Study on preparation of cyclohexanol from lignin-derived phenolic compounds catalyzed by metal oxide-loaded ruthenium
-
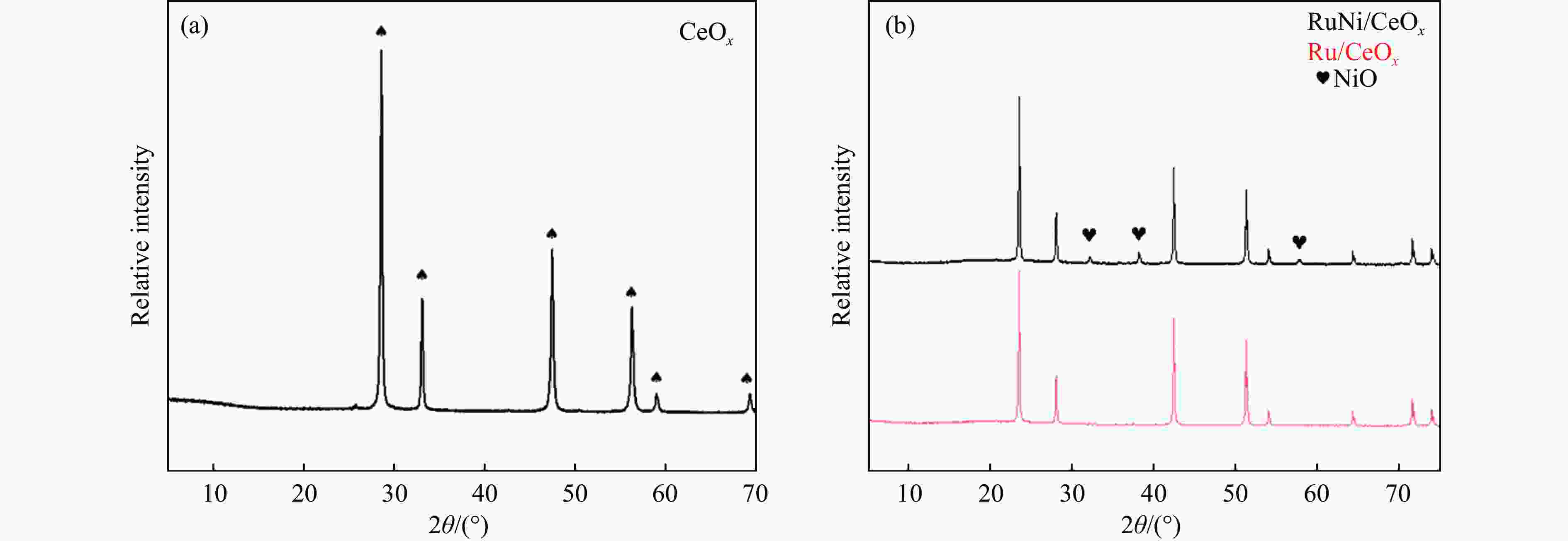
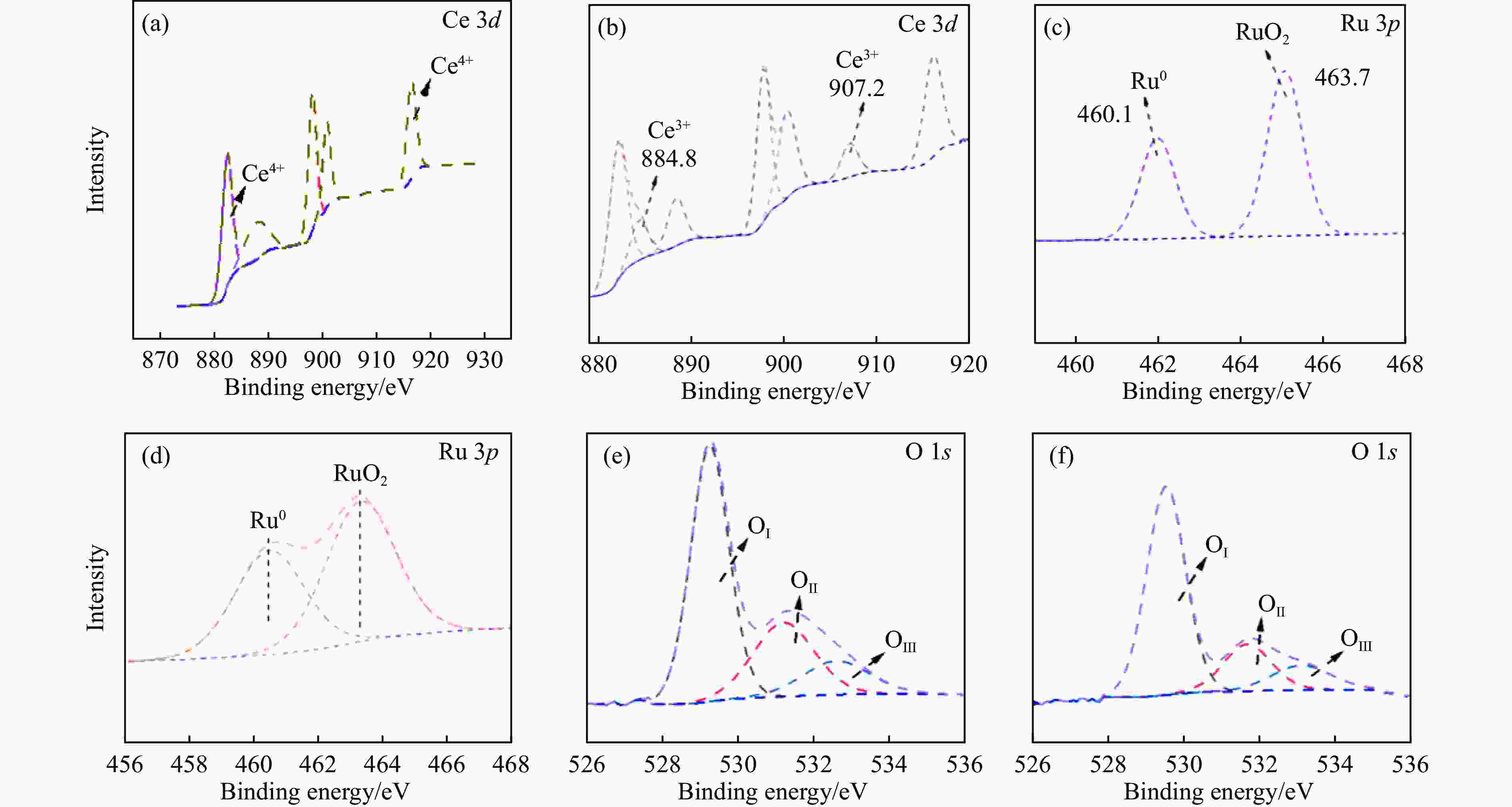
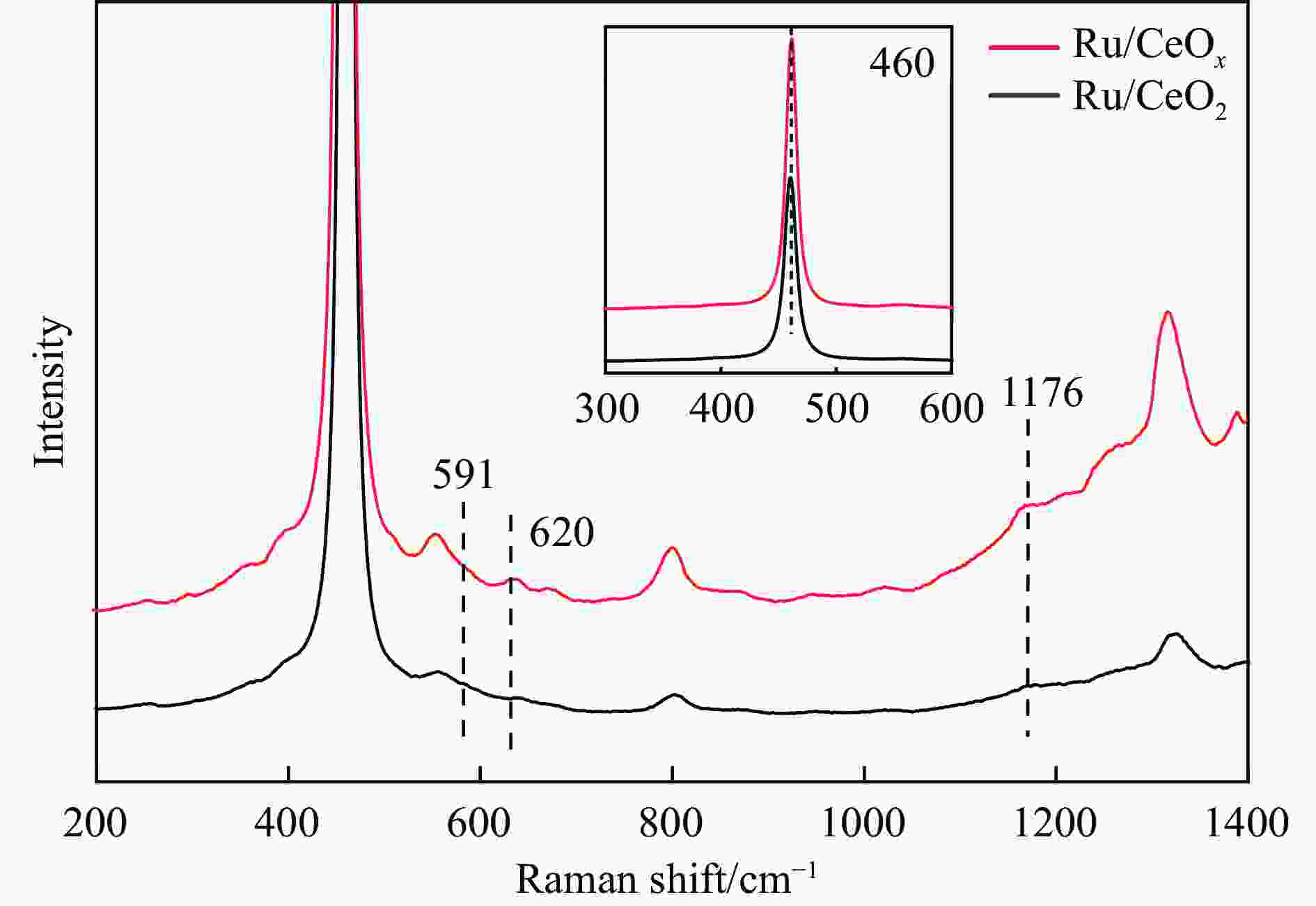
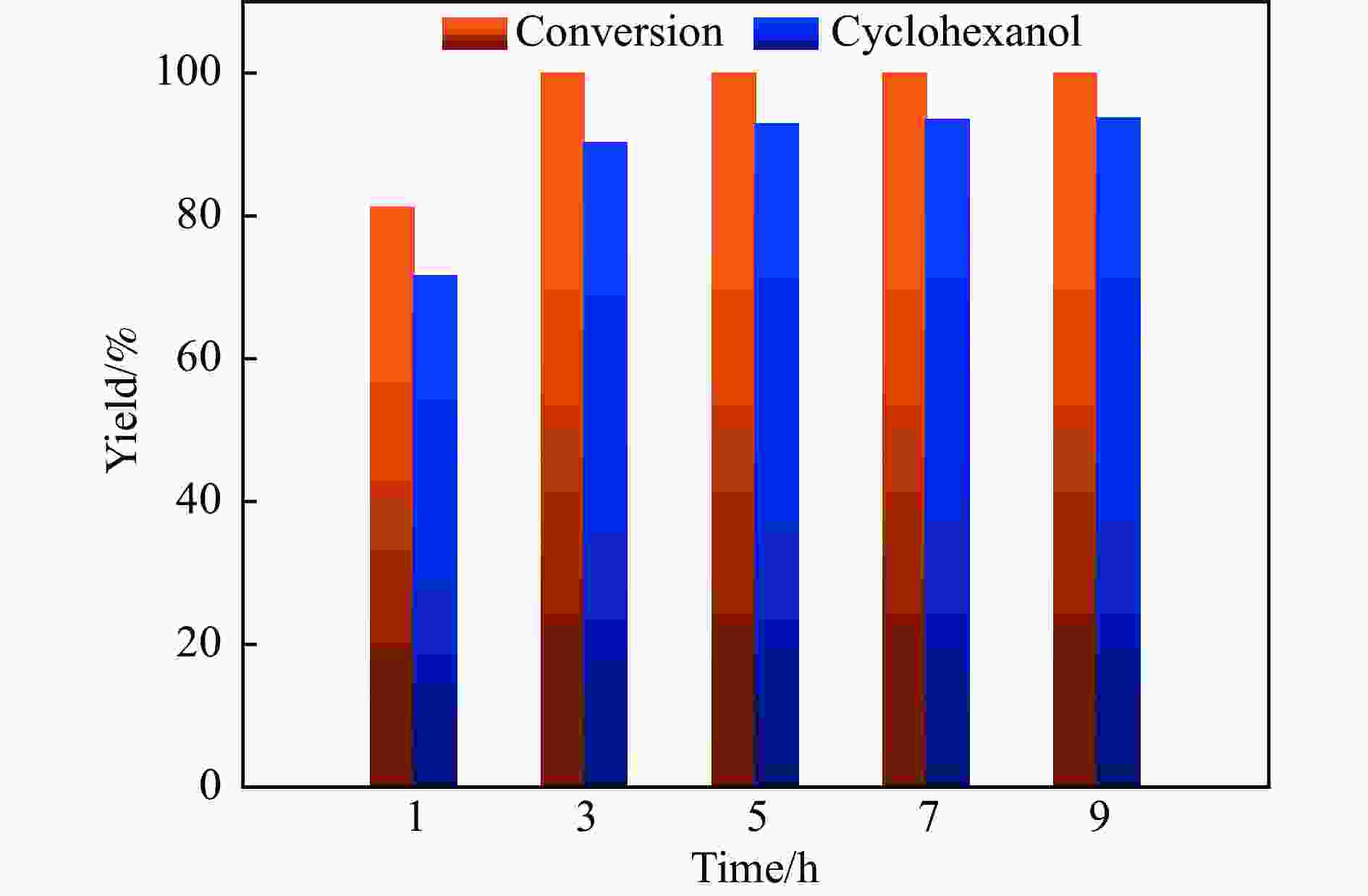
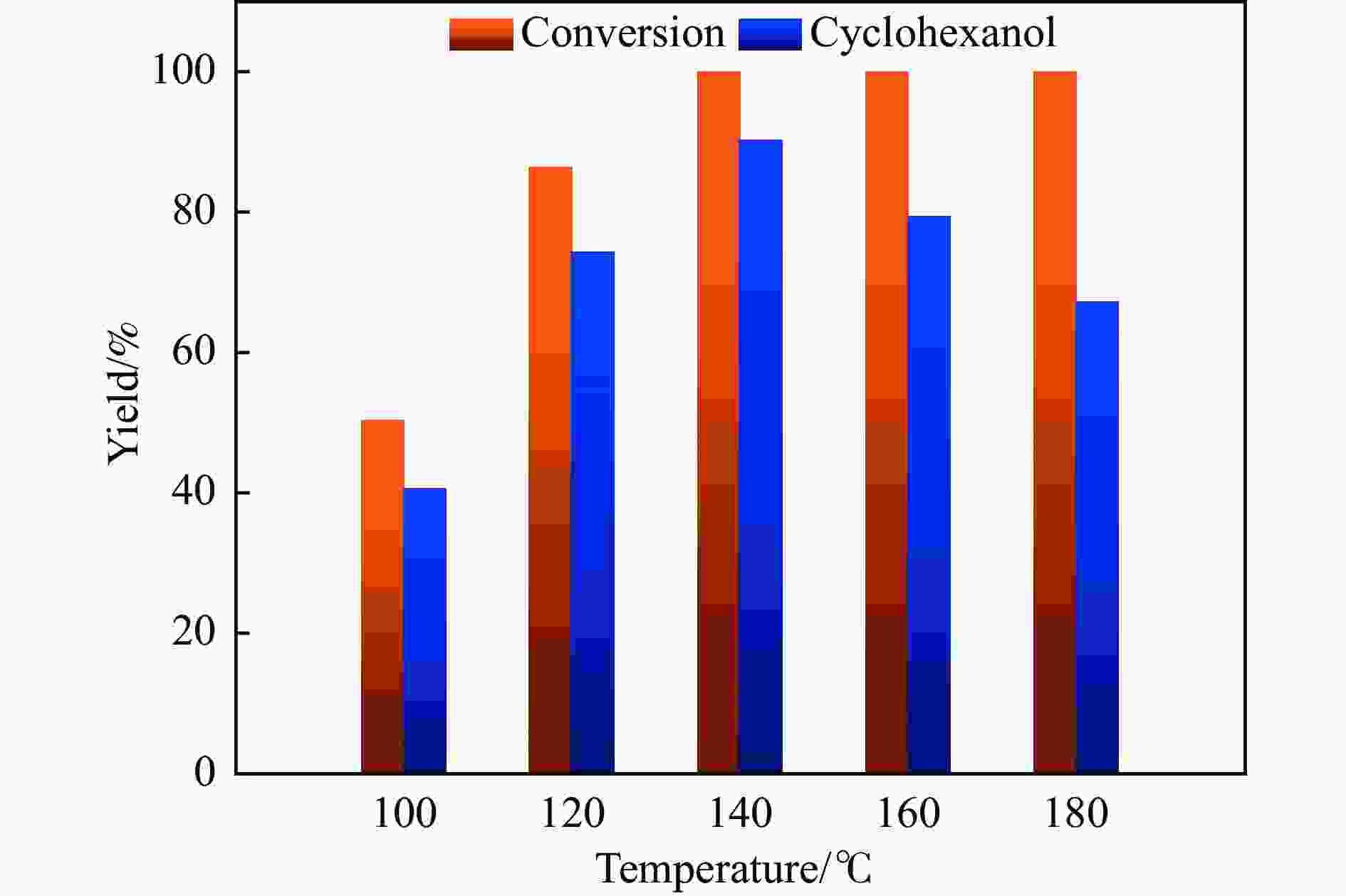
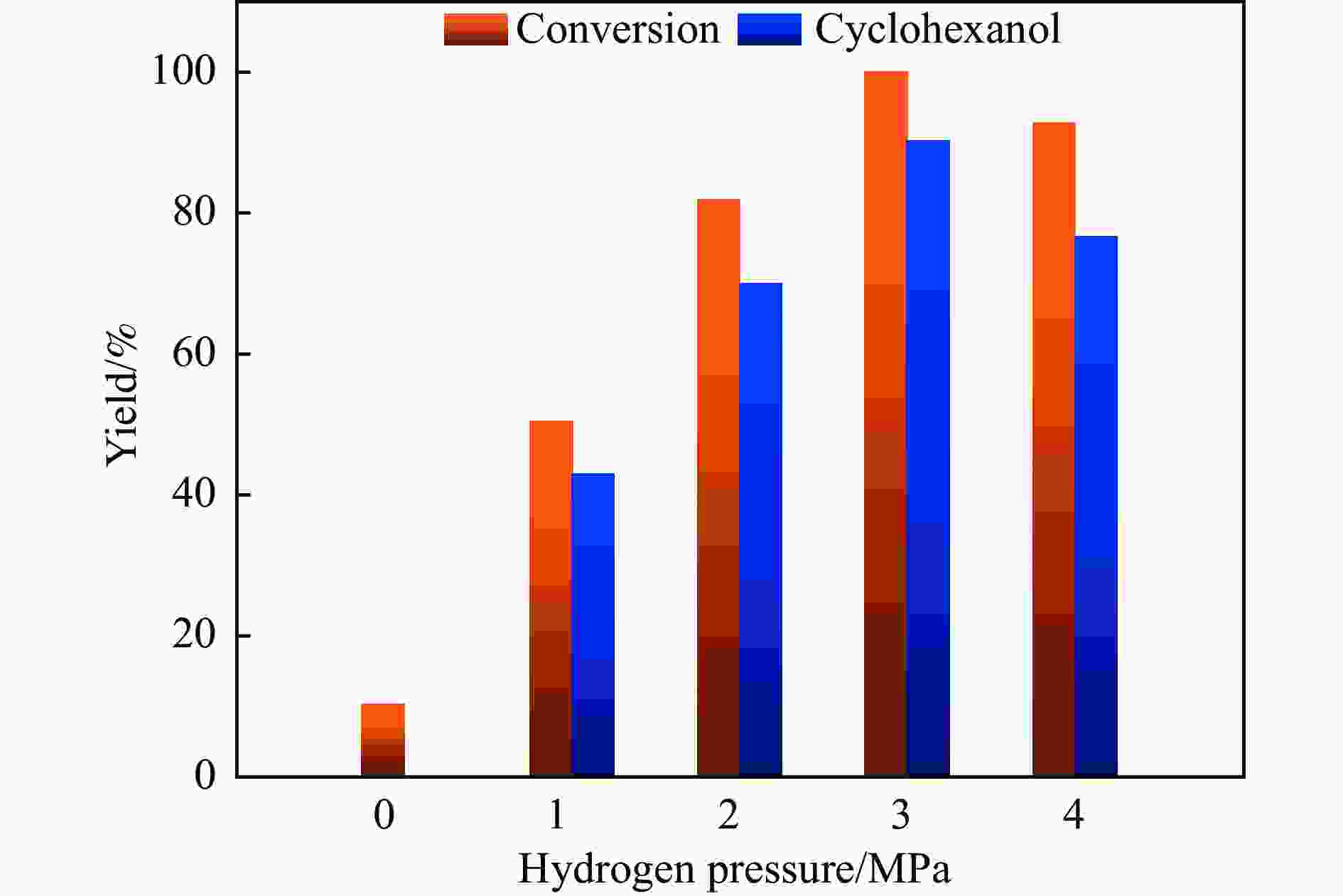
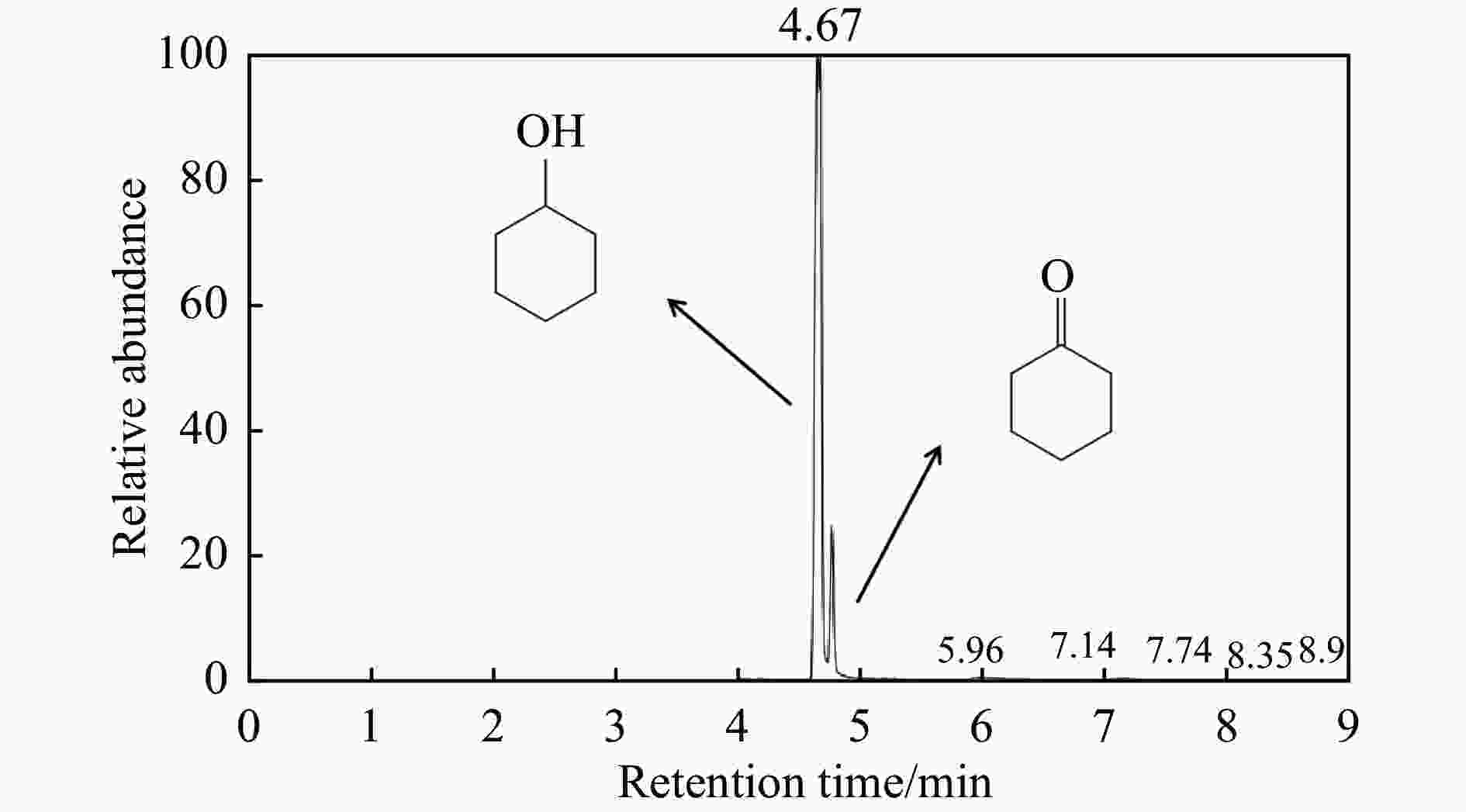
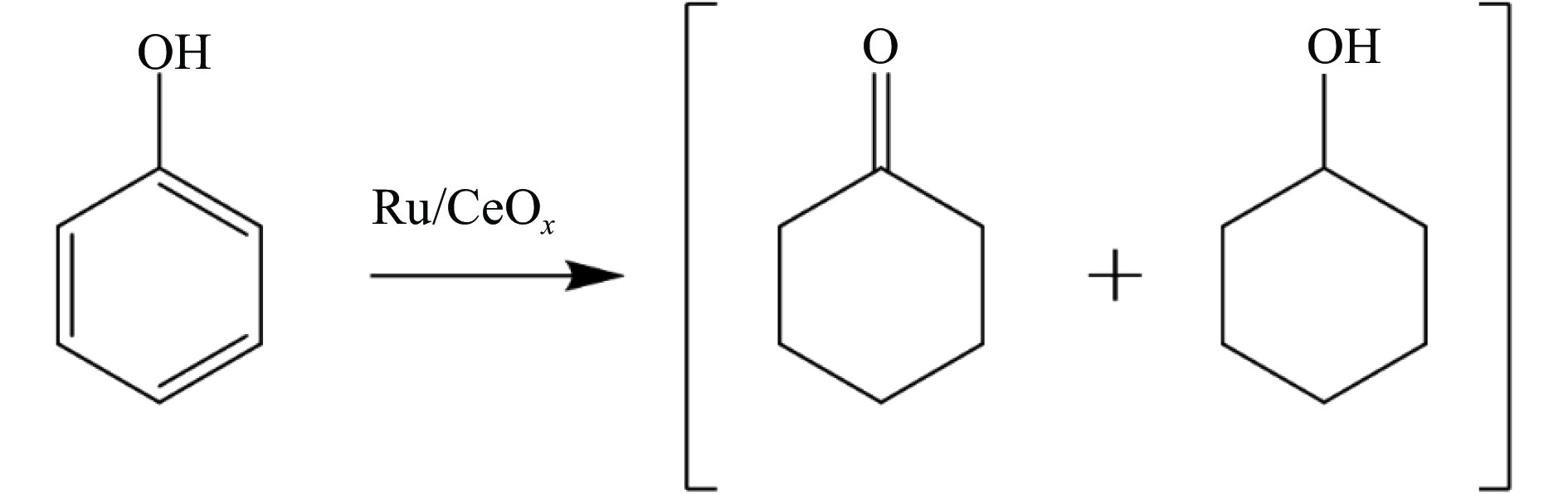
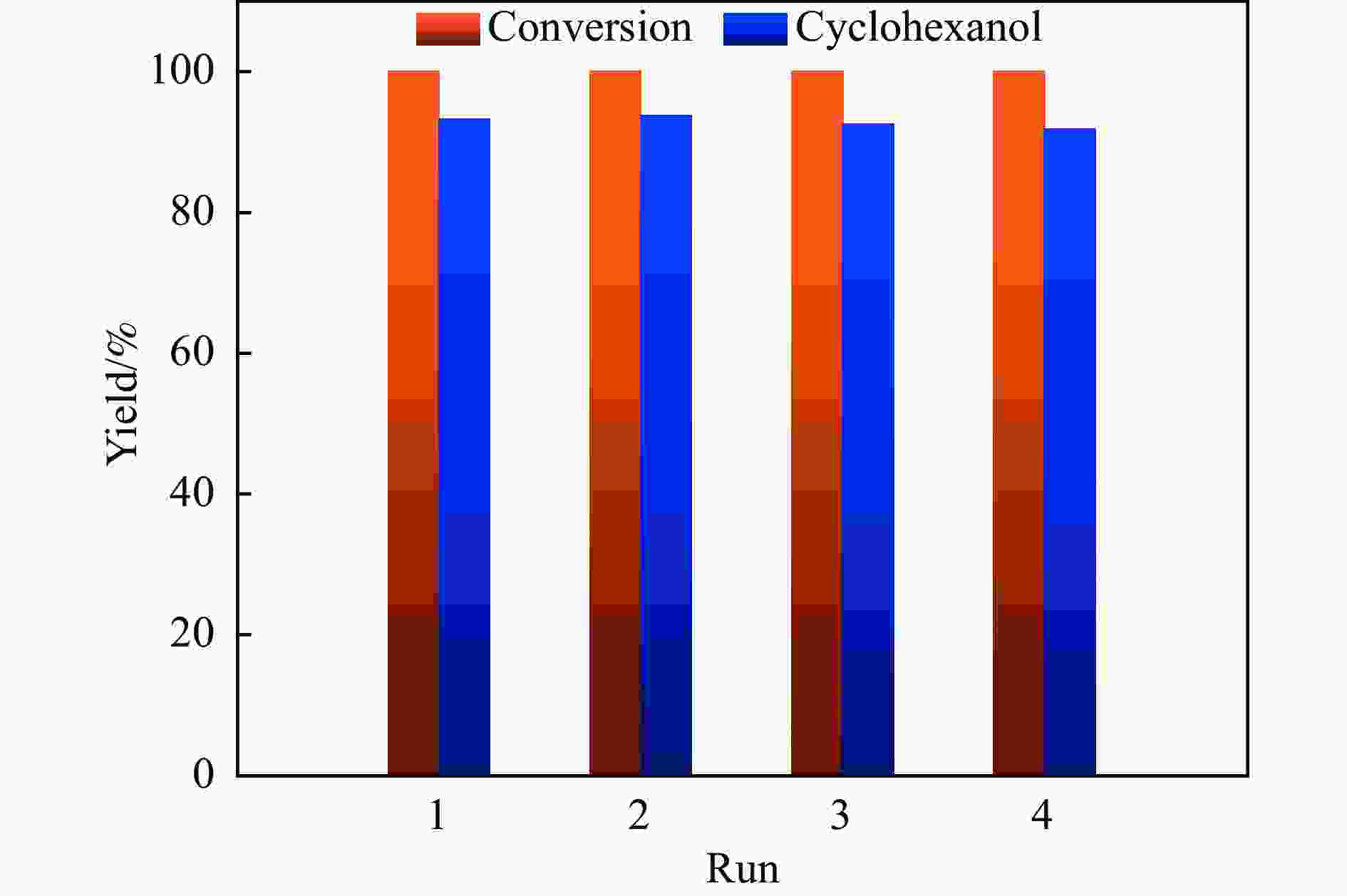
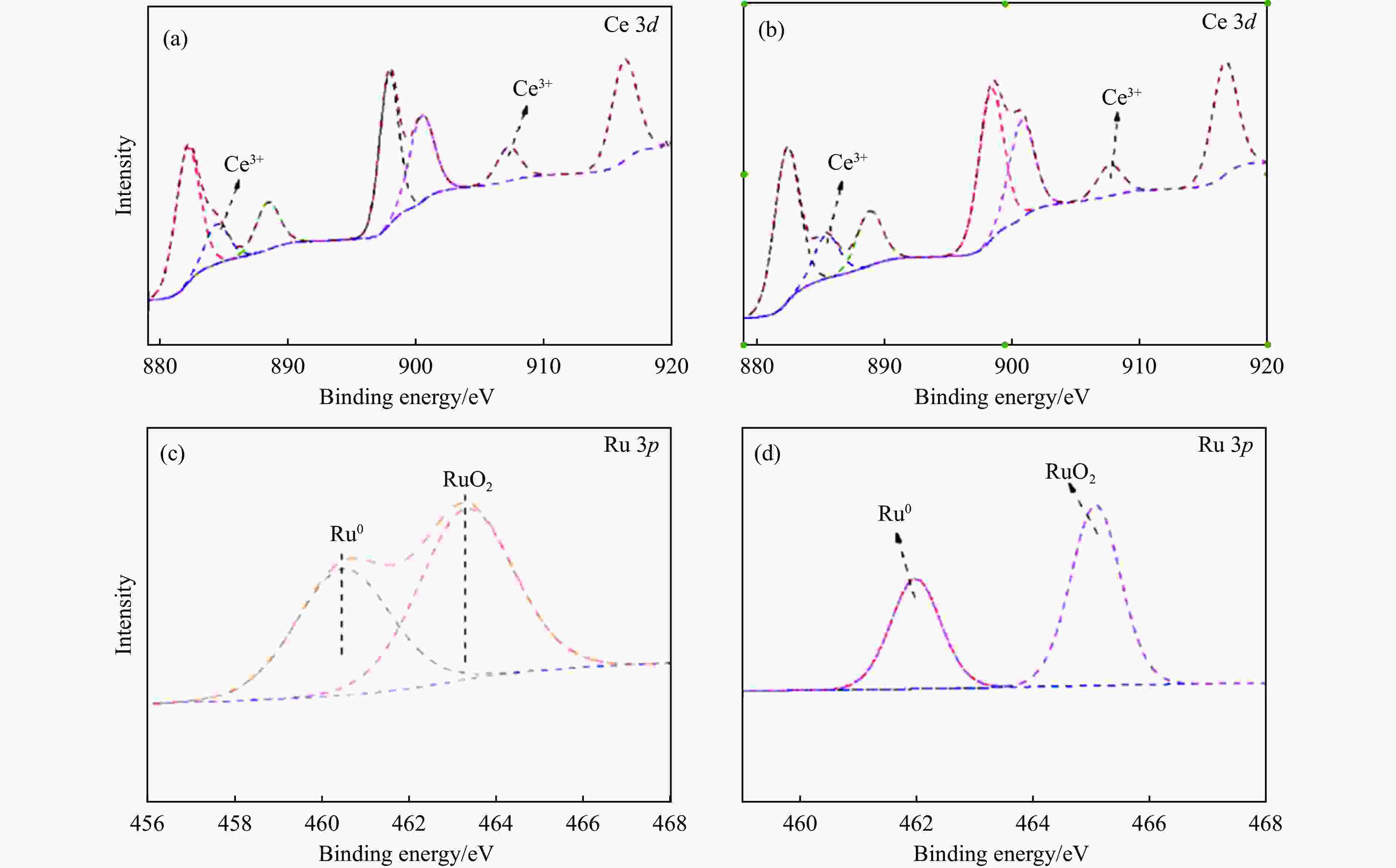
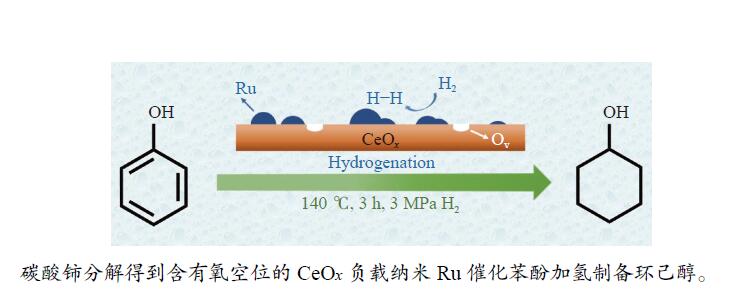
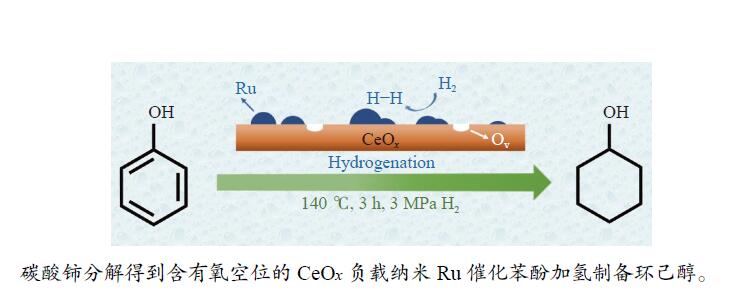
摘要: 本研究采用初湿浸渍法,制备得到一系列钌负载于金属氧化物载体的催化剂(Ru/CeO2、Ru/Nb2O5、Ru/ZrO2、Ru/Al2O3和Ru/CeOx),用于木质素衍生酚类化合物苯酚提质加氢转化为环己醇的研究。通过采用X射线晶体衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、X射线光电子能谱(XPS)等手段对所制备催化剂进行结构和物化特征的表征,发现Ru/CeOx中含有的氧空位可以很好地吸附带有含氧基团的原料,从而有利于苯酚的高效加氢;同时XPS表明,Ru/CeOx中的有效活性中心RuO2和Ru0是催化加氢的活性位点,因此,氧空位和金属活性位点的共同作用使得催化剂有较好的加氢活性。探究了反应温度、压力、时间对加氢效果的影响,发现催化剂能够在140 ℃下使苯酚完全转化,得到目标产物环己醇得率为90.2%,并对催化剂的循环特性进行考察,发现循环使用四次后催化剂仍表现出优异的加氢活性。同时采用GC-MS检测加氢过程的中间产物,进而推断出苯酚加氢过程的反应路径。Abstract: Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin bio-oil to prepare liquid fuels is a very promising route. In this paper, a series of catalysts (Ru/CeO2, Ru/Nb2O5, Ru/ZrO2, Ru/Al2O3 and Ru/CeOx) supported on metal oxides were prepared by incipient wetness impregnation method, which were used to study the upgrading and hydrogenation of lignin-derived phenolic compounds phenol to cyclohexanol. By means of X-ray crystal diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), the structure and physical and chemical characteristics of the prepared catalyst were characterized. It was found that the oxygen vacancies contained in Ru/CeOx could adsorb the raw materials with oxygen groups well, which was beneficial to the efficient hydrogenation of phenol. At the same time, XPS showed that the effective active centers in Ru/CeOx, RuO2 and Ru0, were active sites for catalytic hydrogenation. Therefore, the combined action of oxygen vacancies and metal active sites made the catalyst have good hydrogenation activity. The effects of reaction temperature, pressure and time on hydrogenation were also investigated. It was found that the catalyst could completely convert phenol at a mild temperature (140 ℃) and the yield of cyclohexanol was 90.2%. The cycle characteristics of the catalyst were investigated, and it was found that the catalyst still showed excellent hydrogenation activity after being recycled for 4 times. At the same time, the intermediate products in the hydrogenation process were detected by GC-MS, and then the reaction path of phenol hydrogenation process was deduced.
-
Key words:
- metal oxide /
- lignin /
- phenolic compounds /
- catalytic hydrogenation /
- cyclohexanol
-
表 1 不同催化剂的性能研究
Table 1 Performance study of different catalysts
Catalyst Conversion/% Cyclohexanol yield/% Ni/Nb2O5 31.00 0.00 Ni/CeO2 73.50 62.70 Ru/Nb2O5 41.70 37.50 Ru/CeO2 100.00 82.50 Ru-Ni/CeO2 90.00 80.00 Ru/ZrO2 10.00 0.40 Ru/Al2O3 12.50 0.76 Ru/CeOx 100.00 90.20 Reaction conditions: catalyst 0.05 g, reaction time 3 h, reaction temperature 140 ℃, hydrogen pressure 3 MPa. -
[1] SCHUTYSER W, RENDERS T, VAN DEN BOSCH S, et al. Chemicals from lignin: An interplay of lignocellulose fractionation, depolymerisation, and upgrading[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2018,47(3):852−908. doi: 10.1039/C7CS00566K [2] WANG H, PU Y, RAGAUSKAS A, et al. From lignin to valuable products-strategies, challenges, and prospects[J]. Bioresource Technol,2019,271:449−461. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.072 [3] ZHUOHUA S, BÁLINT F, ALESSANDRA D S, et al. Bright side of lignin depolymerization: Toward new platform chemicals[J]. Chem Rev,2018,118(2):614−678. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00588 [4] SHING W S, RIYANG S, JIAGUANG Z, et al. Downstream processing of lignin derived feedstock into end products[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2020,49(15):5510−5560. doi: 10.1039/D0CS00134A [5] CHANGZHI L, XIAOCHEN Z, AIQIN W, et al. Catalytic transformation of lignin for the production of chemicals and fuels[J]. Chem Rev,2015,115(21):11559−11624. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00155 [6] OUEDRAOGO A S, BHOI P R. Recent progress of metals supported catalysts for hydrodeoxygenation of biomass derived pyrolysis oil[J]. J Clean Prod,2020,253(C):119957. [7] LI X P, CHEN G Y, LIU C X, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived bio-oil using molecular sieves supported metal catalysts: A critical review[J]. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev,2017,71:296−308. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.057 [8] ZHOU M H, GE F, LI J, et al. Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol to cyclohexanol over bimetallic nimo-mof-derived catalysts[J]. Catalysts,2022,12(4):371. doi: 10.3390/catal12040371 [9] MO L Y, YU W J, CAI H J, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of bio-derived phenol to cyclohexane fuel catalyzed by bifunctional mesoporous organic-inorganic hybrids[J]. Front Chem,2018,6:216. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00216 [10] JAFARIAN S, TAVASOLI A, NIKKHAH H. Catalytic hydrotreating of pyro-oil derived from green microalgae spirulina the ( Arthrospira ) plantensis over NiMo catalysts impregnated over a novel hybrid support[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(36):19855−19867. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.182 [11] XIANG L, YUAN X, ZHICHENG Z, et al. Progress on upgrading methods of bio-oil: A review[J]. Int J Energy Res,2017,41(13):1798−1816. doi: 10.1002/er.3726 [12] MINGXING Z, JUN H, SHILIANG W, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenolics over facile prepared bimetallic RuCoNx/NC[J]. Fuel,2022,308:121979. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121979 [13] 曲俊聪, 史成香, 张香文, 等. 用于木质素转化制备生物质燃料多功能催化剂的研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报,2022,44(4):664675−675.QU Juncong, SHI Chengxiang, ZHANG Xiangwen, et al. Research progress of multifunctional catalysts for lignin conversion to prepare biomass fuel[J]. J Eng Sci,2022,44(4):664675−675. [14] ANNE K, CHRISTIAN S, BÉLA T. Application of microwave-assisted heterogeneous catalysis in sustainable synthesis design[J]. Green Chem,2017,19(16):3729−3751. doi: 10.1039/C7GC01393K [15] SUDARSANAM P, ZHONG R, VAN DEN BOSCH S, et al. Functionalised heterogeneous catalysts for sustainable biomass valorisation[J]. Chem Soc Rev,2018,47(22):8349−8402. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00410B [16] 邱泽刚, 尹婵娟, 李志勤, 等. 酚类加氢脱氧催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2019,38(8):3658−3669. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-1987QIU Zegang, YIN Chanjuan, LI Zhiqin, et al. Research progress of phenolic hydrodeoxygenation catalysts[J]. Chem Eng Prog,2019,38(8):3658−3669. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-1987 [17] FENG S S, LIU X D, SU Z S, et al. Low temperature catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenols to cyclohexanols over the Ru/SBA-15 catalyst[J]. RSC Adv,2022,12(15):9352−9362. doi: 10.1039/D2RA01183B [18] JIANG W, CAO J P, YANG Z, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin and its model compounds to hydrocarbon fuels over a bifunctional Ga-doped HZSM-5 supported metal Ru catalyst[J]. Appl Catal A: Gen,2022,633:118516. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118516 [19] DABROS T M H, STUMMANN M Z, HØJ M, et al. Transportation fuels from biomass fast pyrolysis, catalytic hydrodeoxygenation, and catalytic fast hydropyrolysis[J]. Prog Energy Combust,2018,68:268−309. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2018.05.002 [20] SALAKHUM S, SAENLUANG K, WATTANAKIT C. Stability of monometallic Pt and Ru supported on hierarchical HZSM-5 nanosheets for hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived compounds in the aqueous phase[J]. Sustainable Energy Fuels,2020,4(3):1126−1134. doi: 10.1039/C9SE00773C [21] ABREU T C, MAGALHAES D S P, CRISOSTOMO R N R, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived compound mixtures on Pd-supported on various oxides[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng,2021,9(38):12870−12884. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c03720 [22] GRIFFIN M B, FERGUSON G A, RUDDY D A, et al. Role of the support and reaction conditions on the vapor-phase deoxygenation of m-cresol over Pt/C and Pt/TiO2 catalysts[J]. ACS Catal,2016,6(4):2715−2727. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.5b02868 [23] DE SOUZA P M, RABELO-NETO R C, BORGES L E P, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of phenol over Pd catalysts. Effect of support on reaction mechanism and catalyst deactivation[J]. ACS Catal,2017,7(3):2058−2073. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b02022 [24] LICHEN L, AVELINO C. Metal catalysts for heterogeneous catalysis: From single atoms to nanoclusters and nanoparticles[J]. Chem Rev,2018,118(10):4981−5079. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00776 [25] WEI J, JING-PEI C, CHEN Z, et al. Catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic ring over ruthenium nanoparticles supported on α-Al2O3 at room temperature[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2022,307:121137. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121137 [26] JIANG W, CAO J-P, ZHAO X-Y, et al. Highly selective aromatic ring hydrogenation of lignin-derived compounds over macroporous Ru/Nb2O5 with the lost acidity at room temperature[J]. Fuel,2020,282:118869. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118869 [27] WANG X, WANG Z, ZHOU L, et al. Efficient hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol to phenol over Ru/Ti-SiO2 catalysts: The significance of defect-rich TiOx species[J]. Green Chem,2022,24(15):5822−5834. doi: 10.1039/D2GC01714H [28] JONES J, XIONG H, DELARIVA A T, et al. Thermally stable single-atom platinum-on-ceria catalysts via atom trapping[J]. Science,2016,353(6295):150−154. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf8800 [29] NIE L, MEI D, XIONG H, et al. Activation of surface lattice oxygen in single-atom Pt/CeO2 for low-temperature CO oxidation[J]. Science,2017,358(6369):1419−1423. doi: 10.1126/science.aao2109 [30] LIU P, NIU R, LI W, et al. Morphology effect of ceria on the ammonia synthesis activity of Ru/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Catal Lett,2019,149:1007−1016. doi: 10.1007/s10562-019-02674-1 [31] MUDIYANSELAGE K, AL-SHANKITI I, FOULIS A, et al. Reactions of ethanol over CeO2 and Ru/CeO2 catalysts[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2016,197:198−205. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.065 [32] JAFFARI G H, IMRAN A, BAH M, et al. Identification and quantification of oxygen vacancies in CeO2 nanocrystals and their role in formation of F-centers[J]. Appl Surf ScI,2017,396:547−553. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.193 [33] LU M, JIANG Y, SUN Y, et al. Hydrodeoxygenation of guaiacol catalyzed by ZrO2-CeO2-supported nickel catalysts with high loading[J]. Energy Fuels,2020,34(4):4685−4692. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.0c00445 [34] HUANG H, DAI Q, WANG X. Morphology effect of Ru/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene[J]. Appl Catal B: Environ,2014,158−159:96−105. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.062 [35] TAN J, HE J, GAO K, et al. Catalytic hydrogenation of furfural over Cu/CeO2 catalyst: The effect of support morphology and exposed facet[J]. Appl Surf Sci,2022,604:154472. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154472 [36] HUANG L, TANG F, LIU P, et al. Highly efficient and selective conversion of guaiacol to cyclohexanol over Ni-Fe/MgAlOx: Understanding the synergistic effect between Ni-Fe alloy and basic sites[J]. Fuel,2022,327:125115. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125115 [37] 遇治权. Ni3P基催化剂的制备及苯酚加氢脱氧性能[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019.YU Zhiquan. Preparation of Ni3P-based catalyst and its hydrodeoxygenation performance for phenol[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. -




 下载:
下载: