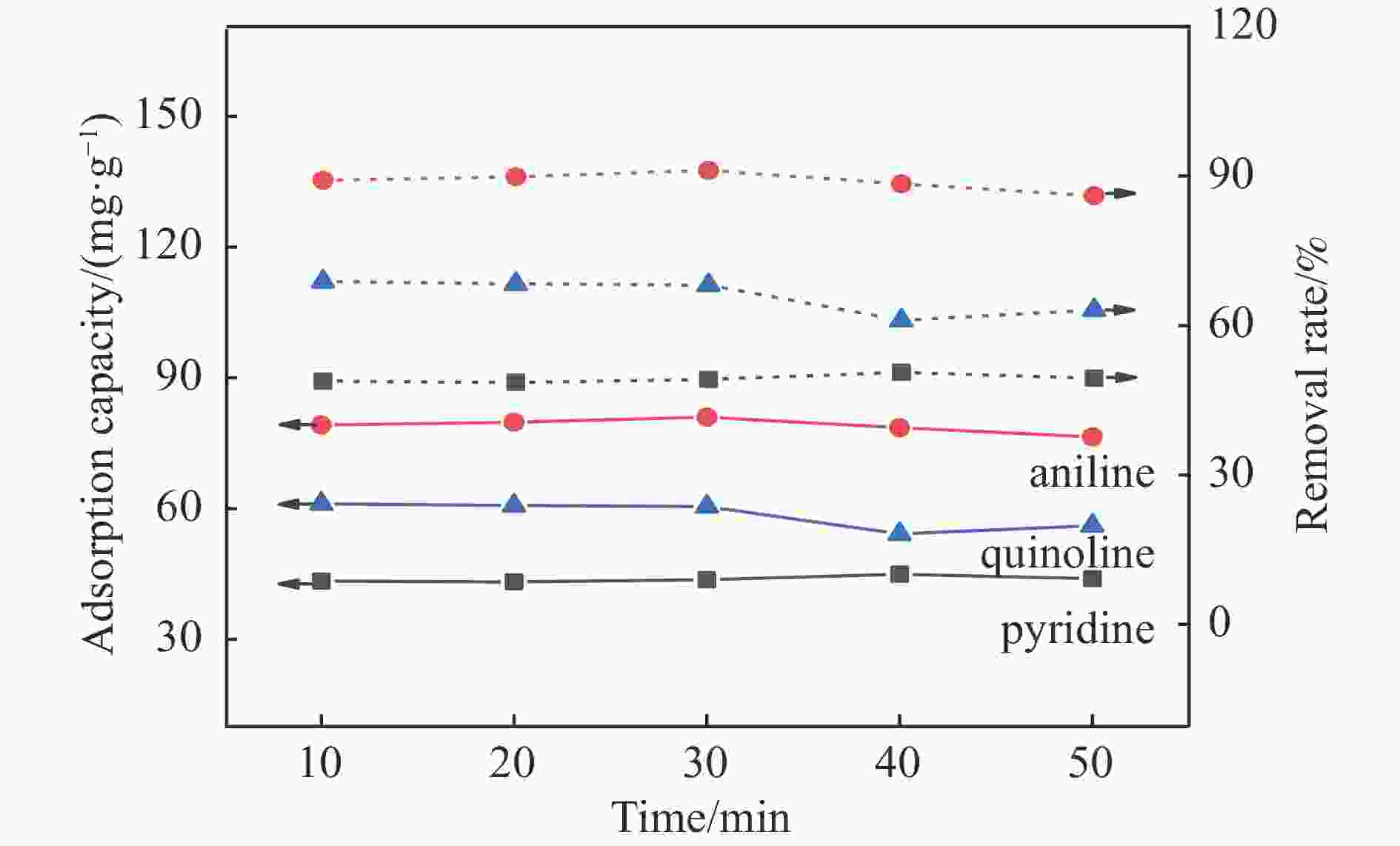
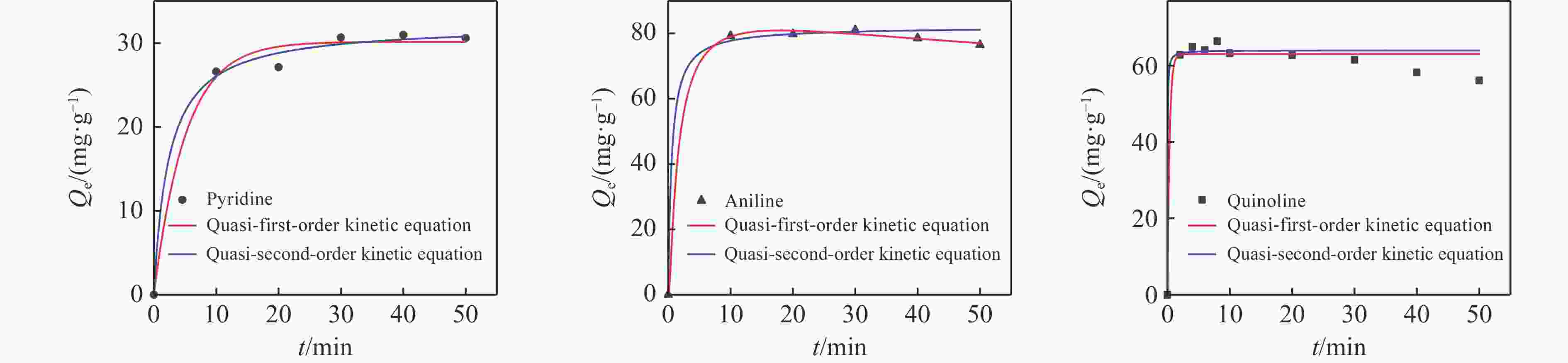
Project Quasi-first-order kinetic equation Quasi-second-order kinetic equation Qe K1 R2 Qe K2 R2 Pyridine 30.162 0.197 0.986 32.252 0.013 0.993 Aniline 79.003 0.473 0.997 82.137 0.022 0.994 Quinoline 63.012 2.936 0.975 64.234 0.627 0.969 -
[1] 梁文杰, 阙国和, 刘晨光, 等. 石油化学(第二版)[M]. 东营: 中国石油大学出版社, 2011: 45-50.LIANG Wenjie, QUE Guohe, LIU Chenguang, et al. Petrochemistry(2nd Edition)[M]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum Press, 2011: 45−50. [2] 郭凤洁, 帅秋艳, 史晨曦. NaY型分子筛的制备及其对微量铁离子的吸附性能研究[J]. 中国高新科技,2019,(20):29−31. doi: 10.13535/j.cnki.10-1507/n.2019.20.06GUO Fengjie, SHUAI Qiuyan, SHI Chenxi. Preparation of NaY-type molecular sieve and its adsorption performance on trace iron ions[J]. China High Sci Technol,2019,(20):29−31. doi: 10.13535/j.cnki.10-1507/n.2019.20.06 [3] 黄坚, 李先锋, 谢军, 等. 离子交换法改性的NaY分子筛对吸附含硫VOCs的性能提升[J]. 环境工程学报,2022,16(10):3335−3345. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202204053HUANG Jian, LI Xianxian, XIE Jun, et al. Performance improvement of NaY molecular sieve modified by ion exchange method for adsorption of sulfur-containing VOCs[J]. Chin J Environ Eng,2022,16(10):3335−3345. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202204053 [4] SEYFORTH J. A literature review of the computational methods used to investigate molecular machines[R]. 2016. [5] DAUBER-OSGUTHORPE P, ROBERTS V A, OSGUTHORPE D J, et al. Structure and energetics of ligand binding to proteins: Escherichia coli di hydrofolate reductase-trimethoprim, a drug-receptor system[J]. Proteins: Struc, Funct, Bioinform,1988,4(1):31−47. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040106 [6] 富添, 洪新, 矫宝庆, 等. 杂原子介孔分子筛Ba-MCM-41的制备及其吸附脱氮性能[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2022,53(5):28−35.FU Tian, HONG Xin, JIAO Baoqing, et al. Preparation of heteroatom mesoporous zeolite Ba-MCM-41 and its adsorption and nitrogen removal performance[J]. Pet Process Petrochem,2022,53(5):28−35. [7] 中国石油化工股份有限公司科技开发部. 石油产品行业标准汇编[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2005: 402−405.Science and Technology Development Department, China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation. Compilation of petroleum products industry standards[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2005: 402−405. [8] 黄乐, 郑健, 李强, 等. 正己烷在不同硅铝比HZSM-5分子筛上吸附的分子模拟研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2022,53(2):84−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2022.02.014HUANG Le, ZHENG Jian, LI Qiang, et al. Molecular simulation study on adsorption of n-hexane on HZSM-5 zeolite with different silicon-aluminum ratios[J]. Pet Process Petrochem,2022,53(2):84−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2399.2022.02.014 [9] 解国应, 宫玉洁, 周东旭, 等. 改性Y型分子筛吸附脱除模拟油品中氯辛烷[J]. 石油学报(石油加工),2021,37(3):619−625.XIE Guoying, GONG Yujie, ZHOU Dongxu, et al. Adsorption and removal of chlorooctane from simulated oil by modified Y-type molecular sieve[J]. Acta Pet Sin (Pet Process),2021,37(3):619−625. [10] 何杰, 王宾, 司圣元, 等. AgY分子筛与甲烷中有机硫化物相互作用研究[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版),2012,32(4):1−5.HE Jie, WANG Bin, SI Shengyuan, et al. Interaction between AgY molecular sieve and organic sulfides in methane[J]. J Anhui Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci Ed),2012,32(4):1−5. [11] 洪新, 唐克. Cr3+改性NaY分子筛的吸附脱氮性能[J]. 燃料化学学报,2016,44(2):251−256.HONG Xin, TANG Ke. Adsorption and denitrification performance of Cr3+ modified NaY molecular sieve[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2016,44(2):251−256. [12] 洪新, 唐克. NaY分子筛的改性及吸附脱氮性能[J]. 燃料化学学报,2015,43(2):214−220.HONG Xin, TUN Ke. Modification and adsorption and denitrification performance of NaY molecular sieve[J]. J Fuel Chem Technol,2015,43(2):214−220. [13] 徐如人, 庞文琴, 于吉红. 分子筛与多孔材料化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.XU Ruren, PANG Wenqin, YU Jihong. Molecular Sieves and Porous Material Chemistry[M] Beijing: Science Press, 2004. [14] 刘飞. NaY、MCM-41分子筛改性及其吸附脱除燃油中有机硫化物的性能[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2017.LIU Fei. Modification of NaY, MCM-41 molecular sieve and their adsorption and removal of organic sulfides from fuel oil[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2017. [15] 王福帅, 李会鹏, 赵华, 等. NaY/β复合分子筛改性及对模拟柴油中氮化物的吸附性能[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2012,43(11):59−62.WANG Fushai, LI Huipeng, ZHAO Hua, etc. NaY/β Modification of composite molecular sieves and their adsorption performance for nitrogen compounds in simulated diesel fuel[J]. Pet Ref Chem Ind,2012,43(11):59−62. [16] 洪新, 李云赫, 赵永华, 等. Cr3+、Ni2+双离子改性NaY分子筛的吸附脱氮性能[J]. 石油炼制与化工,2018,49(2):18−22.HONG Xin, LI Yunhe, ZHAO Yonghua, et al. The adsorption and denitrification performance of Cr3+, Ni2+ double ion modified NaY molecular sieve[J]. Pet Ref Chem Ind,2018,49(2):18−22. [17] 石鑫, 姜云瑛, 王洪博, 等. 4种吡嗪类缓蚀剂及其在Cu(111)面吸附行为的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报,2017,68(8):3211−3217.SHI Xin, JIANG Yunying, WANG Hongbo, et al. Density functional theory study on adsorption behavior of four pyrazine corrosion inhibitors and their adsorption behavior on Cu(111) surface[J]. CIESC J,2017,68(8):3211−3217. [18] 福井谦一. 化学反应与电子轨道[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985, 24−25.Kenichi Fukui. Chemical Reaction and Electron Orbital[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985, 24−25. [19] 张国. 有机分子在分子筛中的吸附和扩散过程的计算机模拟[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008.ZHANG Guo. Computer simulation of adsorption and diffusion process of organic molecules in molecular sieve[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2008. [20] JIRAPONGPHAN S S, WARZYWODA J, BUDIL D E, et al. Simulation of benzene adsorption in zeolite HY using supercage-based docking[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2006,94(1/3):358−363. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.04.011 [21] ZHENG H, ZHAO L, YANG Q, et al. Influence of framework protons on the adsorption sites of the benzene/HY system[J]. Ind Eng Chem Res,2014,53(35):13610−13617. [22] DANG S, ZHAO L, YANG Q, et al. Competitive adsorption mechanism of thiophene with benzene in FAU zeolite: The role of displacement[J]. Chem Eng J,2017,328:172−185. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.011 [23] GHOUFI A, GABEROVA L, ROUQUEROL J, et al. Adsorption of CO2, CH4 and their binary mixture in Faujasite NaY: A combination of molecular simulations with gravimetry-manometry and microcalorimetry measurements[J]. Microporous Mesoporous Mater,2009,119(1/3):117−128. [24] 陈丹. 分子筛限域孔道内扩散行为对产物选择性影响的分子动力学研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉工程大学, 2022.CHEN Dan. Molecular dynamics study on the influence of diffusion behavior in molecular sieve confined pores on product selectivity[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2022. [25] LIU Y B, LI Y Z, DING X. Adsorption simulation of basic nitrogen compounds in ZSM-5 and USY zeolites by grand canonical Monte Carlo method[J]. Adv Mater Res,2015,1096(1):189−193. [26] 雪霈. 硫化物与烯烃在Y型分子筛中竞争吸附和竞争扩散的分子模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.XUE Pei. Molecular simulation study on competitive adsorption and diffusion of sulfides and olefins in Y-type molecular sieves[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. [27] DEHGHANI M, ASGHARI M, ISMAIL A F, et al. Amir H M. Molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulation of the structural properties, diffusion and adsorption of poly (amide-6-b-ethylene oxide)/Faujasite mixed matrix membranes[J]. J Mol Liq,2017,242(6):404−415. [28] 肖永厚, 周梦雪, 白腾飞, 等. 丙烯在X型分子筛上吸附热力学的Monte Carlo模拟[J]. 石油化工,2018,47(5):420−425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2018.05.004XIAO Yonghou, ZHOU Mengxue, BAI Tengfei, et al. Monte Carlo simulation of propylene adsorption thermodynamics on X-type zeolite[J]. Petrochem Technol,2018,47(5):420−425. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2018.05.004 -




 下载:
下载: