High resolution TEM image analysis of coals with different metamorphic degrees
-
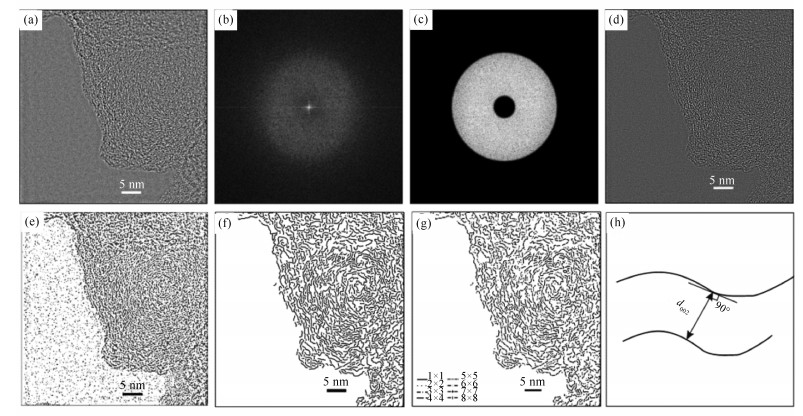
摘要: 利用高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM) 分析了三种不同变质程度煤样的结构特征.基于傅里叶-反傅里叶变换方法, 并结合Matlab、Arcgis和AutoCAD软件, 通过图像分析技术, 获得了HRTEM照片的晶格条纹参数.结果表明, 三种煤样的晶格条纹呈现不同特征, 按条纹长度分别归属于1×1-8×8共计八个类型.以3×3为临界点, 在1×1和2×2中, ML-8中芳香层片的比例高于DP-4和XM-3;在3×3-8×8中, ML-8中芳香层片的比例低于DP-4和XM-3.对比HRTEM和XRD参数d002发现, 随着镜质组反射率的增加d002都呈现递减趋势.
-
关键词:
- 不同变质程度煤 /
- 高分辨率透射电子显微镜 /
- 图像分析
Abstract: The structural characteristics of 3 coals with different metamorphic degrees were analyzed using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). Applying FFT-IFFT method, in association with Matlab, Arcgis and AutoCAD softwares, the lattice fringe parameters obtained from HRTEM image were determined using image analysis. The results indicate that the lattice fringes of all the test coal samples exhibit different characteristics. These lattice fringes can be divided into 8 types (1×1-8×8 aromatic fringes) according to the fringe length distribution. Taking the 3×3 aromatic fringe as critical point, the sample ML-8 abundant in 1×1 and 2×2 aromatic fringes while short of 3×3-8×8 aromatic fringes when comparing with sample DP-4 and sample XM-3. The values of d002 obtained from both HRTEM and XRD show a decreasing trend with increasing vitrinite reflectance. -
表 1 样品的化学和光学参数
Table 1 Chemical and optical parameters for studied samples
Samples no. Coal mine Proximate analysis w/% Ro, max /% Ultimate analysis wdaf/% Mad Aad Vdaf C H O* N S DP-4 Dongpo 1.50 14.27 40.35 0.573 77.89 4.39 13.51 1.16 2.86 ML-8 Malan 0.48 9.00 27.96 1.205 86.32 4.04 6.76 1.11 1.66 XM-3 Ximing 0.70 8.18 15.18 1.838 90.43 3.73 3.95 1.08 0.72 *: by difference 表 2 煤样的微晶结构参数
Table 2 Microcrystalline structure parameters of coal
Sample d002 /nm Lc/nm La /nm DP-4 0.373 2 1.238 6 1.011 9 ML-8 0.354 6 1.749 1 1.232 4 XM-3 0.349 5 1.952 1 1.419 1 表 3 高分辨透射电子显微镜晶格条纹归属分类[11]
Table 3 Classification of HRTEM lattice fringes
Aromatic sheet Mean d/nm Grouping d/nm 1×1 0.39 0.30-0.54 2×2 0.60 0.55-0.74 3×3 0.93 0.75-1.14 4×4 1.27 1.15-1.44 5×5 1.60 1.45-1.74 6×6 1.94 1.75-2.04 7×7 2.28 2.05-2.44 8×8 2.61 2.45-2.84 -
[1] MATHEWS J P, SHARMA A. The structural alignment of coal and the analogous case of Argonne Upper Freeport coal[J]. Fuel, 2012, 95: 19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.046 [2] YANG J, CHENG S, WANG X, ZHANG Z, LIU X R, TANG G H. Quantitative analysis of microstructure of carbon materials by HRTEM[J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2006, 16(S2): S796-S803. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229378496_Quantitative_analysis_of_microstructure_of_carbon_materials_by_HRTEM [3] SHARMA A, KYOTANI T, TOMITZ A. Direct observation of layered structure of coals by a transmission electron microscope[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(2): 515-516. doi: 10.1021/ef990253h [4] SHARMA A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. Comparison of structural parameters of PF carbon from XRD and HRTEM techniques[J]. Carbon, 2000, 34(14): 1977-1984. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Akira_Tomita/publication/244317503_Comparison_of_structural_parameters_of_PF_carbon_from_XRD_and_HRTEM_techniques/links/560b22ef08ae4d86bb14b96c.pdf?inViewer=0&pdfJsDownload=0&origin=publication_detail [5] ASO H, MATSUOKA K, SHARMA A, TOMITA A. Evaluation of size of graphene sheet in anthracite by a temperature-programmed oxidation method[J]. Energy Fuels, 2004, 18(5): 1309-1314. doi: 10.1021/ef030176x [6] SHARMA A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. A new quantitative approach for microsctructural analysis of coal char using HRTEM images[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(10): 1203-1212. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00046-0 [7] SHIM H-S, HURT R H, YANG N Y C. A methodology for analysis of 002 lattice fringe images and its application to combustion-derived carbons[J]. Carbon, 2000, 38(1): 29-45. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(99)00096-2 [8] SHARMA A, KYOTANI T, TOMITA A. Direct observation of raw coals in lattice fringe mode using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy[J]. Energy Fuels, 2000, 14(6): 1219-1225. doi: 10.1021/ef0000936 [9] PALOTÁS A B, RAINEY L C, SAROFIM A F, SANDE J B V, CIAMBELLI P. Effect of oxidation on the microstructure themicrostructure of carbon blacks[J]. Energy Fuels, 1996, 10(1): 254-259. doi: 10.1021/ef950168j [10] WORNAT M J, HURT R H, YANG N Y C, HEADLEY T J. Structural and compositional transformations of biomass chars during combustion[J]. Combust Flame, 1995, 100(1/2): 131. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222216211_Structural_and_compositional_transformations_of_biomass_chars_during_combustion [11] NIEKERK D V, MATHEWS J P. Molecular representations of Permian-aged vitrinite-rich and inertinite-rich South African coals[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(1): 73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.07.020 [12] YEHLIU K, VANDER WAL R L, BOEHMAN A L. Development of an HRTEM image analysis method to quantify carbon nanostructure[J]. Combust Flame, 2011, 158(1): 1837-1851. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/251554845_Development_of_an_HRTEM_image_analysis_method_to_quantify_carbon_nanostructure [13] MATHEWS J P, FERNANDEZ-ALSO V, DANIEL J A, SCHOBERT H H. Determining the molecular weight distribution of Pocahontas No. 3 low-volatile bituminous coal utilizing HRTEM and laser desorption ionization mass spectra data[J]. Fuel, 2010, 89(7): 1461-1469. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.10.014 [14] CASTRO-MARCANO F, LOBODIN V V, RODGERS R P, MCKENNA A M, MARSHALL A G, MATHEWS J P. A molecular model for Illinois No. 6 Argonne Premium coal: Moving toward capturing the continuum structure[J]. Fuel, 2012, 95: 35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.026 [15] 郭亚楠, 唐跃刚, 王绍清, 李薇薇, 贾龙.树皮残植煤显微组分分离及高分辨透射电镜图像分子结构[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(6): 1019-1024. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201306023.htmGUO Ya-nan, TANG Yue-gang, WANG Shao-qing, LI Wei-wei, JIA Long. Maceral separation of bark liptobiolite and molecular structure study through high resolution TEM images[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2013, 38(6): 1019-1024. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201306023.htm [16] CASTRO-MARCANO F, LOBODIN V V, RODGERS R P, MCKENNA A M, MARSHALL A G, MATHEWS J P. A molecular model for Illinois No. 6 Argonne Premium coal: Moving toward capturing the continuum structure[J]. Fuel, 2012, 95: 35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.12.026 [17] 任秀彬, 辛文辉, 张亚婷, 周安宁.基于HRTEM的低阶烟煤微晶结构研究[J].煤炭学报, 2015, 40(S1): 242-246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2015S1037.htmREN Xiu-bin, XIN Wen-hui, ZHANG Ya-ting, ZHOU An-ning. Structural alignment of low rank coal using HRTEM technique[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2015, 40(S1): 242-246. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB2015S1037.htm [18] 张小东, 孔令菲, 秦勇, 张鹏.龙口褐煤萃取后微晶结构的XRD与HRTEM研究[J].煤炭学报, 2013, 38(6): 1025-1030. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201306024.htmZHANG Xiao-dong, KONG Ling-fei, QIN Yong, ZHANG Peng. Research on the microcrystalline structure of the fractionally-extracted Longkou lignite by XRD and HRTEM[J]. J China Coal Soc, 2013, 38(6): 1025-1030. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201306024.htm [19] JU Y W, LI X S. New research progress on the ultrastructure of tectonically deformed coals[J]. Prog Nat Sci, 2009, 19(11): 1455-1466. doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2009.03.013 [20] ENDO M, FURUTA T, MINOURA F, KIM C, OSHIDA K, DRESSELHAUS G, DRESSELHAUS M S. Visualized observation of pores in activated carbon fibers by HRTEM and combined image processor[J]. Supramol Sci, 1998, 5(S3/4): 261-266. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222946259_Visualized_observation_of_pores_in_activated_carbon_fibers_by_HRTEM_and_combined_image_processor [21] TAKAGI H, MARUYAMA K, YOSHIZAWA N, YAMAD A Y, SATO Y. XRD analysis of carbon stacking structure in coal during heat treatment[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(S17/18): 2427-2433. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/223675644_XRD_analysis_of_carbon_stacking_structure_in_coal_during_heat_treatment [22] HUANG Z H, KANG F Y, HUANG W L, YANG J B, LIANG K M, CUI M L, CHENG Z Y. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of activated carbon fibers characterized by using HRTEM[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2002, 249(2): 453-457. doi: 10.1006/jcis.2002.8274 [23] PALOTAS A B, RAINEY L C, FELDERMANN C J, SAROFIM A F, Vander SANDE J B. Soot morphology: An application of image analysis in high-resolution transmission electron microscopy[J]. Microsc Res Technol, 1996, 33(3): 266-278. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0029 [24] 杨起.中国煤变质作用[M].北京:煤炭工业出版社, 1996: 154.YANG Qi. The Coal Metamorphism in China[M]. Beijing: Press of Coal Industry, 1996: 154. [25] 赵峰华, 任德贻.应用高分辨率透射电镜研究煤显微组分的结构[J].地质论评, 1995, 41(6): 564-570. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199506011.htmZHAO Feng-hua, REN De-yi. The application of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy to study the structures of coal macerals[J]. Geol Rev, 1995, 41(6): 564-570. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199506011.htm [26] CABIOC'H T, THUNE E, JAOUEN M. Carbon-onion thin-film synthesis onto silica substrates[J]. Chem Phys Lett, 2000, 320(1/2): 202-205. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235126829_Carbon-onion_thin-film_synthesis_onto_silica_substrates [27] 韩德馨.中国煤岩学[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社, 1996: 260.HAN De-xin. Coal Petrology in China[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 1996: 260. -





 下载:
下载: